Contents
What Is The Glycemic Index?
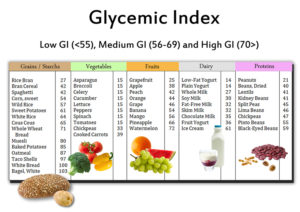
The glycemic index (GI) is worth used to measure how much explicit food sources increment blood sugar levels. Food sources are named low, medium, or high glycemic food varieties and positioned on a size of 0–100. The lower the GI of a particular food, the less it might influence your blood sugar level.
Here are the three GI appraisals:
- Low: 55 or less
- Medium: 56–69
- High: 70 or above
Food varieties high in refined carbs and sugar are processed. All have the rapidly and regularly high glycemic index, while food sources high in protein, fat, or fibre commonly have a low GI. Food varieties that contain no carbs are not allotted a GI and incorporate meat, fish, poultry, nuts, seeds, spices, flavours, and oils.
Different components that influence the glycemic index of food to incorporate the readiness, cooking strategy, type of sugar it contains, and measure of preparing it has gone through. Remember that the glycemic index is unique concerning the glycemic load (GL).
Glycemic Index (GI) and Glycemic Load (GL)
In contrast to the GI, which doesn’t consider the measure of food eaten, the GL factors in the number of carbs in a serving of food to decide what it might mean for blood sugar levels. Therefore, it’s essential to take both the glycemic index and glycemic load into thought while choosing food varieties to help support blood sugar levels.
The rate at which food sources raise blood sugar levels relies upon three factors: the types of carbs they contain, their supplement structure, and the sum you eat. In any case, the GI is a relative measure that doesn’t consider the measure of food eaten. It’s frequently condemned, therefore. To settle this, the glycemic load (GL) rating was created. The GL is a proportion of how a carb influences blood sugar levels, taking both the sort (GI) and amount (grams per serving) into account.
How To Utilize The Glycemic Index?
A glycemic index is a tool that is regularly used to advance blood sugar management. A few variables impact the glycemic index of a food, including its supplement structure, cooking technique, readiness, and the measure of handling it has gone through.
The glycemic index cannot just assistance increment your consciousness of what you’re putting on your plate yet additionally upgrade weight reduction, decline your blood sugar levels, and lessen your cholesterol.
Low Glycemic Diet
The low glycemic diet includes trading out food varieties with a high glycemic index for those with a lower GI.
Medical Advantages of Low Glycemic Diet
Following a low glycemic diet may offer a few medical advantages, including:
- Improved blood sugar guidelines: Numerous testing have tracked down that a low GI eating routine may diminish blood sugar levels and improve blood sugar the board in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Expanded weight reduction: Some tests show that a low glycemic index eating routine may build transient weight reduction. More investigations are expected to decide what it means for long haul weight the board.
- Decreased cholesterol levels: Following a low GI eating regimen may help lower levels of both aggregate and LDL cholesterol, the two of which are hazard factors for coronary illness.
Sources of Low Glycemic Diet
The most effective method to follow a low glycemic diet ought to include generally low GI food sources, for example:
- Organic products: apples, berries, oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruit
- Non-starchy vegetables: broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, spinach, tomatoes
- Whole grains: quinoa, couscous, grain, buckwheat, farro, oats
- Vegetables: lentils, dark beans, chickpeas, kidney beans
Food varieties without a glycemic index value or with a low GI can likewise be delighted in as a feature of a decent low glycemic diet. They include:
- Meat: hamburger, buffalo, sheep, pork
- Fish: fish, salmon, shrimp, mackerel, anchovies, sardines
- Poultry: chicken, turkey, duck, goose
- Oils: olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, vegetable oil
- Nuts: almonds, macadamia nuts, pecans, pistachios
- Seeds: chia seeds, sesame seeds, hemp seeds, flax seeds
- Spices and flavours: turmeric, dark pepper, cumin, dill, basil, rosemary, cinnamon
Foods With High Glycemic Index to Avoid
Although no food sources are strictly forbidden on the eating routine, food varieties with a high GI ought to be restricted. Food sources with a high GI include:
- Bread: white bread, bagels, naan, pita bread
- Rice: white rice, jasmine rice, arborio rice
- Grains: moment oats, breakfast oats
- Pasta and noodles: lasagna, spaghetti, ravioli, macaroni, fettuccine
- Bland vegetables: pureed potatoes, potatoes, french fries
- Baked food: cake, doughnuts, treats, croissants, biscuits
- Bites: chocolate, wafers, microwave popcorn, chips, pretzels
- Sugar refreshments: pop, natural product juice, sports drinks
In a perfect world, try to use these food varieties that have a lower glycemic index at whatever point conceivable.
Elements Impacting GI of Food
Various variables can impact the GI value of food, including:
- Sugar Content
There’s a misinterpretation that all sugars have a high GI. The GI of sugar goes from as low as 23 for fructose to up to 105 for maltose. In this way, the GI of food mostly relies upon the type of sugar it contains.
- Starch Structure
Starch is a carb-containing two particles — amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is hard to process, while amylopectin is handily processed. Food varieties with a higher amylose substance will have a lower GI.
- Refinement of Carbs
Handling strategies, for example, pounding and moving upset amylose and amylopectin particles, raising the GI. As a rule, the more handled a portion of food is, the higher its GI.
- Nutrient composition
Adding protein or fat to dinner can moderate assimilation and help diminish the glycemic reaction to a meal.
- Cooking technique
Arrangement and cooking strategies can influence the GI as well. For the most part, the more extended a food is prepared, the quicker its sugars will be processed and consumed, raising the GI.
- Readiness
Unripe natural product contains complex carbs that separate into sugars as the organic product ripens. The riper the natural product, the higher its GI. For instance, an unripe banana has a GI of 30, while an overripe banana has a GI of 48.
Impacts of Cooking and Aging on Glycemic Index of Food
For specific food varieties, the cooking strategy utilized can influence the glycemic index. For instance, singed food varieties will in general contain a high measure of fat, which can moderate the retention of sugar in the circulatory system and decline the GI.
In the meantime, simmering and preparing can separate safe starch — a sort of starch that opposes absorption and is generally found in food sources like vegetables, potatoes, and oats — consequently expanding the GI. Alternately, bubbling is thought to help hold a greater amount of the safe starch and lead to a lower GI, contrasted and other cooking techniques.
The more you cook food varieties like pasta or rice, the more prominent the absorbability of their starch substance, and hence the higher their GI. Thusly, it’s ideal to just cook these food varieties until they arrive at a still somewhat firm texture, implying that they’re firm while gnawing into them.
Notwithstanding the cooking strategy utilized, the level of readiness may likewise influence the GI of certain natural products, including bananas. This is because the measure of safe starch diminishes during the ripening cycle, prompting a higher GI. For instance, bananas that are completely ripped have a GI of 51, though under-ready bananas have a GI of only 30.
Low GI Eating Routine For Diabetes
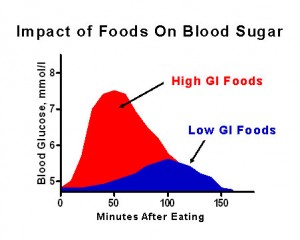
Diabetes is an unpredictable infection that influences a large number of individuals around the world. Individuals who have diabetes can’t deal with sugars successfully, which can make it hard to keep up healthy blood sugar levels. Be that as it may, good blood sugar control forestalls and defer the beginning of confusions, including coronary illness, stroke, and harm to the nerves and kidneys. Various tests recommend that low GI eating regimens lessen blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
A 2019 survey of 54 tests inferred that low GI eating regimens diminished haemoglobin A1C (a drawn-out marker of blood sugar control), body weight, and fasting blood sugar levels in individuals with prediabetes or diabetes.
Likewise, some exploration has connected high GI weight control plans with a more danger of creating type 2 diabetes. One testing in more than 205,000 individuals tracked down that those with the most noteworthy GI weight control plans had up to a 33% more danger of creating type 2 diabetes than the individuals who devoured the least GI eating regimens.
An orderly survey of 24 testings revealed that for each 5 GI focuses, the danger of creating type 2 diabetes expanded by 8%. The low GI eating regimen may likewise improve pregnancy results in ladies with gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that happens during pregnancy. In addition, the low GI eating regimen has been appeared to diminish the danger of macrosomia by 73%. This is a condition wherein babies have a birth weight of more than 8 pounds and 13 ounces, and it’s related to various short-and long haul difficulties for the mother and child.
The Bottom Line
The glycemic index, or GI, is an action used to decide how much a portion of food can influence your blood sugar levels. A few variables influence the glycemic index of a food, including the nutrition composition, readiness, cooking technique, and measure of preparing it has gone through.
Following a low glycemic diet may offer a few medical advantages, as it could help balance your blood sugar levels, bring down your cholesterol, and increment short-term weight reduction.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.


