Do you feel like you’re in a slump? You’re not alone. Many people feel this way at some point in their lives. A slump can be caused by many things, including stress, anxiety, and depression. It can also be caused by physical problems, such as low energy levels or chronic pain. If you are feeling down and out, there is a good chance that your productivity has decreased as well. This is where the slump test comes in handy! In this article, we will discuss what the slump test is and how to perform it.
Contents
- 1 What Is Slump Test?
- 2 What Conditions Can Slump Test Help Diagnose?
- 3 How Is Slump Test Performed?
- 4 What Are the Risks Associated with Slump Test?
- 5 What is the difference between a positive and negative slump test?
- 6 What Are The Benefits Of the slump test?
- 7 What Are The Limitations Of the slump test?
- 8 Conclusion
What Is Slump Test?

The Slump Test is a neural tension test used to detect altered neurodynamics or tissue sensitivity within the nerves. The slump test is also known as the straight leg raise (SLR) test or the leg lift test. It is a clinical test used by physical therapists and other healthcare professionals to help diagnose various conditions involving nerve pain.
What Conditions Can Slump Test Help Diagnose?
Slump test can help diagnose various conditions that cause nerve pain, including:
Sciatica: Sciatica is a condition that causes pain to radiate from the lower back down the leg. It is typically caused by a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. For instance, if a disc herniates and presses on the sciatic nerve, the pain will radiate from the lower back down to the leg. Sciatica can also be caused by spinal stenosis, which is a condition that causes the spine to narrow and compress the nerves.
Radiculopathy: Radiculopathy is a condition that results when nerves are compressed or pinched. It can cause pain, numbness, and tingling. For example, if the nerve root in your neck is compressed, you may have pain and tingling down your arm.
Spinal stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when the spinal canal narrows, resulting in pressure on the nerves. For example, if the spinal canal narrows in the neck, it is called cervical stenosis.
Herniated disc: A herniated disc occurs when the gel-like center of a disc ruptures through a crack in the tough outer layer. A herniated disc can occur in any part of the spine but is most common in the lower back (lumbar region).
Spondylolisthesis: Spondylolisthesis is a condition that occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the vertebra below it. This can happen because of injury, degenerative changes in the spine, or congenital abnormalities. The slipped vertebra can put pressure on the nerves and cause pain. Treatment options include physical therapy, pain medication, and surgery.
Piriformis syndrome: Piriformis syndrome is a condition that occurs when the piriformis muscle irritates the sciatic nerve. For instance, if the piriformis muscle is too tight, it can compress and irritate the sciatic nerve. This can cause pain, numbness, or tingling in your buttocks and down the back of your leg.
How Is Slump Test Performed?

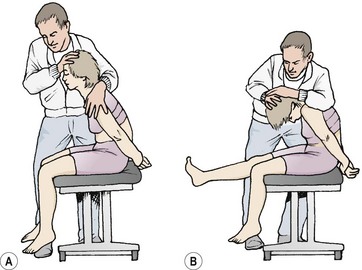
The slump test is performed by having the patient sit on the edge of a table or bed with their legs straight out in front of them. The healthcare provider will then take hold of the patient’s ankles and raise their legs up until they are at a 45-degree angle. The healthcare provider will then ask the patient to slump forward, keeping their head and back straight.
If the patient experiences pain, numbness, or tingling during the test, it may be indicative of nerve dysfunction. The test is generally considered to be positive if the symptoms are reproduced when the leg is raised to a 45-degree angle.
If the patient experiences pain, numbness, or tingling during the test, it may be indicative of nerve dysfunction. The test is generally considered to be positive if the symptoms are reproduced when the leg is raised to a 45-degree angle.
What Are the Risks Associated with Slump Test?
There are no major risks associated with the slump tests. However, the test may cause some discomfort for the patient if it is positive. Additionally, false-positive results can occur in patients with conditions that do not involve nerve pain.
The slump test is a simple and quick test that can be performed in the clinic to help diagnose various conditions involving nerve pain. While the test does have some risks, these are generally considered to be minor. If you are experiencing any symptoms of nerve pain, talk to your healthcare provider to see if the slump test is right for you.
What is the difference between a positive and negative slump test?
A positive slump test is one where the patient experiences pain, numbness, or tingling in their buttocks and down the back of their leg when the test is performed. A negative slump test is one where the patient does not experience any pain, numbness, or tingling in their buttocks or down the back of their leg during the test. In some cases, the test may need to be repeated several times to confirm the diagnosis.
What Are The Benefits Of the slump test?
There are various benefits of slump tests they are as follows:
1. Slump test is a simple and easy-to-perform diagnostic test that can help in identifying the problem related to the pinched nerves.
2. It is considered a highly sensitive test for the diagnosis of radiculopathy.
3. The test is also helpful in diagnosing other conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and spondylolisthesis.
4. Slump test is a cost-effective diagnostic tool that is widely available.
5. The test can be performed in the clinic as well as at home with the help of a family member or friend.
What Are The Limitations Of the slump test?
There are various limitations of the slump test they are as follows:
1. The test is not specific for any particular condition and can lead to false-positive results.
2. The test is not recommended for pregnant women and children.
3. The test may cause some discomfort to the patient if it is positive.
4. In some cases, the test may need to be repeated several times to confirm the diagnosis.
5. The test is not a replacement for other diagnostic tests like MRI or CT scan.
Thus, we see that the slump test is a simple diagnostic tool that has both advantages as well as disadvantages. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before undergoing the test so that the right diagnosis can be made.
Conclusion
It may be concluded that the slump test is a simple and quick diagnostic test that can be performed in the clinic to help diagnose various conditions involving nerve pain. While the test does have some risks, these are generally considered to be minor. If you are experiencing any symptoms of nerve pain, talk to your healthcare provider to see if the slump test is right for you.
Physical Therapy help patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.