Contents
What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
For that, you first need to understand how your body functions.
The food you eat contains carbohydrates that are broken into sugar molecules, called glucose. Then, the glucose passes into the bloodstream. Simultaneously, your pancreas produces a hormone called insulin.
Insulin transports this glucose from the bloodstream to different cells or parts of the body. Insulin gives the message to the body cells to open up so that glucose can enter into them. Body cells use this glucose and convert them into energy for the proper functioning of the body.
In the case of Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas is not able to produce insulin. As a result, glucose is not transported to the cells and stays in your blood, resulting in high blood sugar levels in the body.
How Is It Different From Type II Diabetes?
In the case of type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, the pancreas creates insulin, however, the cells resist its proper use or there is insulin resistance. In turn, the pancreas creates more insulin to transfer glucose in the cells, however, due to insulin resistance, the glucose eventually builds up in the blood.
So to summarize in the case of type 1 there is a lack of insulin, and in the case of type 2 insulin is present, but is not functioning properly.
Causes of Type-1 Diabetes
When it comes to the causes, experts are still unsure what actually causes Type 1 diabetes. However, they have come up with some factors that might be playing a role leading to such conditions. The first one is
- Your genes. Yes, you heard it right, if someone in your family or your parents are type 1 diabetic, there increases a chance for you to suffer as well.
- Secondly, talking about diet, the experts are still trying to figure out if your diet plays any role resulting in this disease.
What the experts confidently say about the causes is that Type 1 diabetes is caused because your immune system gets weak.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the body’s own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes
Let’s now find out what are the symptoms and alarming indications towards this disease. So, if you have type 1 diabetes, you might notice that:
- You pee a lot. As your kidneys try to excrete the excess glucose through urination

- You’re a lot thirstier than usual as frequent urination starves your body of water

- Your vision is blurry. As when blood sugar levels are high for a long time, body water is pulled into the eye lens, causing it to swell.

- You’re a lot more tired than usual because, under diabetes, glucose which is the key source of energy remains in your blood and is not transported well to the cells.
- You are losing weight suddenly.


- You Have a fruity smell in his breath.

Also, in most cases, these symptoms start to show up in childhood. For the same reason, Type 1 diabetes is also called “juvenile diabetes”.
If you are facing any or some of these symptoms, I would advise you to act immediately and meet your doctor.
Risks And Complications of Type-1 Diabetes
The intensity of risks and complications related to Type 1 diabetes ranges from minor to severe.
As you know the absence of insulin is the cause of Type 1 diabetes which leads to high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) which further causes a lot more issues in your body. So what are they:
1. DKA (Diabetes Ketoacidosis)
Under this condition (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) when your body cells do not get glucose for energy production, they hunt for the stored fats and break them down to produce energy. In this process, a called “ketones” are produced, and make your blood acidic.
2. Damage To Nerves And Blood Vessels
If your blood sugar levels are constantly high over a longer period of time, it can cause harm to your nerves and blood vessels present in the eyes, kidneys, and heart.
3. Cardiovascular Disease
You can also suffer from blood clots, high blood pressure, cholesterol. And all these issues together can further cause you chest pain, heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
4. Diabetic Nephropathy
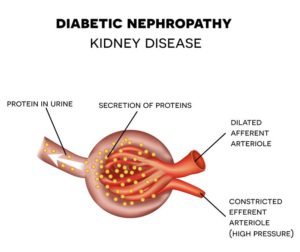
This is a name given to kidney damage being caused by diabetes. Around 20 to 30 percent of people with type 1 diabetes undergo this damage (Diabetic Nephropathy). In simple terms, it is a kidney failure after which your kidneys are unable to process the excess waste, salt, and water out of your body, and your body becomes toxic.
5. Retinopathy
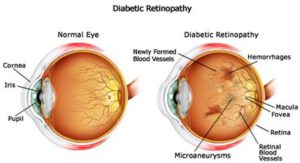
Retinopathy is an eye problem that is caused due to diabetes. And it is noticeable in around 80% of adults who have been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes for 15 to 25 years now. It can even lead to blindness.
Poor blood flow and nerve damages cause loss of sensitivity in your body parts, especially in your feet area. Because of this, you are not able to feel any sensation, even if you get any cuts or wounds, that further result in large and unmanageable wounds.
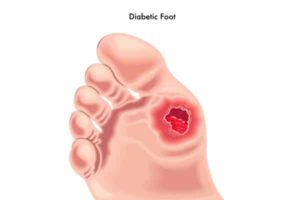
And the only option left to the doctor is to cut off that area from your body. So by now, you must have realized how important it is to keep control of blood sugar levels and manage your life with Type 1 diabetes.
Treatment For Type-1 Diabetes
The primary cure for managing blood sugar levels under type 1 is insulin. Almost everyone with type 1 diabetes needs insulin shots to manage their sugar level. You might take it through injection Or through the pump.
Insulin Shots
Your doctor would suggest you take insulin as per your body’s needs. There are multiple types of insulin shots available including Rapid-acting insulin that starts working in about 15 minutes after the shot is taken in the body.
It works for about 2 to 4 hours, out of which the first 1 hour is the peak time. Another one is Regular or short-acting insulin and it takes 30 minutes to act and reaches its peak in 2 to 3 hours. It lasts 3 to 6 hours.
So with insulin shots, you need to manage and adjust your food timings and other activities as required. Your doctor is going to help you find out how many shots you would need in a day.
In addition to all this, you need to consider other measures to lower your blood sugar level including diet, exercise, and lifestyle.
Diet
- Cut off sugary contents from your food.
- Follow a healthy diet to lose 5% to 10% of your weight (in case you are obese).
- Shift to a whole-grain and vegetable-rich diet.
- Drinks lots of water.
Exercise
- Pick moderate-intensity exercises such as brisk walking and perform them for at least 30 minutes daily.
Lifestyle
- Reduce the stress level in your life through ways such as meditation.
- Get sound sleep of at least 7-8 hours a day.
- Keep your cholesterol and blood sugar level under control.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
Making these changes in your daily routine will not only help you in lowering your blood sugar level but also keeps your overall health good as well.
If you are finding it difficult to manage diabetes on your own, Diabetes Mantra can help. We provide you with the right food products, diet charts, doctors, health coaches, exercise courses to keep diabetes at bay. Download the diabetes mantra app to know more.
Also, If you found this video helpful, then please like and share our video. Don’t forget to subscribe to this channel, so you never miss any diabetes-related updates.
Points To Remember While Taking Insulin Shots
There are three important points your doctor looks into while suggesting insulin shots.
The first one is “onset”. That is, what time the insulin takes to reach down your bloodstreams and start acting to reduce the blood sugar level
Second, comes the “peak time” which is the time period that inulin is working with its full capacity to lower down the sugar level in your blood.
And the third is called “duration”. This is the period for which the insulin taken inside your body keeps working after the onset.
Based on these factors, namely “onset”, “peak time”, and “duration”, there are several types of insulin available. For example:
- Rapid-acting insulin: It starts working in about 15 minutes after the shot is taken in the body. It works for about 2 to 4 hours, out of which the first 1 hour is the peak time
- Regular or short-acting insulin: It takes 30 minutes to act and reaches its peak in 2 to 3 hours. It lasts 3 to 6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: When injected or pumped into your blood, it does not work for about 2 to 4 hours. It is highly active from 4 to 12 hours and works for 12 to 18 hours.
- Long-acting insulin: It acts for a day in your body but takes long hours to enter your bloodstream.
Keep tracking your blood sugar levels, and immediately consult the doctor in case if it comes constantly high.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.