Contents
- 1 What Are Diabetic Foot?
- 2 How Can Diabetes Affect Foot and Legs?
- 3 Other Causes of Foot Problems
- 4 Symptoms of Diabetic Foot
- 5 Who Is More Prone To Diabetic Foot Problems?
- 6 Diagnosis of Diabetic Foot
- 7 Diabetic Foot Complications
- 8 Treatment of Diabetic Foot
- 9 Tips For Healthy Foot
- 10 A Word From MantraCare
- 11 Post navigation
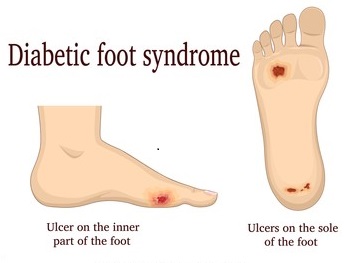
What Are Diabetic Foot?
Diabetic foot are one of the complications of diabetes. Over time, people with diabetes start feeling numbness in their foot because of poor blood flow. Nerve damage is the main reason for this. One can have nerve damage in any part of the body. But nerves in your legs and foot are mostly affected areas.
Frequent infection, slow healing power, and weak immunity being some of the symptoms that contribute to it. Even small cuts and bruises can turn into serious complications. A diabetic foot would develop sores, deformities, and infections more easily.
There are about 15% chances that a diabetic patient is going to develop diabetic feet at some point in his/her life.
How Can Diabetes Affect Foot and Legs?
If you have had diabetes for a long time now, and you have been suffering from high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), it causes severe complications in your foot.
Problems caused by diabetes that can affect your foot are:
Diabetic Neuropathy
It is a type of nerve damage that happens in the body if you have diabetes. Frequent fluctuations in blood sugar levels affect the nerves adversely throughout the body. The primary target is our foot and legs. They are relatively more prone to damage in the case of diabetic neuropathy.
It can be a complicated situation for a diabetic patient to deal with diabetic neuropathy as he already deals with ulcers, skin cracks, etc. in diabetes.
Approximately 50% of people who have diabetes inherit this problem with time. The only way to prevent yourself from diabetic neuropathy is to manage your blood sugar level and lead a healthy life. You must monitor what you eat and how much you eat.
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Diabetes affects the flow of blood in your body also. This condition of poor blood flow or poor blood circulation all through the body is called peripheral vascular disease. With the lack of good blood flow, it becomes tough for your sores, cuts, and injuries to heal. So if you catch any infection that is taking time and is not being healed because of poor blood flow, then it might develop into ulcers or gangrene. These are the serious conditions wherein the tissues of the affected areas die due to a lack of blood.
Calluses
In people with diabetes, calluses develop on their foot very easily and more quickly. Because the pressure under the foot is high. If left untreated, they form thick layers. Then, they break down and appear as ulcers.
Other Causes of Foot Problems
Corns
Corns are the buildup tissues or hard skin in the toes, especially near the bony area of a toe or between them. They might be the result of pressure or friction generated in the toes by the shoes.
Moisture left between your toes after you take shower can also cause corn.
Blisters
These are formed when a particular area is being rubbed again and again. Your shoes might be the reason. Shoes with improper fitting or wearing shoes without socks can lead to blisters.
Bunions
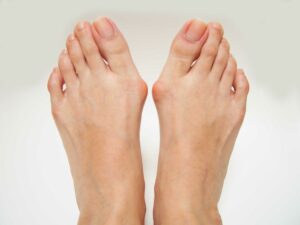
It is noticed that people wearing high heels footwear suffer through this problem more. What happens in this condition is that your biggest toe turns towards your second toe. The area where your biggest toe joins may become hard.
Dry skin

Lack of moisture will make the skin crack, and this allows the germs to enter.
Ingrown nails
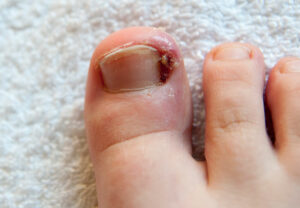
Sometimes it so happens that the edges of the nail grow onto your skin. The edge of the nail enters into the skin causing redness, pain, swelling, and infection. The following can be the reasons for ingrown nails:
- Pressure from shoes
- Improperly trimmed nails
- Crowding of the toes
- Trauma to the feet from activities such as running, walking, or doing aerobics.
Symptoms of Diabetic Foot
The signs and symptoms of diabetic foot are:
- Numbness
- Pain
- Tingling
- Loss of sense
- Redness
- Skin discolouration
- Swelling
Some of the severe symptoms of the diabetic foot that turn into diabetic foot ulcers are:
- Changes in skin or toenails
- Fluid or pus discharge
- Foul smell
Who Is More Prone To Diabetic Foot Problems?
People who are more likely to catch this disease are the people who:
- Either has nerve damage or poor blood flow
- Have managed blood glucose levels
- Are obese
- Also, have High blood pressure or high cholesterol
Diagnosis of Diabetic Foot
To diagnose diabetic foot, the experts will:
- Ask if you are able to manage your blood sugar levels
- Ask about the symptoms the patient is facing
- Examine the affected area (toes, feet, or legs)
- Check for the sensation or the feel of touch using different tools
In case the patient has reached the extent of diabetic ulcer or blister, the doctor will:
- Look for the signs such as redness, swelling, warmth, and skin discoloration, and skin discharge.
- Prescribe some tests like X-ray or MRI, to examine conditions deeper than the skin
- Take a sample of skin discharge to figure out the kind of infection.
Diabetic Foot Complications
Well, diabetic feet themselves are one of the severe complications of diabetes. But this doesn’t stop here. Diabetic feet further cause complications as well. Some are:
Abscess
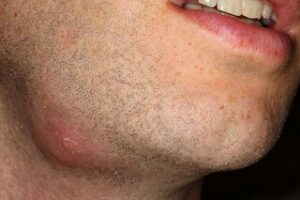
It is basically a pocket or accumulation of pus. When infections reach your bones or tissues, pus develops. It is normally treated by removing the abscess. However, in some severe cases, bone removal or tissue removal might be needed.
Gangrene
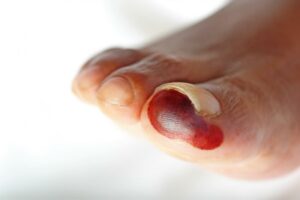
High blood sugar levels affect the blood vessels that supply blood to your fingers. This is why the tissues present there become dry and dead. The treatment for gangrene is oxygen supply therapy or removal of the affected area through surgery.
Deformities
Basically, it’s nerve damage that makes the muscles weak leading to the following problems:
- Hammertoes
- Claw feet
- Prominent metatarsal heads
- Pes Cavus
Charcot’s foot is a rare but deadly condition that can occur in people with peripheral neuropathy, particularly in those who have diabetes. The bones, joints, and soft tissues of the foot and ankle are all affected by Charcot. The bones of the foot or ankle grow weak and can shatter, and the joints can dislocate.
Amputation
You may understand this situation as an end-stage. Because of poor blood circulation and nerve damage, the patient is not able to feel and realize the worsening condition of the affected area. And it is so badly injured that there is no option left but amputation.
Treatment of Diabetic Foot
Of course, the treatment for diabetic feet depends upon the severity of the wound. Both surgical and nonsurgical treatments are available.
Non-surgical Treatment
First, the doctor will make attempts to treat the diabetic foot without doing any kind of surgery.
Some of the non-surgical methods are:
- Keeping wounds clean and dressed
- Keeping close track of the growing gangrene on the toes
- Wearing cast boot or total contact cast or any other immobilization devices.
Surgical Treatment
When the non-surgical treatments do not help or do not give the expected results, the doctors suggest surgical treatment, which might include:
- Removing decaying or dead tissue
- Amputating parts, ranging from one toe to a section of the foot, to the leg below, and finally to the extent of amputating even above the knee.
- Arterial bypass to restore blood flow to the affected area
- Endovascular surgery to keep blood vessels open.
Tips For Healthy Foot
- Don’t leave your foot unchecked even for one day. You need to avoid cuts and injuries. Checking for swelling, redness, blisters, corns, calluses, if any should be caught initially itself. Ask for someone’s help to check the bottom side of the feet. You can use a mirror also.
- Wash your feet every day. Use warm water to do so. But never soak your foot. You just need to wash them, make them completely dry and don’t forget to apply lotions.
- Whenever needed, trim your toenails. Don’t wait for the time to grow them long enough to cause cuts.
- Use diabetes-friendly footwear and socks. While shopping for shoes and socks, you need to be a little more attentive if you are a diabetic. Go for full coverage shoes with more depth in the toe box.
- Never step out barefoot. However, you should not move barefoot even when you are indoors.
- Go easy on your foot while exercising.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.