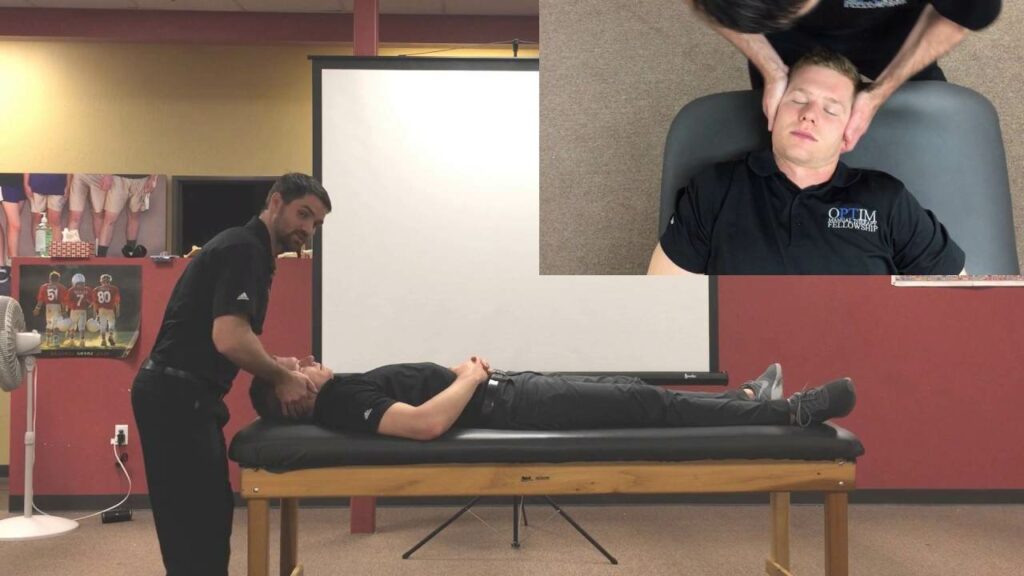
The vertebral artery test is a simple procedure that can be used to determine whether or not you have a problem with your vertebral arteries. This test is performed by checking the pulse in your neck and measuring how long it takes for blood to flow back to your heart. If you have a problem with your vertebral arteries, the pulse in your neck will be weak and slow, and it will take a long time for blood to flow back to your heart. In this blog post, we will discuss the steps involved in performing the vertebral artery test, as well as what the results of this test mean.
Contents
What Is the Vertebral Artery Test?
The vertebral artery test is a physical examination performed to assess the function of the vertebral arteries, which are located in the back of the neck and provide blood flow to the brain. It is part of a general neurological assessment that can help diagnose conditions such as stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Preparation
Before performing the vertebral artery test, it is important to properly prepare both the physician and the patient.
1. The physician should be able to explain the procedure in detail and answer any questions that may arise from the patient before it begins.
2. Patients should have a complete physical exam, including recent blood pressure readings, prior to the test as this will provide valuable information for interpreting the results of the test accurately.
3. In addition, the patient should be in a relaxed and comfortable position on an examination table as this will help ensure that the results of the test are accurate.
How Is The Vertebral Artery Test Performed?

The vertebral test may be performed in the following ways:
- The vertebral artery test involves inserting a thin tube called a catheter into the neck and through the vertebrae. Once in place, a dye is injected into the artery and x-ray pictures are taken of the dye’s flow. This helps to determine the diameter of the arteries, any narrowing or blockages, and any other abnormalities in the blood vessels that could indicate a risk for stroke. The test typically takes about 30 minutes to complete.
- After the vertebral artery test is completed, the patient can usually go home that same day. However, it is important to note that the patient should avoid strenuous activities for at least 24 hours after the procedure.
- The vertebral artery test is a simple and safe procedure that can help to detect any potential problems with the vertebral arteries. Although this test cannot prevent strokes, it can be an effective tool in diagnosing and treating any underlying medical conditions.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, be sure to speak to your doctor about having a vertebral artery test done right away. It could help save your life!
It is important to note that the vertebral artery test should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional in order for it to be effective. This ensures that the procedure will be done properly and any results obtained will be accurate. If you suspect that you or someone close to you may have arterial blockage, it is best to seek medical attention and request the vertebral artery test. Doing so can help detect any underlying problems and provide peace of mind.
What Are The Techniques Used?
The vertebral artery test is a diagnostic procedure performed to assess the health of the vertebral arteries. It involves performing several tests, including Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, and MRI angiography.
Doppler ultrasound
It is an imaging test that uses sound waves to measure blood flow in the body. It can create a map of the artery, allowing doctors to visualize any blockages or narrowing in the vessel.
CT angiography
It is an imaging technique that uses X-rays and contrast dye to produce detailed images of the arteries. It can detect blockages and narrowing of the vessels as well as any abnormalities present.
MRI angiography
It uses magnetic fields and radio waves instead of X-rays to produce detailed images of the arteries. It can detect any abnormalities or blockages in the vessels, as well as any narrowing.
The vertebral artery test is a safe procedure with minimal risk and discomfort for the patient. However, it is important to consult your doctor before undergoing the test to ensure it is the best option for you.
The technician will also use Doppler ultrasound imaging to create a map of the arteries and look for any blockages or narrowing. They will then use CT or MRI angiography to look for any abnormalities, such as aneurysms and plaques.
Once the images have been collected, they will be analyzed by a doctor to look for any potential issues with the vertebral arteries. If needed, the doctor may recommend further tests or treatments.
When Should This Test Be Done?
The vertebral artery test is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the function and health of the vertebral arteries. This test should be done when a patient experiences dizziness, vertigo, or symptoms of an impending stroke. It can also be performed if a doctor suspects that there are any blockages in the vertebral artery due to atherosclerosis or any other underlying medical condition.
The vertebral artery test is usually done in combination with other tests, such as a carotid artery test, an electrocardiogram (ECG), and an ultrasound scan of the neck. It is important to note that this procedure cannot detect small stroke-producing lesions; however, it can help to identify blockages that may lead to a future stroke.
Purpose
The purpose of the vertebral artery test is to evaluate the functioning of the vertebral arteries, which are two small blood vessels located at the base of the neck on either side of the spine. These arteries provide a vital supply of oxygen-rich blood to the brain and other parts of the body, so it is important to make sure that they are functioning properly.
What Does The Test Result Mean?
The results of the vertebral artery test can be interpreted in a variety of ways:
A positive result means that there is significant narrowing or occlusion (blockage) of the artery, which can indicate an underlying cardiovascular disorder. If the patient has no history of cardiovascular disease, the result may indicate a risk factor for future stroke or heart attack.
A negative result means that the vertebral artery is open and functioning normally, which suggests the absence of underlying disease. It is important to note that a negative result does not guarantee an absence of disease; other tests may be necessary to provide further information about risk factors or diseases in progress.
It is also possible for an inconclusive result to be obtained, which means that further tests are necessary in order to make a definitive diagnosis. In this case, the doctor may order additional imaging tests or consult with a specialist for further evaluation.
It is important to remember that the vertebral artery test should always be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical data and investigations. Only a medical professional can draw the appropriate conclusions from the test results. With this in mind, it is important that individuals consult with a doctor to discuss any questions or concerns they have about the results of their vertebral artery test.
It is also worth noting that while a positive result indicates some level of risk, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and eating a healthy diet can help improve overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack. In addition, regular exercise is important for maintaining optimal health and can play an important role in reducing the risk associated with any positive vertebral artery test results.
Benefits
There are various benefits:
1. The vertebral artery test is a relatively simple diagnostic procedure that can be used to accurately detect a variety of vascular issues in the neck, including stroke or aneurysm.
2. It is also non-invasive, meaning it does not require any cutting of the skin or internal exploration of the body’s systems.
3. Furthermore, the vertebral artery test is a quick and efficient way to check for poor circulation in the neck, as well as determine whether or not a patient has any blockages in the carotid arteries.
Limitations
There are various limitations to the vertebral artery test:
- First, it is not feasible to accurately measure blood flow through an artery because of the number of small vessels and capillaries in the area.
- Second, the test can be difficult to perform on patients who have reduced flexibility or limited neck range of motion due to age or injury.
- Finally, there is a risk that the test could cause an artery to become occluded, leading to a stroke.
Therefore, it is important that the test be performed by a qualified healthcare provider and only under the supervision of a doctor.
It should also be noted that due to its limitations, the test cannot replace more comprehensive imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scan.
Therefore, it is important to consult with your doctor before undergoing any kind of testing related to the vertebral artery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the vertebral artery test is a useful tool for medical professionals to assess cerebral blood flow in patients who may be at risk of artery stenosis. By understanding how to perform this important test, medical personnel can provide proper care and treatment to their patients. With the help of Doppler ultrasound technology and other advanced imaging techniques, results from this test can be used to detect and monitor any blockages or other issues in the vertebral artery. Through accurate diagnosis, medical personnel can provide corrective measures to ensure better health outcomes. With the help of the vertebral artery test, doctors can work towards providing their patients with a better quality of life.
Physical Therapy help patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.