If you are experiencing pain in your shoulder, you may be wondering if you have a rotator cuff injury. The anterior drawer test is a common diagnostic tool used to determine if there is damage to the rotator cuff. In this blog post, we will discuss everything you need to know about the anterior drawer test!
Contents
What is the Anterior Drawer Test?
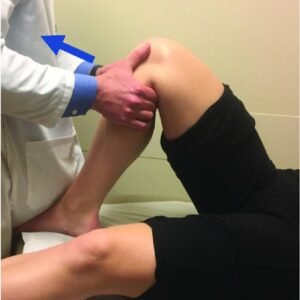
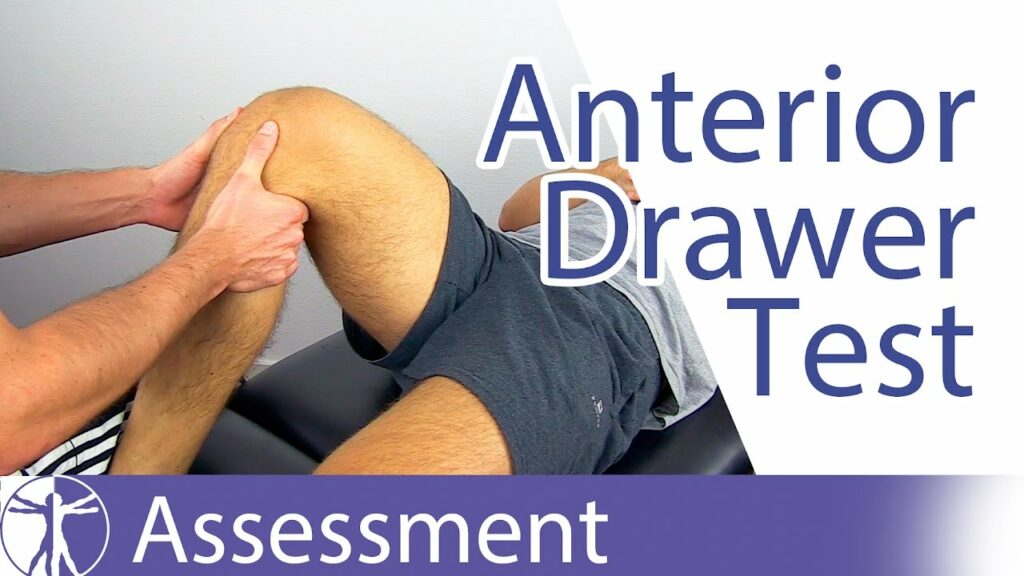
Anterior drawer test is used to assess the integrity of knee ligaments. It measures the amount of anterior displacement of the tibia on the femur and can be used to diagnose injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), or both.
This type of test is used to assess the stability of the knee joint and is commonly done with a physical therapist or doctor. By stabilizing the thigh bone (femur) and pushing on the shin bone (tibia), they can determine if there is too much freedom of movement in the knee joint.
Sometimes, the anterior drawer test is combined with other tests to provide a more comprehensive assessment of knee stability. One of the most common tests is the Lachman test, which evaluates ACL integrity, as well as stability.
How Is the Anterior Drawer Test Performed?
The test begins with the patient lying face down on a table or reclining chair. The examiner then stabilizes the thigh bone by placing one hand on it and holding it in place.
Using their other hand, they press firmly on the shin bone near the ankle joint towards the knee joint (called an ‘anteromedial force’). This movement should create some resistance and slight displacement of the tibia – this displacement is known as ‘drawer motion.
The amount of displacement can be measured using a goniometer and is graded on a scale of 0, 1+, 2+, 3+, or 4+. The higher the grade, the greater the displacement.
After completing the drawer test, it’s important to perform a posterior drawer test by applying pressure on the shin bone in the opposite direction (posterolateral). This helps to differentiate between laxity due to ligament injury or weak muscles.
The overall results of both tests can then be used to diagnose ligament injuries such as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear or muscle weakness and instability issues that may be affecting joint stability.
It’s also important for practitioners to keep in mind that false-positive results are common with this test, so it’s important to consider other clinical signs and symptoms before making a diagnosis.
The performance of an anterior drawer test is a simple way to measure the amount of displacement in a joint. Practitioners need to understand how to correctly administer this test and interpret its results as part of their overall evaluation. With proper knowledge and understanding, healthcare professionals can use this test to accurately diagnose ligament injuries or muscle weakness and instability issues.
What to Expect During an Anterior Drawer Test?
The expectations of the patient during the test depend on the reason for the test. If it’s a diagnostic measure, then no preparation is necessary. However, if the anterior drawer test is being done to evaluate an injury or other medical condition, then some kind of anesthesia will likely be required.
Some of these expectations can be expected during the procedure:
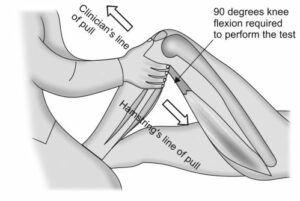
- The patient will be asked to lie on their back while their knee is bent at a 90-degree angle.
- The healthcare professional will apply pressure to the front of the knee and move it around in various directions, testing for signs of laxity or stability.
- Measurements may be taken to determine the amount of laxity or stability.
- The patient may experience discomfort during this test, but it should not be painful.
- Once the testing is complete, the healthcare professional will provide feedback on their results and discuss any treatment plans that need to be followed.
Overall, an anterior drawer test is a fast and non-invasive way for healthcare professionals to measure knee joint stability in patients. It’s an important tool used to accurately diagnose medical conditions and injuries to develop effective treatments. With proper preparation, expectations should be clear for both the patient and healthcare provider involved in the procedure.
Elements of Anterior Drawer Test
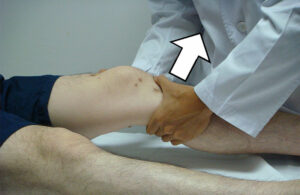
The elements of the Anterior Drawer Test involve the assessor applying an anterior force to the tibia while stabilizing the knee. The tibia should not move more than two cm forward, or else a positive result may be indicated. The assessor needs to pay attention to any pain that is reported by the patient during this test. A positive sign could indicate a laxity of ligaments such as the ACL, PCL, and MCL.
Some of the elements can be modified to increase accuracy. For instance, the assessor can use a posterior force instead of an anterior force and may also apply external rotation or abduction to the tibia while stabilizing the knee. This could help measure different ligaments and further indicate laxity if any is present.
An assessor needs to be aware that this test may not always provide accurate results due to factors such as hip position, patient discomfort, or muscle tonicity. It should be performed in conjunction with other tests before making definitive statements about ligament laxity. If a positive result is seen during this test, imaging studies are recommended for more information regarding the severity of the injury and treatment options.
Uses of Anterior Drawer Test
An anterior drawer test is a type of medical examination that is used to diagnose various diseases. The test is generally done to check for problems in the lower spine.
There are many different uses for the anterior drawer test. Some common reasons are as follows:
To diagnose a herniated disc in the lower back
This is one of the most common uses of the test. It can help to detect a herniated disc, which is a condition where the discs in the spine are damaged or displaced.
To evaluate ligament tears and sprains
The anterior drawer test can also be used to diagnose and evaluate ligament tears and sprains in the lower back area. These tears occur when one of the nerves that run through the spine becomes pinched, leading to pain and discomfort in the affected area.
To assess spinal joint stability
The anterior drawer test can also be used to assess spinal joint stability. This means it can help determine whether there is any instability in the joints of the spine, which can cause long-term damage if left untreated.
To investigate structural issues of the spine
An anterior drawer test can also be used to investigate structural issues in the spine. This could include scoliosis, which is an abnormal curvature of the spine, or any other structural anomalies that may be present.
To measure nerve root compression
Finally, an anterior drawer test can also be used to measure nerve root compression. This is when a nerve is compressed due to spinal abnormalities, resulting in pain and discomfort. The anterior drawer test can help diagnose this condition and provide information about its severity.
How to Prepare for an Anterior Drawer Test?

Preparation for an anterior drawer test is relatively simple.
First, the patient should be placed in a supine position and have their knee flexed to 90 degrees. The physician will then stabilize the tibia by pressing against it while they assess the mobility of the ankle joint with one hand—this is typically done at the level of the malleoli. On the other hand, the doctor will apply force to the talus bone to get an assessment of stability and movement.
It’s important that during this evaluation, both externally rotated (ER) and internally rotated (IR) tests are performed as these will provide additional information on any instability or asymmetries present within the ankle joint and help diagnose pathology more accurately.
Another step that can help improve the accuracy of the test results is to have the patient actively dorsiflex their ankle or push against the doctor’s hand. This is important because it can give a better indication of ligamentous injury or laxity if there are differences between voluntary and passive movement.
Finally, after completing all assessments, the physician should compare findings from both ankles before making any conclusions about pathology. Anterior drawer tests require careful examination as even subtle differences in movement can point to serious pathology. Therefore, it’s critical that they are conducted correctly and compared between both sides for accurate diagnosis.
Side Effects of the Anterior Drawer Test
An anterior drawer test is a simple but effective way to determine if someone has a herniated disc. Patients who experience moderate to severe pain when doing simple tasks such as lifting their arm above their head, bending at the waist, or getting up from a seated position should undergo this test.
There are many side effects of the Anterior Drawer Test that should be considered before undergoing this procedure. Most commonly, the test may cause some discomfort or pain in the knee due to the pressure of the examiner’s hand on the joint. Additionally, a popping sensation may be felt as the joint is moved and manipulated during testing. It is also possible for swelling or bruising to occur in the area around the knee where pressure was applied.
Another side effect is the risk of injury to the structures in the knee joint. If the force used during testing is too great, it can cause ligament damage or even a fracture. Additionally, if an incorrect diagnosis is made based on the Anterior Drawer Test results, further medical evaluations may be required which could lead to increased medical costs and time lost from work or other activities.
Finally, there are risks associated with any medical procedure and this test should not be undertaken without consulting your doctor first. Your doctor will assess your condition and determine whether or not you would benefit from undergoing this test before making any treatment decisions.
Conclusion
An anterior drawer test is a widely used physical examination that can be conducted by medical professionals to assess the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It is a simple, non-invasive, and cost-efficient clinical assessment tool. The results of this test can help in determining whether further diagnostic tests or treatments are necessary. In summary, an anterior drawer test is an important tool for diagnosing ACL injuries. It provides clinicians with valuable information about the stability of the knee joint and can be used to guide management decisions.
Physical Therapy help patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.