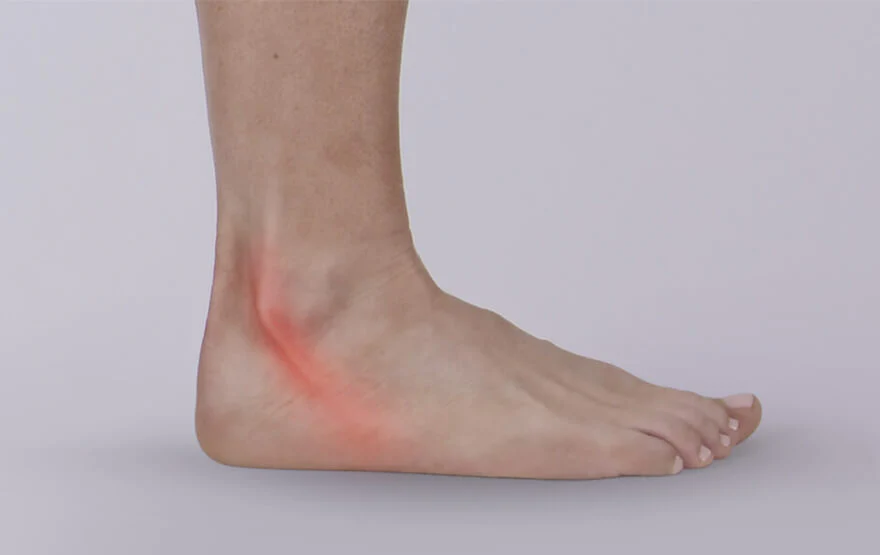
Do you suffer from pain in the ankle and lower leg? If so, you may have peroneal tendonitis. This condition is caused by inflammation or irritation of the peroneal tendons, which run along the side of the ankle. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of peroneal tendonitis. We will also provide tips for preventing this condition from occurring.
Contents
What Is Peroneal Tendonitis?
 This is the inflammation of the peroneal tendons, which are located on the outside of your lower leg. The peroneus longus and brevis muscles attach to these tendons and help stabilize your ankle. These muscles work together to plantarflex (point your toes downward) and evert (turn your foot outward) your foot.
This is the inflammation of the peroneal tendons, which are located on the outside of your lower leg. The peroneus longus and brevis muscles attach to these tendons and help stabilize your ankle. These muscles work together to plantarflex (point your toes downward) and evert (turn your foot outward) your foot.
It is common for people who participate in sports that involve running or jumping to develop peroneal tendonitis due to the repetitive stress placed on these tendons. The condition can also be caused by an ankle injury or overuse of the peroneal muscles.
If you feel like you might have peroneal tendonitis, it is important to consult with a doctor or certified physical therapist to get an accurate diagnosis. Once you have been diagnosed, your healthcare professional will work with you to create a treatment plan that meets your needs.
What Are Some Common Symptoms?
There are several peroneal tendonitis symptoms, which may occur singly or in combination.
- Pain is the primary symptom and is usually worse with activity. It may be sharp, aching, or throbbing. The pain often starts gradually and gets worse over time. You may also have tenderness when you press on the affected area.
- Another common symptom is swelling. This can occur around the tendon or in the ankle joint. Swelling may make it difficult to move your ankle or foot.
- You may also have weakness in the affected leg. This is because the peroneal tendons help stabilize the ankle joint. When they are inflamed, they cannot do their job as well.
While these are a few of the most common symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor if you think you may have peroneal tendonitis. Only a professional can give you an accurate diagnosis. However, there are other signs that may point to the condition.
For example, you may hear a snapping sound when you move your ankle. This is because the tendon is rubbing against the bone. You may also have trouble moving your foot up or down.
If you have peroneal tendonitis, it’s important to see a doctor right away. The sooner you start treatment, the sooner you’ll be on the road to recovery.
What Causes Peroneal Tendonitis?
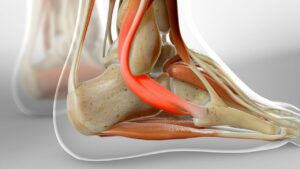 There are several things that can lead to peroneal tendonitis, including:
There are several things that can lead to peroneal tendonitis, including:
- Overuse: This is the most common cause of the condition. It often occurs in people who participate in activities that involve repetitive motions of the foot and ankle, such as running, tennis, or basketball.
- Trauma: A direct hit to the ankle can cause peroneal tendonitis. This is more likely to occur in contact sports, such as football or hockey.
- Ankle instability: This occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle are too loose. It can cause the peroneal tendons to rub against the ankle bone, which leads to inflammation.
- Flat feet: This condition occurs when the arch of the foot collapses. It can put extra strain on the peroneal tendons and lead to inflammation.
- Arthritis: This condition causes inflammation in the joints, which can also lead to inflammation in the peroneal tendons.
These causes are often related to each other. For example, someone with flat feet is more likely to develop peroneal tendonitis from overuse because the condition makes the foot less stable and puts extra strain on the tendons.
Moreover, there are some risk factors that can increase your chances of developing peroneal tendonitis, such as:
- Age: The condition is more common in adults over the age of 40.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop peroneal tendonitis than men.
- Obesity: Carrying extra weight puts extra strain on the tendons and can lead to inflammation.
How Is It Diagnosed?
This is generally a clinical diagnosis, meaning that your doctor will be able to diagnose you based on your symptoms and a physical examination. However, if your doctor is unsure or there are other possible causes for your pain, they may order imaging tests such as an MRI or ultrasound.
A diagnosis is important because peroneal tendonitis can be mistaken for other conditions, such as a sprained ankle, Achilles tendonitis, or even arthritis. It is important to understand the difference so you can receive the proper treatment.
What Are the Treatment Options?
 The good news is that peroneal tendonitis is treatable and usually doesn’t require surgery. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and pain while allowing the tendon to heal. Treatment options include:
The good news is that peroneal tendonitis is treatable and usually doesn’t require surgery. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and pain while allowing the tendon to heal. Treatment options include:
Rest
It is important to rest the tendon and give it time to heal. This may mean taking a few days off from work or avoiding activities that put stress on the tendon. For example, if you have peroneal tendonitis caused by running, you will need to take a break from running and switch to another form of exercise.
Ice
Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, 3-4 times per day. Also, it is important to not apply ice directly to the skin, but rather wrap the ice in a towel or shirt.
Compression
Compressing the affected area with an ace wrap can also help reduce pain and inflammation. The ace wrap should be applied snugly but not so tight that it cuts off circulation. It is important to remove the ace wrap at night so that the area can breathe.
Elevation
Elevating the affected leg can help to reduce pain and swelling. Try to keep the affected leg elevated for at least 30 minutes, 3-4 times per day. This works best if you prop your leg up on a pillow or other comfortable object.
Anti-inflammatory Medication
It is important to reduce the inflammation around the peroneal tendon as soon as possible. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Be sure to follow the package directions carefully and do not take more medication than recommended.
Bracing
This is the most common form of conservative treatment and is often very effective. A brace helps to unload the peroneal tendons by taking over some of the work normally done by these muscles and tendons. The peroneuslongus and Brevis attach to the outside of the foot and help stabilize the foot and ankle during walking.
Surgical treatment
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to fix the underlying problem causing peroneal tendonitis. For example, if there is a tear in the tendon, surgery may be necessary to repair the tear. The process is not much different than other tendon surgery, and the success rate is very high. Recovery from peroneal tendonitis surgery is typically pretty quick. Most people are back to their normal activities within a few weeks.
So, these are some common treatment options that can help with peroneal tendonitis. As always, it’s important to check with your doctor to see what’s best for you and your individual case.
Can You Prevent Peroneal Tendonitis?
 While it’s not always possible to prevent peroneal tendonitis, there are some things you can do to lower your risk:
While it’s not always possible to prevent peroneal tendonitis, there are some things you can do to lower your risk:
- Wear shoes that fit well and provide good support.
- Wear appropriate footwear for the activity you’re participating in.
- Stretch and warm up before exercising.
- Avoid sudden changes in activity level.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
These might seem like common-sense measures, but they can help reduce the strain on your peroneal tendons and lower your risk of developing peroneal tendonitis. According to studies, most cases of peroneal tendonitis are the result of overuse, so anything you can do to reduce the amount of stress on your tendons will help.
If you’re already experiencing symptoms of peroneal tendonitis, then please follow some treatment options. Because the problem is usually caused by overuse, the best thing you can do is rest the affected area and give your body a chance to heal.
With the right treatment and some patience, you should be able to fully recover from peroneal tendonitis and get back to your normal activities.
Conclusion
To conclude, peroneal tendonitis is a condition that can cause pain and inflammation in the lower leg. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have this condition, as it can worsen over time and potentially lead to other complications. Treatment typically involves a combination of rest, ice, and physical therapy.
However, please consult your physician before beginning any new treatment regimen. Because it can be difficult to properly diagnose peroneal tendonitis without a certified medical professional, it is always best to seek help from a doctor or other healthcare provider before beginning any sort of self-treatment.
Physical Therapy help patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.