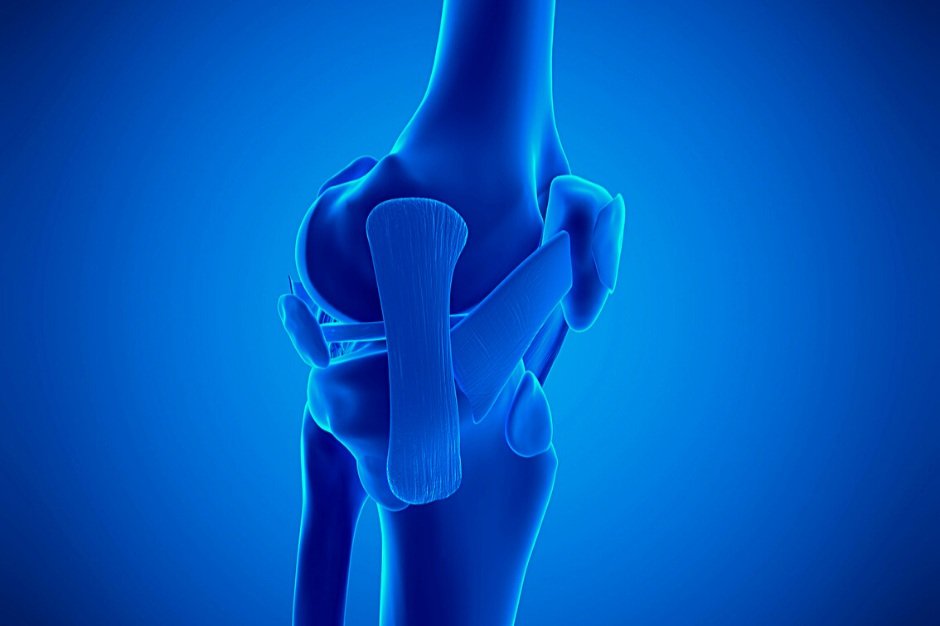
The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is a band of tissue that helps to stabilize the knee. It is often injured in athletes and can cause pain and instability in the knee. Treatment for an MPFL injury varies depending on the severity of the injury. In this blog post, we will discuss how you can treat an MPFL injury and get your life back to normal!
Contents
What Is MPFL (Medial Patellofemoral Ligament)?
 The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is the main restraints to patella (knee cap) dislocation. It is a flat, broad, and relatively thin band of tissue that originates from the inner aspect of the femur (thigh bone) just below the knee joint and inserts into the back side of the patella.
The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is the main restraints to patella (knee cap) dislocation. It is a flat, broad, and relatively thin band of tissue that originates from the inner aspect of the femur (thigh bone) just below the knee joint and inserts into the back side of the patella.
MPFL is important in stabilizing the patella and keeping it in its proper place during knee movement. A tear or rupture of this ligament can result in kneecap instability and dislocation.
Many people consider MPFL injury as a sports injury because it is commonly seen in athletes who participate in contact sports such as football, rugby, and hockey. However, MPFL tears can also occur in non-athletes due to trauma (e.g., car accidents) or pre-existing conditions (e.g., patellar instability).
If you are suffering from an MPFL injury, it is important to seek medical treatment as soon as possible. Depending on the severity of your injury, treatment may involve conservative measures or more aggressive treatments.
Is MPFL Tear Serious?
In most cases, medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) tears are not serious. However, if the MPFL is completely torn, it can lead to instability of the kneecap. This can be a problem if you participate in activities that put a lot of stress on your knees, such as running or playing soccer.
There are several signs of an MPFL tear, including:
- knee pain
- swelling
- warmth around the kneecap
- a feeling of instability in the knee
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor. An MRI can confirm whether or not you have an MPFL tear. It can be serious and cause long-term problems if the MPFL is not treated.
Treating an MPFL Tear
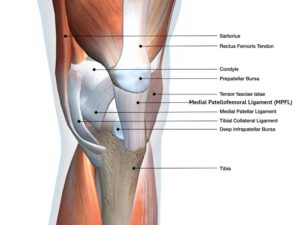 There are various ways that you can treat an MPFL tear, depending on the severity of the tear. If the tear is small, then you may only need to do some physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint. However, if the tear is large or if there is instability in the knee joint, then you may need to have surgery to repair the condition.
There are various ways that you can treat an MPFL tear, depending on the severity of the tear. If the tear is small, then you may only need to do some physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint. However, if the tear is large or if there is instability in the knee joint, then you may need to have surgery to repair the condition.
Let’s discuss each of these treatment options in more detail.
Physical Therapy
This is one of the most common treatments for an MPFL tear. The goal of physical therapy is to help you regain strength in the muscles around your knee joint and to help stabilize your knee joint. Your physical therapist will design a specific rehabilitation program for you that will gradually help you improve your range of motion and strength.
There are various examples that can be used to help treat an MPFL tear. One common exercise is the clam exercise. This is where you lie on your side with your affected leg on top. You then raise your knee up while keeping your foot in contact with the ground. This helps to strengthen the muscles around your knee joint and can help stabilize your knee joint.
Other physical therapies include:
- Iontophoresis: This is where medication is delivered through the skin using an electrical current. This can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Massage: This can help to reduce pain and muscle spasms.
- Joint mobilization: This is where your physical therapist will move your knee joint around in different directions. This can help to reduce stiffness and improve the range of motion.
- Ultrasound: This uses sound waves to deliver heat to the tissues around your knee joint. This can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgery
If the MPFL is completely torn, it will not heal on its own. In this case, you will need to have surgery to repair the ligament. The type of surgery will depend on the severity of the injury and whether you have any other knee problems. One of the common surgery types is arthroscopic surgery.
This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is used to repair the MPFL. During the surgery, the surgeon will make a small incision in your knee and insert a tiny camera into your joint. This camera is called an arthroscope. The surgeon will use the arthroscope to look inside your knee and locate the torn MPFL.
Once the ligament is located, the surgeon will stitch it back together. In some cases, the surgeon may need to use a graft to repair the ligament. This is when a piece of tissue is taken from another area of your body and used to replace the damaged ligament.
Steroid injections
This is one of the most common treatments for medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) tears. The idea is to reduce the inflammation around the ligament so that it can heal properly. However, there is no guarantee that this will work and it may only be a temporary fix.
For example, steroid injections may be used to:
- Relieve pain
- Reduce inflammation
- Promote healing
- Improve range of motion
If you do opt for this treatment, you’ll likely need a series of injections over the course of several weeks. But always, be sure to follow your doctor’s orders.
Self-care
In addition to the treatments your doctor may recommend, there are several self-care measures you can take to ease the pain and discomfort of MPFL:
- Rest: Avoid activities that put stress on your knees, such as running or playing sports. Instead, focus on low-impact activities, such as walking, swimming, or biking.
- Ice: Apply ice to your knees for 20-30 minutes at a time, several times a day. This can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Use a compression wrap or bandage to support your knee and help reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Raise your leg above the level of your heart when you’re resting or sleeping to help reduce swelling.
If you have any questions or concerns about your condition, be sure to talk to your doctor. MPFL is a treatable condition, and with the right treatment plan, you can get back to your normal activities.
How Long Does a Torn MPFL Take To Heal?
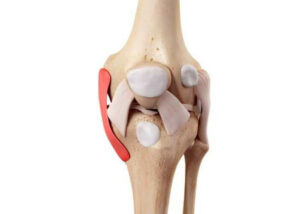 Well, this largely depends on the severity of your injury and how well you follow your rehabilitation protocol. There are three grades of MPFL tears.
Well, this largely depends on the severity of your injury and how well you follow your rehabilitation protocol. There are three grades of MPFL tears.
Grade 1 is a partial tear of the ligament with microtrauma to the fibers. This is generally considered a minor injury that can be treated conservatively. Grade 2 is a complete tear of the ligament with some fiber rupture. This is a more serious injury that may require surgery. Grade 3 is a complete tear of the ligament with total fiber rupture. This is the most severe type of MPFL injury and definitely requires surgical intervention.
Assuming you have suffered a grade 2 or 3 tear, your timeline for healing will be much longer than someone who has only sustained a grade 1 tear. In fact, depending on the severity of your particular injury, it could take up to 6 months for a complete recovery.
During that time, you will likely experience some discomfort and swelling. The good news is that there are several things you can do to help speed up the healing process and get you back on your feet as quickly as possible.
How Can You Speed Up The Healing Process?
Sometimes, you may want to recover soon and get back to your previous activity levels as soon as possible. Here are some tips to help you speed up the healing process:
- Avoid high-impact activities: It’s important to avoid high-impact activities, such as running or playing soccer, until the MPFL has healed completely. This will help prevent further injury and allow your ligament to heal properly.
- Warm up before activity: Warming up before participating in any activity can help prevent injury. A good warm-up will increase your heart rate and body temperature, and loosen your muscles and joints.
- Stretching: Stretching can also help prevent MPFL injuries. Be sure to stretch all of your muscles, including your hamstrings, quads, and hip flexors.
- Strength training: Strength training can help improve the function of your muscles and prevent MPFL injuries. Be sure to focus on exercises that target the muscles around your knees, such as leg presses and squats.
- Good shoes: Wearing good shoes that fit well can help prevent MPFL injuries. Avoid worn-out shoes and high heels, which can put extra strain on your knees.
With these things in mind, you can help speed up the healing process and get back to your regular activities as soon as possible. Also, there are various treatments available to help address MPFL injuries, so be sure to talk to your doctor about which option is best for you.
Otherwise, the healing process can take some time, but it is important to be patient and let your body heal properly. In most cases, the MPFL will heal on its own with rest, ice, and elevation. However, if the injury is severe or does not improve with conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MPFL can be treated with both conservative and surgical methods. However, the decision on which treatment to use depends on many factors, such as the severity of the injury, the age of the patient, and the activity level of the patient. If you have any questions about your individual case, be sure to ask your doctor.
There are numerous types of treatment to help you, so do not feel discouraged if one treatment does not work for you. There are many options available, and with the help of your doctor, you will be able to find the best treatment for you!
Physical Therapy help patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.