Contents
What Is Diabetes Mellitus or Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus commonly known as diabetes is a disease in which your body cannot absorb the energy from the food you eat. Your body does not make insulin or your body cells can’t use it properly. In diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar level is abnormally elevated. There is no cure for diabetes mellitus but it can be controlled with some remedies.
In diabetes mellitus either your body does not make insulin or can’t effectively use it. That leaves too much sugar in your blood; this condition is popularly known as high blood sugar. High blood sugar can cause severe health problems if not treated.
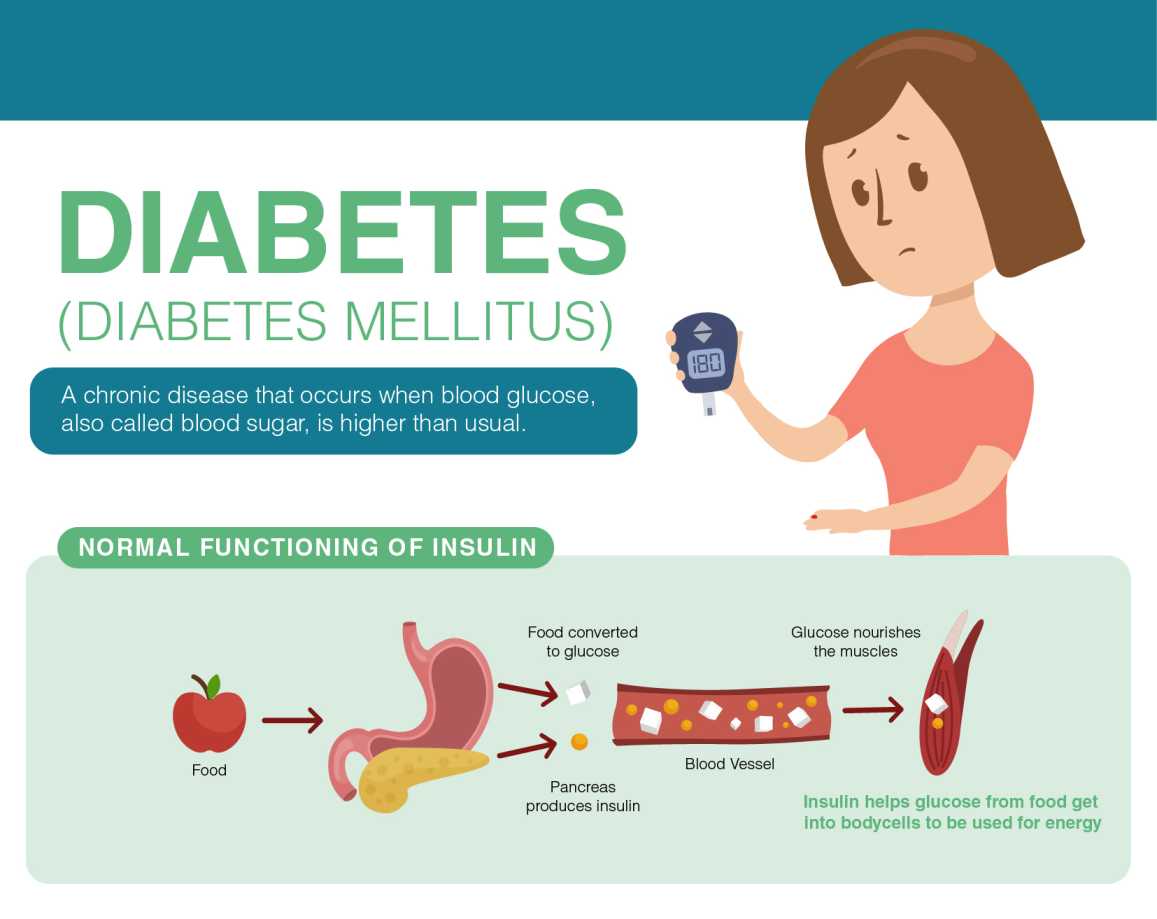
How We Get Energy From The Food?
The food we eat has fat, protein, and carbohydrates; our body breaks carbohydrates down into sugar or glucose. Glucose is an important source of energy for our blood. This sugar is sent to the bloodstream and eventually gets absorbed by various body cells for energy. Insulin hormone helps sugar move from the bloodstream to body cells.
Insulin– is a hormone released by the pancreas. The pancreas is an organ behind the stomach that releases several digestive enzymes as well. Secretion of the Insulin hormone is stimulated when there is sugar present in the bloodstream. Insulin is responsible for the absorption of glucose by body cells; glucose is used for energy, instantly, once inside the body cells.
Types of Diabetes/ Diabetes Mellitus
1. Prediabetes
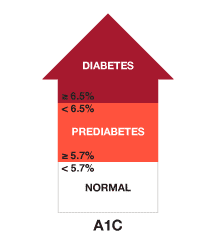
Prediabetes is a serious health condition in which your blood sugar is higher than normal but it is not high enough to be called diabetes. Prediabetes can cause severe health issues as it has a high chance of developing into Type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Therefore, prediabetes should not be ignored as it is reversible but Type 2 diabetes is not. A person with a fasting blood sugar level of 100mg/ dL to 125mg/ Dl has diabetes. Blood sugar levels may vary a little from person to person.
A person can have prediabetes without any clear symptoms for a long period. A person with risk factors written below should get checked up before any further serious health issues show up.
Symptoms of Prediabetes
Symptoms of prediabetes are caused by high/low blood sugar.
- Increased thirst & dry mouth- thirst is increased in diabetes mellitus
- Increased hunger
- Dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Weakness, lack of energy
- Blurred vision
- Unhealed sores
Risk Factors For Prediabetes
- Overweight– Being overweight increases the risk of high blood sugar.
- Ageing– If you are above 45 or older, you should get your blood sugar level tested frequently.
- Heredity– Having someone in your family with diabetes can put you at risk of developing diabetes.
- Some other factors like race and gender can play their part too.
Preventions For Prediabetes
Although prediabetes has a higher risk of developing heart diseases once if it develops into Type 2 Diabetes, it’s not easy to handle. Diabetes damages all your body parts and causes major health problems like blindness, kidney damage, nerve damage. A person with diabetes has to be very conscious of the food that he/she eats. Overall it affects the quality of life severely. Prediabetes can be prevented by-
- Exercising every day for 30 minutes can help in reducing your blood sugar level.
- Lose at least 5% of your body weight; in short, being physically active helps in preventing prediabetes.
- Find out how to eat healthily and cut out unhealthy food from your diet.
2. Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus
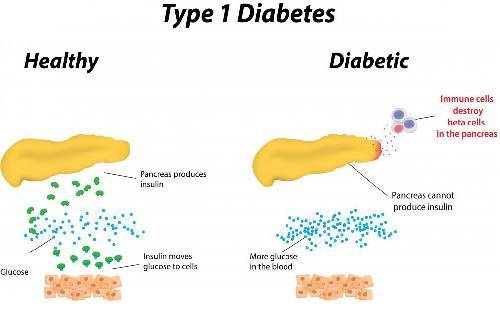
Type 1 Diabetes also called insulin-dependent diabetes is a chronic type of diabetes mellitus. In this condition, the body cannot make insulin hormones because the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system. This diabetes usually begins in childhood, therefore called juvenile-onset diabetes.
Most of the pancreatic cells are permanently destroyed in this condition, leaving little or no insulin in your body. About 10% of people with diabetes have this type of diabetes. This auto-immune disease is caused by external factors like viral infection in childhood or a nutritional factor. Genetic factors can also be a major cause of developing this type of diabetes.
Type-1 diabetes can damage blood vessels in many internal organs of your body like eyes, nerves, and kidney causing, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy.
Symptoms of Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Fruity breath
- Irritation /mood swings
- Excessive thirst
Risk Factors of Type-1 Diabetes
Numerous factors increase the risk of developing Type 1 diabetes.
- Viral infections– Some viral infections in childhood can play a part in developing Type 1 diabetes.
- Race – Certain races and ethnicities have a higher risk of developing Type 1 diabetes than others e.g. Caucasian Americans.
- Family history– If someone in your family has Type 1 diabetes then susceptibility to develop the disease is higher.
- Diet in Childhood– A research study shows that the quality of early diet affects the overall health of a person but certain foods like cow milk increase the risk of triggering type 1 diabetes in children.
- Weak immune system– As Type 1 diabetes is an auto-immune disorder, in which the immune system turns against itself. Therefore, having a weak immune system could be one of the risk factors.
Treatment of Type-1 Diabetes
- Get your blood sugar levels tested regularly and make changes in your lifestyle accordingly.
- Daily exercise and healthy eating are a must for keeping your blood sugar normal.
- Take insulin through suitable methods and medicines as prescribed.
- Metformin is another diabetic medication. It was earlier used for treating Type 2 Diabetes, but it is also prescribed to patients who develop insulin resistance in Type 1 diabetes.
3. Type-2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is formerly called non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes. In this condition, the pancreas secretes more than enough insulin during the initial stage of diabetes but the body develops resistance towards insulin and restricts its use. Blood sugar level decreases in this stage causing hypoglycemia. The presence of excess insulin in the body makes the pancreas stop producing insulin or produces it in a minimal amount later on. People with type 2 diabetes may develop ketoacidosis, which can result in extremely high blood sugar. High blood sugar can cause severe dehydration, drowsiness, mental confusion, and even seizures in the worst-case scenario.
In type 2 diabetes your body cells do not respond to insulin how they should. Type 2 diabetes is more common and often milder than type 1 diabetes. But it still can cause serious health complications like type 1 diabetes plus increase the chance of heart disease.
Symptoms of Type-2 Diabetes
- Family history of diabetes
- Tingling/numbness in the feet
- Excessive thirst
- Obesity
- Blurred vision
- Leg cramps
- Itching
- Drowsiness/ mental confusion
- Mood swings
Risk Factors of Type-2 Diabetes
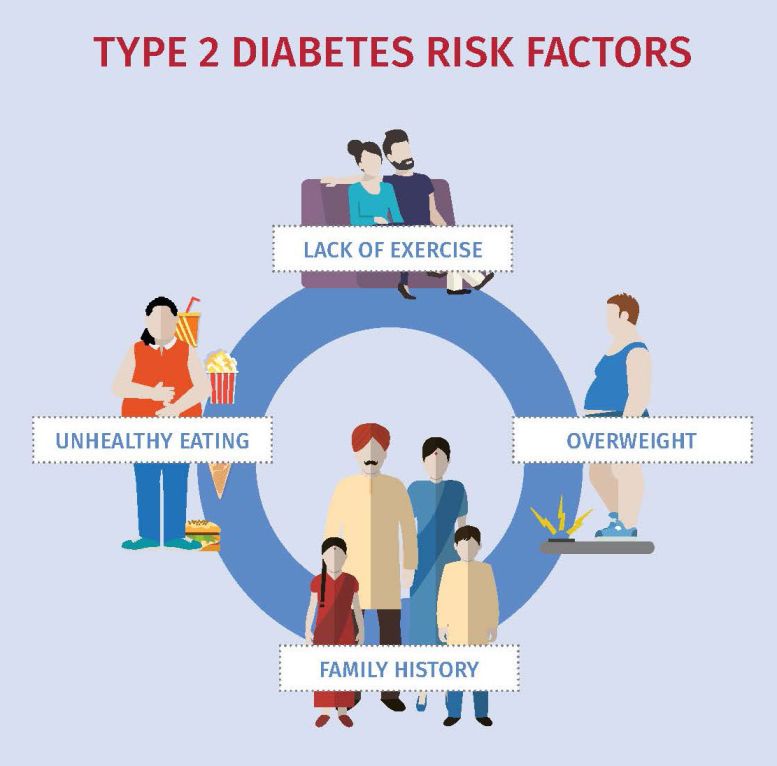
- Being obese or overweight.
- Having prediabetes
- Having health issues like high cholesterol, PCOD, heart diseases.
- Race
- Gender
- Eating unhealthy
- No physical activity.
- Drug consumption is highly dangerous for patients with diabetes.
Treatment For Type-2 Diabetes
A person with the above risk factors has extremely high chances of developing Type-2 diabetes. Although there is no permanent cure for type 2 diabetes it can be controlled by-
- Dieting
- Exercising
- Losing weight
- Insulin injections
- Taking prescribed medications.
Doing lifestyle changes like exercising, eating healthy can control your blood sugar level. It can help in preventing some of the complications of diabetes.
Losing weight and dieting is beneficial for all cases of diabetes mellitus.
4. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a pregnant woman develops higher sugar levels. Gestational diabetes is developed in women who did not have any type of diabetes before pregnancy. This type of diabetes is caused by the various types of hormones that are being secreted from the placenta. Some of these hormones increase the blood sugar level or the body’s insulin resistance, and in some conditions mother’s pancreas cannot produce that much insulin, leading to a higher level of blood sugar. Gestational diabetes disappears after the birth of the baby. However, it can cause some complications in pregnancy and the health of mother and child before birth and increases the risk of developing diabetes in mother and child later in life.
Gestational diabetes is of two types. Class A1 gestational diabetes can be controlled by diet and exercise. Whereas, Class A2 gestational diabetes needs insulin or other oral medications to be controlled.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Symptoms of this type of diabetes are similar to diabetes mellitus such as

- Increased thirst
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Blurred vision
Complications of Gestational Diabetes In Pregnancy
If the blood sugar level is controlled then there is nothing to be worried about, but if it’s not that well-controlled then it can cause some complications in pregnancy like-
- An extra fat baby- In uncontrolled gestational diabetes, the sugar level of both mother’s and baby’s rises which can cause the baby to be extra-large.
- C-section- The baby grows extra-large in case of gestational diabetes leading to complications in childbirth. Therefore, a c-sec is the method of delivery for a mother with gestational diabetes.
- There could be other complications of gestational diabetes depending on the level of sugar increased.
Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is usually temporary and disappears after childbirth. To control it during pregnancy here is what you should do-
- Eat right– First of all, do not skip your meals at any cost. Eat three meals a day at least. The second thing, eat healthy foods that are low in sugar. You should also replace foods like cakes and ice creams with fruits, nuts, and seeds.
- Exercise regularly– Exercise regularly so you don’t gain weight and for normal delivery. You can choose to just for 20 minutes or do light exercises. However, before including any exercises into your routine, do consult your doctor. Heavy exercises are not advised.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels- Keep checking your blood sugar level. In any discomfort, talk to your doctor immediately.
- Monitor your pregnancy- Do keep checking your baby’s health more often if you have gestational diabetes. And the most important thing you can do is keeping in touch with your doctor and opting healthy daily habits.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.


