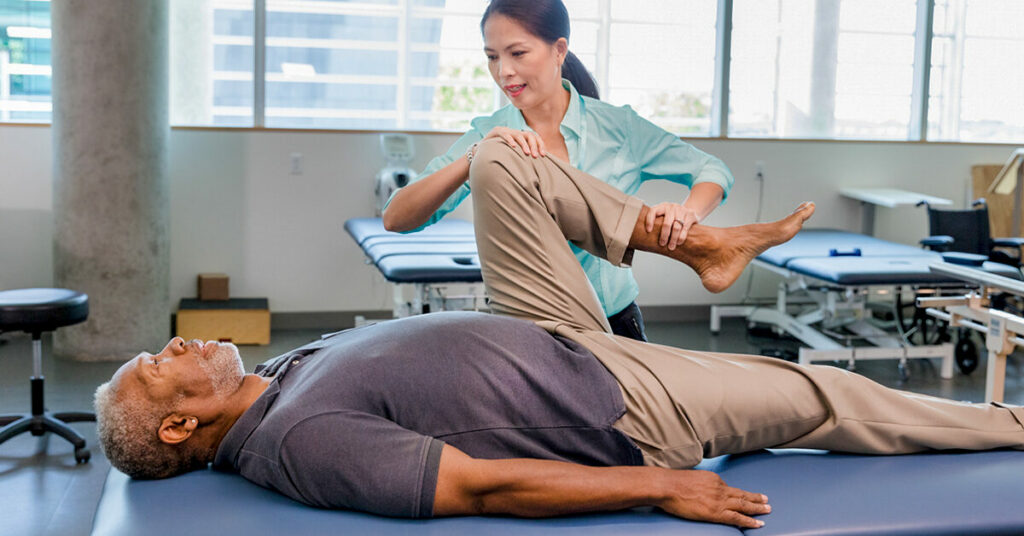
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder that can cause muscle weakness, tingling, and numbness. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues. Physical therapy can be an effective treatment for GBS, helping to improve muscle strength and function. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms of GBS, how physical therapy can help, and what you can expect during treatment.
Contents
What Is Guillain-Barré Syndrome ?

Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the peripheral nervous system. Symptoms can include weakness, paralysis, and occasionally death. The cause is unknown, but GBS is thought to be related to a viral or bacterial infection. There is no cure for GBS, but treatment focuses on relieving symptoms.
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a rare disorder that causes the body’s immune system to attack the nerves. This can lead to muscle weakness, tingling, or numbness in the arms and legs. In some cases, it can also cause difficulty breathing or swallowing.
This syndrome can be caused by an infection or a reaction to a vaccine, but the exact cause is still unknown.
Sometimes, the symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome can be severe and require hospitalization. The most common treatment for this condition is physical therapy.
Physical Therapy For Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
Physical therapy can be an important part of the treatment process for people with Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Also, Physical therapy can help improve balance, coordination, muscle strength, and range of motion. It can also help reduce fatigue and swelling.
Physical therapy can be done in a group setting or alone. Group physical therapy may be more beneficial for people who are more motivated to improve their condition. Physical therapists will often customize the program based on the individual’s needs.
The main goal of physical therapy is to promote movement and strength in the affected muscles and joints. Depending on the severity of the condition, physical therapists may use various techniques such as stretching, strengthening exercises, massage, hot/cold packs, and electrical stimulation. The therapist will also advise on posture, body mechanics, and ergonomics to help prevent further damage.
Physical therapy sessions typically last 30–60 minutes and are tailored to meet each individual’s needs. Patients may be advised to do exercises at home as well.
Most physical therapists recommend regular visits to keep up with the progress made during therapy.
Types of Physical Therapy For Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
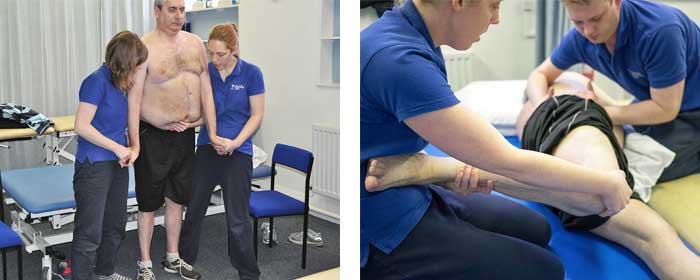
Depending on the severity of your Guillain-Barré Syndrome, several types of physical therapy may be recommended. Physical therapists may use a combination of active and passive exercises to help you increase strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Some of these physical exercises for Guillain-Barré Syndrome may include:
Strengthening Exercises
One of the most common forms of physical therapy for Guillain-Barré Syndrome is strengthening exercises. These exercises can help build muscle and improve strength in the affected area, which can help with activities such as walking or lifting objects. Strengthening exercises usually involve using light weights, resistance bands, or stretching exercises.
Range of Motion Exercises
Another type of exercise used for Guillain-Barré Syndrome is range of motion (ROM) exercises. These are designed to increase flexibility and range of motion in the joints throughout the body. This may be done through gentle stretches and movements that focus on specific areas of your body where you may have stiffness or tightness.
Balance Training
Physical therapists will also use balance training to help with stability and coordination. This type of exercise can help improve your ability to walk or perform activities that require balance, such as climbing stairs. It may involve standing on an unstable surface like a balance board or performing exercises while standing in one place or walking around.
Aquatic Therapy
For people who cannot easily tolerate traditional land-based exercises, aquatic therapy can be beneficial. Aquatic therapy is done in a pool and uses the properties of water (e.g., buoyancy) to reduce gravity’s effect on the body, allowing for easier movement and less strain on the joints and muscles. It can also be used to improve strength, flexibility, ROM, balance, and coordination while providing support and safety during movements.
Aerobic Exercises
n addition to the above exercises, aerobic exercises can also be beneficial for people with Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Aerobic exercise helps increase endurance and overall strength. Examples of aerobic activities include walking, jogging, biking, swimming, and using an elliptical machine or rowing machine.
Your physical therapist will work with you to develop a customized plan that meets your individual needs and goals. The type and intensity of your physical therapy may vary depending on the severity of your condition and your level of fitness.
Benefits of Physical Therapy For Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Benefits of why physical therapy is important for Guillain-Barré Syndrome include:
1. Improved Strength and Mobility: Physical therapy helps to improve strength and mobility for patients suffering from Guillain-Barré Syndrome by providing tailored exercise programs designed to increase muscle strength, flexibility, coordination, balance, and range of motion.
2. Pain Reduction/Management: Physical therapists can help to reduce pain associated with Guillain-Barré Syndrome through a variety of treatment modalities such as massage, strengthening exercises, stretches, hot/cold therapies, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, and kinesiotaping.
3. Improved Quality of Life: By improving physical capabilities through therapeutic exercise and reducing the effects of chronic pain or discomfort, physical therapists can help to improve a patient’s quality of life and lower the risk of experiencing complications or secondary conditions.
4. Injury Prevention: By restoring strength and mobility to affected areas, physical therapy helps to reduce the risk of future injuries. Physical therapists also educate patients on how to modify their activities to prevent further injury or pain.
5. Education and Support: Physical therapists provide education, support, and guidance throughout the recovery process which is important for people with Guillain-Barré Syndrome to maintain motivation during treatment and remain compliant after discharge. This may include goal setting, self-management strategies, lifestyle modifications, and suggestions for resources outside of physical therapy treatments such as local support groups or home-care programs.
How To Take Physical Therapy For Guillain-Barré Syndrome?

Taking physical therapy for Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) involves following a specific plan that is tailored to the individual needs of the person. A physical therapist will work with you to develop an appropriate treatment that meets your unique needs and goals while taking into account any medical conditions or other limitations.
These are some of the steps for taking physical therapy for GBS:
1. Assessment – A physical therapist will assess your muscle function and strength, balance, coordination, posture, range of motion, and other factors that may be affected by the condition.
2. Treatment Plan – Based on the results from the assessment, a treatment plan can be developed which may include exercises to strengthen weakened muscles and improve coordination, as well as stretches to increase flexibility and range of motion as well as activities to maintain joint mobility.
3. Exercise Program – A physical therapist will design an individualized exercise program that takes into account your medical history, the current level of functioning, and goals for recovery. The exercise program should focus on increasing endurance and strength while promoting proper body mechanics. It may also include balance and coordination exercises to improve movement quality and decrease the risk of falling.
4. Education – Your physical therapist will also provide education on topics such as how to properly do activities, how to pace yourself while doing them, energy conservation techniques, and lifestyle changes that may be beneficial for your condition.
5. Follow-up Visits – Regular follow-up visits with your physical therapist are important to track progress, make adjustments in your treatment plan as needed, and ensure that you meet your goals.
By following these steps, taking physical therapy for GBS can help you recover from this condition and live a more active life!
Conclusion
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a serious condition that requires medical attention. However, physical therapy can be an important part of the treatment plan and may help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Before beginning any type of physical activity or exercise program, it is important to consult with a doctor or physical therapist to ensure it is the right treatment for you.
There may be many other treatments and options available for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, so it is important to discuss all potential treatment plans with your doctor. With a comprehensive treatment plan that includes physical therapy, many people can lead healthy, active lives despite the diagnosis of this syndrome.
Physical Therapy help patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back pain, Shoulder pain, Knee pain, Neck pain, Elbow pain, Hip pain, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at MantraCare can help: Book a physiotherapy session.


