If you suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, you know how painful and debilitating it can be. You may have tried various treatments, such as medication and surgery, but they haven’t helped enough. It’s time to try physical therapy. Physical therapy is a type of treatment that helps reduce pain and improve function. It involves a variety of exercises and techniques that are tailored to your specific needs. In this blog post, we will discuss how rheumatoid arthritis physical therapy works and the benefits you can expect!
Contents
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
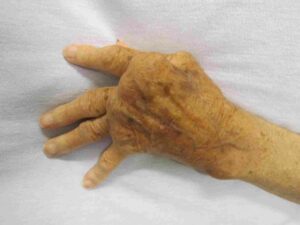 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of chronic inflammatory arthritis that affects more than 1.3 million adults in the United States, according to the American College of Rheumatology. RA is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of chronic inflammatory arthritis that affects more than 1.3 million adults in the United States, according to the American College of Rheumatology. RA is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
In the case of RA, the joints are typically affected first. The symptoms of RA can vary from person to person, but they usually include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and warmth. RA can also cause fatigue, loss of appetite, and fever. If the disease is left untreated, it can lead to joint damage and disability.
How Can Physical Therapy Help In Rheumatoid Arthritis?
There are different types of physical therapy that can be useful in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The goal of physical therapy is to help reduce pain and swelling, improve joint range of motion, and maintain or improve muscle strength.
It is often believed that rheumatoid arthritis physical therapy can help by:
- Reducing Pain: It is important to understand that physical therapy will not “cure” your pain, but it can help to reduce the intensity of your pain. There are a number of different techniques that can be used by physical therapists to help reduce pain.
- Improving Joint Range Of Motion: One of the goals of physical therapy is to improve the joint range of motion. This is important because RA can cause stiffness and loss of range of motion in the joints.
- Maintaining Or Improving Muscle Strength: Muscle weakness is a common symptom of RA. Physical therapy can help to improve muscle strength, which can in turn help to improve function.
- Improving Function: Another goal of physical therapy is to improve function. This can be done through a variety of different techniques, such as exercises that improve range of motion or strength training.
- Reducing Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom of RA, and it can be made worse by inactivity. Physical therapy can help to reduce fatigue by helping you to maintain or improve your level of activity.
- Improving Quality Of Life: The goals of physical therapy are not just to improve physical symptoms, but also to improve quality of life. This is because RA can have a significant impact on a person’s ability to participate in activities that they enjoy.
If you are considering physical therapy for your RA, it is important to speak with your doctor first. Physical therapy can be an effective treatment for many people with RA, but it is not right for everyone. Your doctor will be able to help you determine if physical therapy is right for you.
What Are Some Physical Therapies For Rheumatoid Arthritis?
There are many types of physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. The type of physical therapy you receive will depend on the severity of your arthritis, as well as any other health conditions you may have. Here are some of the most common types of physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis:
Exercise
 Exercise is one of the most important things you can do to manage your rheumatoid arthritis. This can help reduce pain, increase joint flexibility, and improve overall physical function. Physical therapists can help design an exercise program that is right for you.
Exercise is one of the most important things you can do to manage your rheumatoid arthritis. This can help reduce pain, increase joint flexibility, and improve overall physical function. Physical therapists can help design an exercise program that is right for you.
There are numerous types of exercise that can be beneficial for people with rheumatoid arthritis, including:
- Aerobic exercise – Aerobic exercise is any activity that increases your heart rate. Walking, jogging, swimming, and biking are all examples of aerobic exercise. Regular aerobic exercise can help reduce pain and fatigue and improve overall physical function.
- Strengthening exercises – Strengthening exercises help to build muscle around the joints. This can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Range of motion exercises – Range of motion exercises help to improve joint flexibility and range of motion. These exercises are often combined with strengthening exercises.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can help relieve pain and stiffness associated with rheumatoid arthritis. This type of heat therapy, such as using a heating pad, can help relax muscles and ease the pain. Cold therapy, such as ice packs or cool compresses, can help reduce inflammation. There is some evidence that alternating between heat and cold therapy may be more effective than using one or the other.
The reason heat and cold work are not entirely clear, but it is thought that the heat dilates blood vessels, which increases blood flow and delivers more oxygen and nutrients to muscles. The cold numbs pain receptors and reduces inflammation.
Massage Therapy
In some cases, massage therapy may be recommended as part of a rheumatoid arthritis physical therapy program. Massage can help to relieve pain and stiffness in the joints, and increase blood flow and circulation to the affected area. In fact, there are different types of massage that can be beneficial for people with rheumatoid arthritis, including:
- Swedish massage
- Deep tissue massage
- Trigger point massage
These all can be performed by a licensed massage therapist. Your doctor or physical therapist can also teach you how to perform self-massage, which may help you to manage your symptoms at home.
Electrical Stimulation
 It is common for people with rheumatoid arthritis to experience pain and stiffness in their joints. Electrical stimulation is a type of physical therapy that can help to reduce these symptoms. During electrical stimulation, low-voltage electrical currents are applied to the affected area. This helps to block pain signals from reaching the brain and can also help to increase blood flow to the area.
It is common for people with rheumatoid arthritis to experience pain and stiffness in their joints. Electrical stimulation is a type of physical therapy that can help to reduce these symptoms. During electrical stimulation, low-voltage electrical currents are applied to the affected area. This helps to block pain signals from reaching the brain and can also help to increase blood flow to the area.
In fact, stimulation triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals. It also helps to reduce inflammation and swelling.
Motivation And Encouragement
This might be the most important part of your therapy. It can be very easy to become discouraged when you’re in pain and dealing with the fatigue and other symptoms of RA. Your physical therapist can help you stay positive and focused on your goals. For example, if you’re struggling to walk up the stairs, your PT can help you come up with a plan to make it happen.
They can choose different techniques to motivate you. For example, some people might respond well to a gentle but firm approach while others prefer more of a cheerleader-type personality. No matter what, your PT should always be encouraging and make you feel like you can achieve your goals.
Overall, these are the top 5 techniques that can be used in rheumatoid arthritis physical therapy. If you think physical therapy could help you, talk to your doctor or a licensed PT today.
What Are Some Limitations?
When you are seeking physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis, your first step will be to consult with your doctor. He or she can help you understand the limitations of physical therapy and how it may affect your condition. You should also ask about what you can expect from treatment.
The limitations of physical therapy may include:
- The severity of your condition
- The amount of pain you are in
- Your range of motion
- Your ability to tolerate specific exercises
Keep in mind that physical therapy is not a cure for rheumatoid arthritis. However, it can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. And, this benefit is only seen when physical therapy is used in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and rest.
Can I Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis?
 It might not be possible to prevent rheumatoid arthritis, but there are things you can do that may lower your risk.
It might not be possible to prevent rheumatoid arthritis, but there are things you can do that may lower your risk.
- Don’t smoke. If you do smoke, quitting will help reduce your risk.
- Get regular exercise. It’s not clear how exercise affects RA risk, but staying active is generally good for your health.
- Eat a healthy diet. Some evidence suggests that people who eat a lot of processed meats and saturated fats may have a higher risk of RA.
- Warm up before and cool down after exercise.
- Maintain posture and alignment when you exercise.
- Use proper form when lifting weights.
Finally, if you have any risk factors for RA, such as a family history of the disease, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk. With the right precautions, you may be able to prevent RA or at least lower your chances of developing the disease.
Moreover, you should not forget about the importance of physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Physical therapy can help you in various ways. So, consider consulting a physical therapist today!
Conclusion
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis physical therapy can help improve your symptoms and quality of life. It is important to find a therapist that you trust and feel comfortable with. Be sure to discuss your goals and expectations with your therapist.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition and therapists may use a combination of exercises, stretches, and massage to help relieve pain and improve function. A physical therapist can also teach you how to properly use assistive devices, such as canes or splints.
Physical Therapy has always been proven to help patients recover from pain. Hence, if you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.


