Pre-Diabetes And Its Prevention Around 30% of the world’s adult population is pre-diabetic. i.e. 1 in every 3 people is pre-diabetic. But the sad part is, that most of us don’t even know if we are suffering from pre-diabetes or not. There is an immense lack of awareness about pre-diabetes among people. Because of this the right treatment and care are not acquired at the correct time and it gets converted into diabetes followed by other health complications.
Contents
What Is Pre-Diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is a condition where your blood sugar level is higher but not too high to be called diabetes. If this condition is not treated at the right time, it can get converted into diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes almost always had prediabetes first. A vast majority of people have pre-diabetes. The number of pre-diabetes patients is higher than diabetic patients.
Symptoms of Pre-Diabetes
If you have symptoms of pre-diabetes, you might notice that:
- Frequent Urination: You pee a lot as your kidneys try to excrete the excess glucose through urination
- Thirsty: You are thirstier than usual as frequent urination starves your body of water
- Excessive Tiredness: You are a lot more tired than usual as under diabetes, glucose which is the key source of energy, remains in your blood and is not transported well to the cells
The sad part is, that around 85% of the people do not experience any symptoms and remain unaware of their condition. This factor of pre-diabetes makes it more hazardous.
Causes And Risk Factors of Pre-Diabetes
You’re more likely to get prediabetes if you:
- Are older, especially over age 45
- You have a family history of diabetes
- Are overweight or obese, especially if you have belly fat
- Have a sedentary lifestyle and don’t exercise
- Eat a lot of meat, drink sugary beverages, and don’t eat much fruit, veggies, nuts, whole grains, or olive oil
- Have a sleep problem, or work changing shifts or night shifts
- Have high cholesterol, high triglycerides
Pre-diabetes or diabetes should not be taken lightly. It has multiple risks and health complications associated with it such as:
- High blood pressure
- Nerve problems (peripheral neuropathy)
- Loss of a limb (amputation)
- Kidney failure
- Blindness
How Pre-Diabetes Can Be Diagnosed?
If you fall under any of the above risk factors or are experiencing symptoms, then you should immediately get yourself diagnosed. Pre-diabetes can be diagnosed with the help of any of the 3 simple blood tests including fasting glucose test, Glucose tolerance test, and HbA1c test.
Fasting Glucose Test
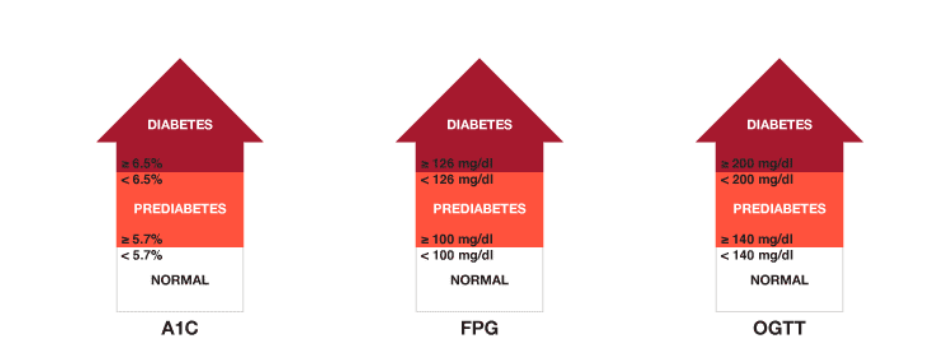
In this test, a person is asked not to eat anything for 8 hours, after which they have to submit blood samples to test their sugar level. If the results show a blood sugar level less than 100 milligrams per deciliter, then your health is normal, whereas, if the report shows a blood sugar level between 100 to 125 milligrams per deciliter, then you are pre-diabetic, followed by a sugar level of 126 milligrams per deciliter for a diabetic patient.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Once you are done with the fasting plasma glucose test, you will have to drink something sugary. Then the technician will again take a blood sample, to which, the results will be normal if your blood sugar is less than 140 mg/dl, pre-diabetic if your blood sugar level is between 140 to 199 mg/dl, followed by diabetes if your blood sugar level is 200 mg/dl.
Haemoglobin A1c Test
The above 2 tests measure your point in time sugar. HBA1C measures your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. The test result will show normal if the blood sugar level is 5.6% or less, pre-diabetic if it’s between 5.6 to 6.4, followed by diabetic if your blood sugar level is 6.5% or above.
Diabetes Prevention

How to prevent or treat pre-diabetes?
Pre-diabetes can be reversed with early diagnosis & treatment. Pay attention to your health and get yourself diagnosed if you fall in a high-risk group such as obese, aged, pregnant, or heart patient. Follow the following precautions or treatments:
Diet
- Cut off sugary contents from your food
- Follow a healthy diet to lose 5% to 10% of your weight (in case you are obese).
- Shift to a whole-grain and vegetable-rich diet.
- Drinks lots of water
Exercise
- Pick moderate-intensity exercises such as brisk walking and perform them for at least 30 minutes daily
Lifestyle
- Reduce the stress level in your life through ways such as meditation
- Get sound sleep of at least 7-8 hours a day
- Keep your cholesterol and blood sugar level under control.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
Making these changes in your daily routine will not only help you in preventing prediabetes but also keeps your overall health good as well.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.