Contents
- 1 What Is Glucose?
- 2 Why Is Glucose Important?
- 3 How does The Human Body Deal With Glucose?
- 4 What Are Normal Glucose Levels?
- 5 How Do You Check Your Blood Glucose Levels?
- 6 What Foods Are High In Glucose?
- 7 Is Glucose Harmful To Our Bodies?
- 8 What To Do When Blood Glucose Level Is Unstable?
- 9 A Word From MantraCare
What Is Glucose?
Glucose is also known as blood sugar. The body’s system must function properly. It often goes unnoticed when our glucose levels are at their best. When the level of glucose is high then you can feel the unhealthy functioning effects.
So, what exactly is glucose? It is a monosaccharide the simplest form of carbohydrates. This indicates that it has only one sugar. Fructose, galactose, and ribose are examples of monosaccharides.
It is one of the body’s preferred sources of fuel in the form of carbohydrates and fat. Bread, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products are all good sources of glucose. Food is required to produce energy.
Energy is required to keep you alive. While it is essential, like so many other things, it is best consumed in moderation. Unhealthy or out-of-control glucose levels can have long-term and dangerous consequences.
Why Is Glucose Important?
Energy is required by every cell in the human body. It is to carry out the metabolic functions that keep us alive. Glucose is a tiny, simple sugar that is used as a key source of energy for the brain, muscles, and a variety of other organs and tissues in the body.
It is also a component of the body’s bigger structural molecules, such as glycoproteins and glycolipids. These levels in the human body are tightly regulated. Abnormally high or low levels might cause significant results. However, causes some other life-threatening consequences.
Develops Brain Fuel
The brain’s energy needs are generally met almost entirely by glucose. Our brain requires a steady supply of glucose due to its high energy demands and inability to retain it. Multiple systems exist in the body to prevent a large drop in blood sugar, sometimes known as hypoglycemia. However, if this happens, brain functioning may begin to fail.
Headache, dizziness, confusion, lack of attention, anxiety, irritability, restlessness, slurred speech, and poor coordination are all common hypoglycemia brain symptoms. Seizures and coma can result from a quick, severe drop in blood sugar.
Develops Muscle Fuel
Skeletal muscles typically account for 30 to 40% of total body weight. Though this varies depending on sex, age, and fitness level. During the reading activity, the skeletal muscles consume a lot of glucose. Skeletal muscles, unlike the brain, store blood sugar as glycogen, which is quickly broken down to provide glucose during physical exercise.
Acts As Fuel For Tissues And Organs
Different types of fuels can be used by different organs and tissues in the body. Other vital organs and tissues, in addition to the brain and skeletal muscles, use glucose as their primary or sole source of energy. The cornea, lens, and retina of the eyes, as well as red and white blood cells, are examples of other tissues and organs.
Even though the cells of the small intestine are responsible for collecting glucose from meals and transferring it into the bloodstream. It largely uses glutamine as a source of energy. This frees up more glucose for organs and tissues that are more sugar-dependent.
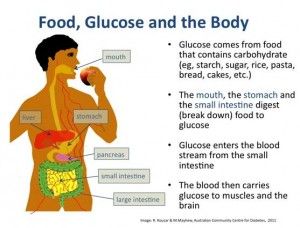
How does The Human Body Deal With Glucose?
Ideally, our bodies digest glucose several times a day. When we eat, our bodies instantly begin the process of processing glucose. With the help of the pancreas, enzymes begin the breakdown process.
The pancreas, which generates hormones such as insulin, is crucial to our body’s glucose management. When we eat, our bodies signal the pancreas to release insulin to deal with the growing blood sugar levels.
Some people, on the other hand, can’t rely on their pancreas to do what it’s intended to do. When the pancreas does not produce insulin as it should, diabetes can develop. People in this situation require outer help (insulin injections) to digest and manage glucose in the body.
Insulin resistance is another cause of diabetes, in which the liver fails to recognize insulin in the body and continues to produce excessive amounts of glucose.
The liver is a key organ for blood sugar regulation since it helps glucose storage and produces glucose as needed. When the body does not create enough insulin, free fatty acids are released from fat storage.
Ketoacidosis is a condition that can result from this. Ketones, which are waste products produced by the liver when fat is broken down. It can be harmful in excessive amounts.
What Are Normal Glucose Levels?
Depending on how much glucose is in a body’s system, blood sugar levels might be normal, high, or low. It is a simple sugar that is always present in the bloodstream. When someone fasts, eats, or has eaten, normal blood glucose levels can be monitored.
Adults without diabetes with a fasting blood glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL have a normal blood glucose level. Two hours after eating, a normal level for persons without diabetes is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Maintaining your blood sugar levels in the normal range is crucial for your body to function properly and healthily. Diabetes patients must keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels. A safe range before eating is 90–130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). It should be less than 180 mg/dL after an hour or two.
Blood sugar levels might trigger a variety of causes. The following are some examples of triggers:
- Heavy meal
- Stress
- Other illness
- Lack of physical activity
- Missed diabetes medications
How Do You Check Your Blood Glucose Levels?
People with diabetes should test their glucose levels regularly. The majority of people with diabetes are dealing to have blood sugar readings as part of their routine.
A simple blood test is one of the most common techniques to test glucose at home. A drop of blood is obtained by pricking the finger with a little needle called a lancet and placing it on a test strip. The strip is inserted into a blood sugar meter, which measures the amounts of sugar in the blood. In most cases, it can provide you with reading in less than 20 seconds.
| Time to check | Blood sugar level for people without diabetes | Blood sugar level for people with diabetes |
| Before meals | less than 100 mg/dl | 80–130 mg/dl |
| 1-2 hours after the start of the meal | less than 140 mg/dl | less than 180 mg/dl |
| Over a 3-month period, which an A1C test can measure | lower than 5.7% | less than 180 mg/dl |
What Foods Are High In Glucose?
Food is converted into energy by our body. Humans acquire energy and calories from glucose, protein, and fat. Although carbohydrate is our primary source of energy. Carbohydrates are converted to glucose, a form of sugar, in our bodies.
Carbohydrates, protein, and fat are all present in many foods. How rapidly our bodies convert meals into glucose is influenced by the amount of each in the food we eat.

The following is an example of how different foods affect our blood sugar levels:
- Carbohydrate
Bread, rice, pasta, potatoes, vegetables, fruit, sugar, yogurt, and milk include carbohydrates. Our bodies convert all of the carbohydrates we consume into glucose. This has an immediate effect on our blood sugar levels, within an hour or two of eating.
- Protein
Fish, meat, cheese, and peanut butter are all included in proteins. Although our bodies convert some part of the protein we consume into glucose. The majority of this is stored in our liver rather than being released into the bloodstream. Protein consumption has a minor effect on blood sugar levels.
- Fat
Butter, salad dressing, avocado, and olive oil are all included in fats. We convert fewer than 10% of the fat we consume into glucose. The sugar in fat is slowly digested and does not induce a rise in blood sugar. Even while fat does not provide much glucose, a high-fat diet can impact how quickly our bodies digest carbohydrates.
Fat inhibits the digestion of carbohydrates, which in turn delays the rise in blood sugar levels. This can result in a rise in blood sugar several hours after eating.
This delayed reaction may come as a shock to some people. Before going to bed, a person could have a blood sugar reading that is close to normal after eating a high-fat dinner. However, he or she may have a fasting blood sugar of over 200 the next morning. This is because the carbs in the meal took the body overnight to digest.
The most essential thing to remember is that eating balanced meals with protein, carbohydrates, and a modest bit of fat can help maintain blood sugar levels from going too high or too quickly.
Is Glucose Harmful To Our Bodies?
If left untreated, having too much sugar in the blood for an extended length of time can lead to major health complications. Hyperglycemia damages the blood arteries that supply blood to important organs. It can also raise the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, vision issues, and nerve problems.
These issues rarely appear in children or teenagers. Those who have just had the disease for a few years. However, they can occur in adults with diabetes, especially if their diabetes has not been effectively managed or controlled.
High blood sugar level (Hyperglycemia) can be considered when it is above your target range. Your diabetes health care team will inform you about your target levels.
A single high blood sugar measurement isn’t typically the reason for concern. It happens to people with diabetes on occasion. You could need to alter your insulin or meal plans.
However, you might have a problem with your equipment, such as an insulin pump not working. In any event, get medical assistance as soon as possible to regain control of your blood sugar levels.
What To Do When Blood Glucose Level Is Unstable?
When your blood glucose level is too high, insulin will help you to lower it. Blood sugar levels that are excessively high are giving warning to the person with diabetes. This may need to use synthetic insulin. Physical activity can help you to lower your levels in less critical situations.
When a glucose level falls below 70 mg/dL, it is considered dangerously low. Hypoglycemia is another name for this illness, and it can be quite dangerous. When persons with diabetes forget to take their prescription, then hypoglycemia can occur. It can also happen when people eat less than they should and exercise excessively. Increasing glucose levels can be as simple as eating a meal or drinking juice.
Some tablets, which may be acquired over-the-counter at a pharmacy, are also commonly used by diabetics. A loss of consciousness can occur as a result of low blood sugar. It’s important to get medical attention if this happens.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.