Contents
Diabetes And Life Expectancy
Life Expectancy of Diabetes
Diabetes relates to shorter life spans and lower quality of life for those who suffer from it. It is not the case when you are able to manage your blood sugar levels. Anyone with diabetes can change the direction of their health with the right tools, guidance, and health management system.
People with diabetes have a higher probability of early death. On the other hand, people without diabetes have fewer chances of early death when it comes to heart-related cardiovascular diseases. It depends on how a person maintains blood sugar that will affect your lifespan.
Type 1 Diabetes life expectancy
Despite improved treatment for type 1 diabetes and its consequences, people now lose more of their lives with this chronic disease. The researchers also discovered that type 1 diabetics under the age of 50 are dying in huge numbers. It relates to the complications of disease treatment, such as diabetic coma and diabetic ketoacidosis, which are caused by a shortage of insulin in the body.
There is, however, some good news: people with type 1 diabetes have been known to survive up to 85 years with the disease. People with type 1 diabetes develop diabetes at a younger age than those with type 2 diabetes. Hence, living with the disease for a longer period of time.
Recent studies on life expectancy suggest that patients with type 1 diabetes who are born later in the twentieth century have a much longer life expectancy.
- Diabetic for over 75 years
- Living with diabetes for 85 years
Type 2 Diabetes life expectancy
Type 2 diabetes usually progresses more slowly than type 1 diabetes. As a result, some people can be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (as well as other types of diabetes) years after they initially develop the disease. In other circumstances, diabetes is only discovered after the onset of diabetic complications, which is a dangerous situation.
It is unfair to judge which disease is more serious. All varieties of diabetes have a significant influence on people’s health. It is a tough condition to give a treatment that necessitates a great deal of time, persistence, and care. The estimated life expectancy of a person varies significantly, depending on their age, lifestyle variables, and treatments.
For instance, at the time:
- A 55-year-old man with type 2 diabetes can expect to live another 13.2–21.1 years, with a general life expectancy of 24.7 years.
A 75-year-old man with the condition should expect to live for another 4.3–9.6 years, compared to a 10-year average life expectancy.
The following are some of the figures and findings from the above are:
- what is the range of life expectancy for people with diabetes
- how this varies depending on medical intervention
For example, a person who does not manage their glucose levels efficiently smokes, and does not exercise, is likely to live a shorter life than someone who leads a healthy, active lifestyle, does not smoke, and maintains stable blood glucose levels.
Causes of Shorter Life Expectancy
Higher blood sugar levels over time can lead to diabetes problems such as:
- Diabetic retinopathy is a kind of retinopathy caused by diabetes.
- Kidney disease is a condition that affects the kidneys.
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is a condition that affects (heart disease).
These diseases decrease the life expectancy of people with diabetes. There are other factors that may affect the life quality. Higher blood sugar levels are frequently accompanied by complications such as.
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
Both contribute to poor circulation. This further results in damage to organs like the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Short-term consequences including hypoglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis might be lethal in some circumstances.
Measures To Improve Life Expectancy
Many don’t even know that they have diabetes complications. The first way to manage diabetes is to have its diagnosis. If you have diabetes and looking for the healthiest way then you may follow the below steps to maintain a healthy diet:
Regulation of blood glucose levels
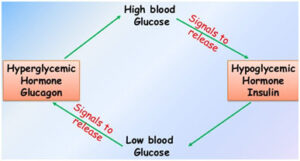
- Monitoring your blood glucose levels regularly helps in identifying the peaks and their causes.
- Diabetics can also use metformin to stabilize blood sugar.
- It should only be taken on the doctor’s advice.
Eating healthy

- Consume fewer foods that contain simple sugars such as juices and candies.
- Eat simple carbohydrates rather than complex carbohydrates.
- Keep your alcohol consumption to a minimum.
Exercising

- Adults should acquire at least 150–300 minutes of moderately strenuous cardiovascular activity per week, such as brisk walking or dancing.
- It will help in burning high calories.
- Also, improves your health.
Losing Weight

- Losing 5–10 per cent of body weight can dramatically minimize the burden of diabetes in those who are overweight.
- Calorie burn helps in elevating metabolism.
- It will also help in improving your health
Follow The Treatment Plan

- This involves going to regular checkups.
- Follow the doctor’s recommendations for lifestyle changes and medications.
- Blood glucose monitoring kits, you can purchase to check your blood glucose level.
Learn about diabetes

- People with diabetes can learn more about the condition to control their diabetes than those who rely only on their healthcare practitioner.
- A person learns the skills they need to manage their condition through a self-management education program.
- This can increase one’s quality of life while also lowering costs and lowering the chance of any problems.
Moreover, with the evolution in types of insulin, the quality of life with diabetes has changed rapidly. Many monitoring tools are improving the mechanisms of delivering insulin to control blood glucose levels. Innovations in insulin have made it easier to use and long-lasting. However, in terms of side effects and their complications, the risks factors have been reduced.
Advances In Diabetes Care
Improvements in diabetic life expectancy lead to more precise data on death rates and reasons for death. Treatment and management of diabetes, on the other hand, is improving in a variety of ways, including:
Effective Medications
Diabetes care is now advanced more in recent times. Medications include intensive insulin therapy, injectable insulin, inhaled insulin, and other oral medications. It will help in regulating insulin and blood glucose.
The advantages of medications are the beneficial effects you obtain from them, such as pain relief, blood sugar control, blood pressure reduction, or infection cure. The dangers of medications are the unintended or unexpected side effects that may occur when you take them.
Blood Glucose Monitoring Tools
Blood glucose monitor tools are now easy to use which includes less painful lancing devices and also continuous glucose monitoring tools. These tools will also tell how you are working with your diet, exercise, and medicine.
More Support For Self-Management
Now you will be getting more support from professionals such as certified nurse educators and diabetes educators. They have great experience in training patients with the most effective self-management tips for diabetes.
Myths And Facts

There are many myths about life expectancy in diabetes. Therefore, making facts about diabetes life expectancy difficult. To clear the confusion about these common myths, here are some of them for you to acknowledge.
Diabetes Is Not Serious
Fact: No such thing as “mild” diabetes exists. Diabetes is a dangerous disease that can lead to problems if it is not treated properly. Diabetes can have a negative impact on one’s quality of life and shorten one’s lifespan.
All Types of Diabetes Are The Same
Fact: Diabetes comes in a variety of forms. Type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes are the most frequent. Other diabetes types are less common. Each kind of diabetes has its own set of causes and treatment options.
However, all types of diabetes, except gestational diabetes, must be treated at regular times. Although gestational diabetes disappears after delivery, it dramatically increases a person’s chance of acquiring type 2 diabetes later in life. Diabetes is a complex and life-threatening disease that affects people of all ages.
Overweight or Obese Develop Diabetes
Fact: Obesity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, although it is not a cause of the disease. Some persons who are overweight may not get type 2 diabetes, but others who are of a healthy weight may develop it.
Only Type 1 Diabetes Needs Insulin
Fact: Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease that worsens with time. Because the pancreas generates less insulin over time, 50% of persons with type 2 diabetes will require insulin, 6-10 years after being diagnosed. Taking medicine as needed can lead to fewer long-term consequences.
It is an important element of controlling type 2 diabetes. Insulin replacement therapy is essential for people with type 1 diabetes on a daily basis. Throughout the day, they must monitor their blood glucose levels multiple times.
Conclusion
The above study shows that diabetes patients had a higher risk of death and a shorter life expectancy than the general population. When compared to persons diagnosed with diabetes later in life, young people with diabetes lost more years of their life. The above article also explains, the comparison with the persons who do not have diabetes or older adults with diabetes who had a shorter life expectancy at every age.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.


