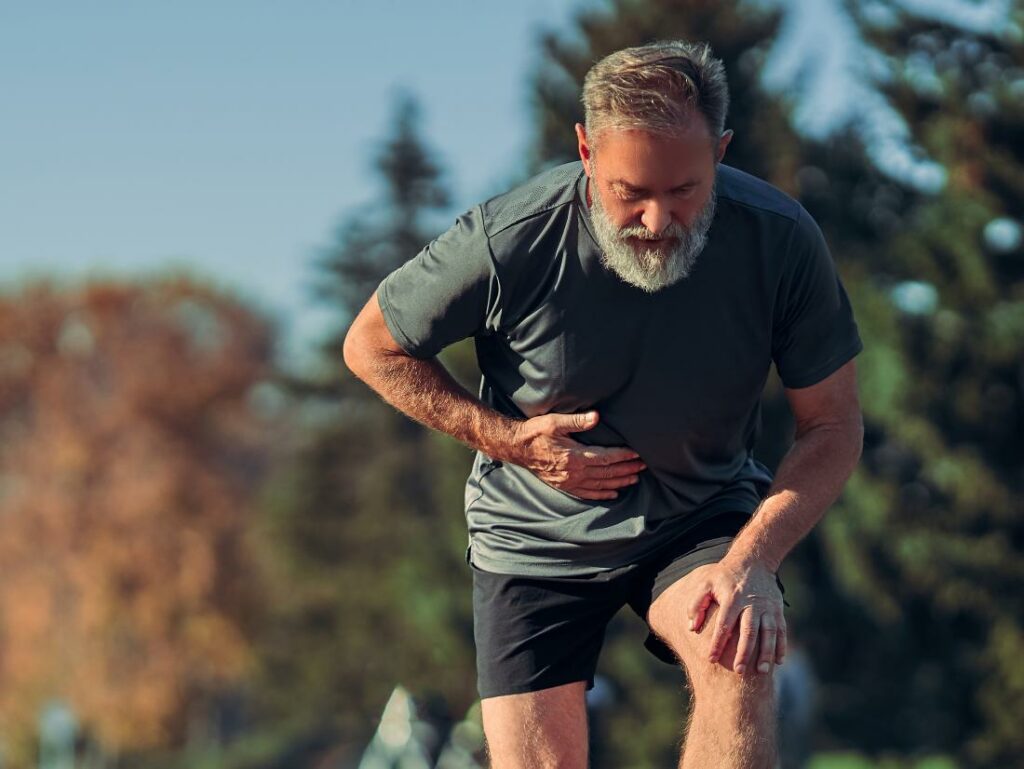
Core muscle injuries are a common occurrence in both athletes and the general population. These injuries can be caused by a variety of factors and can result in a number of different symptoms. If you are experiencing any pain or discomfort in your core muscles, it is important to seek treatment right away. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for core muscle injuries.
Contents
What Is Core Muscle Injury?
 Core muscle injury is a common musculoskeletal condition involving damage to the muscles in the abdomen, pelvis, and lower back. It can either be an acute injury caused by sudden trauma or repetitive strain from activities such as overuse. This is described as an overuse injury because it involves excessive strain on the muscles that can lead to tears or other damage.
Core muscle injury is a common musculoskeletal condition involving damage to the muscles in the abdomen, pelvis, and lower back. It can either be an acute injury caused by sudden trauma or repetitive strain from activities such as overuse. This is described as an overuse injury because it involves excessive strain on the muscles that can lead to tears or other damage.
According to studies, this type of core muscle injury can be extremely disabling and can limit physical activity. Without proper treatment, it may lead to long-term chronic pain. Many people misunderstand core muscle injuries and think of them as back pain, but the symptoms and treatments can differ greatly.
How Does It Feel?
The feeling of a core muscle injury depends on the severity of the damage, but typically people feel pain in the abdominal area where the muscles were affected. The pain is often localized and can range from mild to severe depending on how badly the muscles are damaged. It may also radiate outwards or into other parts of your body.
You may also experience tenderness, swelling, or bruising in the area where the injury occurred. It’s possible for you to experience a burning sensation when using the muscles that have been injured. Some other common signs might include:
- Difficulty performing basic movements
- Loss of range of motion in the area injured
- Weakness or instability when standing, sitting, or walking
- Inability to perform certain physical activities that involve core muscles
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention right away as core muscle injuries can worsen without proper treatment.
What Causes Core Muscle Injuries?
 Core muscle injuries are usually caused by overuse or sudden movement that causes the muscles to tear. For example, if a person is doing crunches or any type of strenuous activity that involves the core, they are more likely to suffer from this type of injury.
Core muscle injuries are usually caused by overuse or sudden movement that causes the muscles to tear. For example, if a person is doing crunches or any type of strenuous activity that involves the core, they are more likely to suffer from this type of injury.
Some other causes might include:
- Poor warm-up or stretching before exercise
- An underlying medical condition such as arthritis or osteoporosis
- The unsafe technique when lifting heavy objects
- Overreaching during physical activities
- Imbalance in muscles around the core area
It is often believed that core muscle injuries are caused by a single incident of trauma, such as excessive lifting or a strain during physical activity. However, in many cases, core muscle injuries can be the result of repetitive movements and overuse.
All in all, these are a few causes of core muscle injuries. You should be aware of these to help prevent them from occurring.
What Are The Treatment Options For Core Muscle Injury?
There are several treatment options available for core muscle injury, depending on the severity and location of the injury. Some common options include:
- Rest: Rest is often the best treatment for core muscle injury. It allows the muscles to heal and can prevent further damage. For example, if a muscle is strained, rest can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the injured area can help decrease inflammation and swelling associated with the injury. This ice therapy is often used in conjunction with rest to help reduce pain and swelling.
- Compression: Wrapping or compressing the injured area with a bandage helps support the muscles, reducing pain and aiding in healing. For example, if the core muscle is strained, wrapping it with a support bandage may help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Elevation: Elevating the injured area above your heart helps reduce swelling and inflammation and can provide relief from pain. Many people find this to be a helpful treatment for core muscle injury.
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium can help decrease pain and inflammation associated with muscle injuries. Medicines are usually taken orally or can be applied topically.
- Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help you to strengthen the muscles around the injured area and improve your range of motion. Strengthening the muscles can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with core muscle injuries.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary if there is a tear or rupture of the muscle. The process of surgery will vary depending on the severity of the injury.
No matter which treatment option you choose, it is important to follow up with your doctor or physical therapist to ensure that the injury is healing properly. They may adjust your treatment plan as needed to help you move toward full recovery.
Which Is The Most Effective Way To Treat Core Muscle Injury?
 As there are many different types of core muscle injuries, the most effective treatment plan is dependent on the individual injury and its severity. Generally, treating a core muscle injury involves a combination of physical therapy, and strengthening exercises.
As there are many different types of core muscle injuries, the most effective treatment plan is dependent on the individual injury and its severity. Generally, treating a core muscle injury involves a combination of physical therapy, and strengthening exercises.
Physical therapy can help strengthen weak muscles and improve the stability of the core, helping to reduce pain and speed up recovery. Common physical therapy techniques include:
- Muscle stretching
- Massage
- Electrical stimulation
- Heat/ice treatments
- Ultrasound
Strengthening exercises are important for developing strong muscles that can help protect against injury in the future. Exercises may involve using weights or resistance bands to target the core muscles.
These are some common treatments for core muscle injuries, but it is important to discuss your particular injury with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action. They can help determine which treatment options are most suitable and provide advice on how to prevent future injuries. With the right guidance and support, you can reduce the severity and duration of your injury and get back to an active life!
How Can You Prevent Core Muscle Injury?
It is possible to significantly reduce the risk of suffering a core muscle injury. Here are some tips on how to do that:
- Develop and maintain core strength through regular exercise and stretching
- Wear appropriate protective gear when engaging in contact sports or strenuous physical activity
- Maintain good posture, especially during repetitive lifting or bending motions
- Take breaks during long periods of strenuous physical activity
- Listen to your body and stop when you feel pain or discomfort
By taking measures to prevent core muscle injury, you can significantly reduce the chances of suffering from this painful condition. In addition, if an injury does occur it is important to seek medical attention immediately in order to properly diagnose and treat the injury.
Once properly diagnosed, a medical professional can provide rehabilitation exercises and treatments to help you recover from your core muscle injury as quickly and safely as possible. With the right preventative measures and treatment, you can get back to living life pain-free!
Conclusion
In conclusion, core muscle injury may range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, depending on the severity of the condition. It is important to be aware of the causes, symptoms, and treatments available for core muscle injuries in order to prevent them from worsening.
Complete recovery times can take between two weeks to several months. It is important to consult a medical professional to diagnose the injury accurately and receive the proper treatment. If left untreated, core muscle injuries can lead to chronic pain and disability in the future.
Physical Therapy has always been proven to help patients recover from pain. Hence, if you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.


