Contents
- 1 Gestational Diabetes
- 2 Classes of Gestational Diabetes
- 3 Causes of Gestational Diabetes
- 4 Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
- 5
- 6 Risk Factors of Gestational Diabetes
- 7
- 8 Prevention of Gestational Diabetes
- 9 Complications of Gestational Diabetes
- 10 Gestational Diabetes Diagnosis
- 11 Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
- 12 Will Gestational Diabetes Affect The Baby?
- 13 Diet Plan For Gestational Diabetes
- 14 A Word From MantraCare
Gestational Diabetes
It is the condition in which blood sugar is raised in women during pregnancy. This type of diabetes is noticed in pregnant women for the first time. Another term for pregnancy is gestation, thus called gestational diabetes.

Gestational diabetes-like other types of diabetes start when your body is unable to make or use insulin in the way it should. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter cells for energy. It leads to the accumulation of glucose or sugar into the blood. This type of diabetes can affect the health of the baby and the mother.
However, the good news is that gestational diabetes can be controlled with some healthy changes in daily life. There are no major or serious complications of gestational diabetes and it disappears after childbirth. Some precautions should be taken to control the blood sugar of the expecting mother. They can adopt a healthy diet, regular exercise and if it is necessary, they can also take the medications to control this condition.
Classes of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is of two types.
- Class A1 gestational diabetes: It can be controlled by diet and exercise.
- Class A2 gestational diabetes: This type of gestational diabetes needs insulin or other oral medications to be controlled.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes
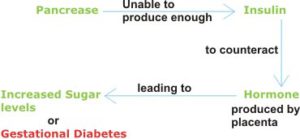
Although the exact reason for gestational diabetes is still unknown. However, it can be caused by various types of hormones that are being secreted from the placenta. Such as:
- Human placental lactogen/ hPL
- Other hormones that increase insulin resistance
These hormones sustain the pregnancy, therefore over time their amount in the body is increased. This can increase the blood sugar level or the body’s insulin resistance.
During pregnancy, the mother’s body naturally becomes insulin resistant, so more glucose is there in the blood to be provided for the baby. But if insulin resistance becomes subtle then it could be harmful to health. Usually, our body produces insulin that helps the body cells, absorb this sugar for energy. But in some conditions mother’s pancreas cannot produce that much insulin, leading to a higher level of blood sugar. These are the factors that can cause gestational diabetes.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes rarely shows the symptoms, and if it does, they are usually mild. Symptoms of this type of diabetes are similar to diabetes mellitus such as-
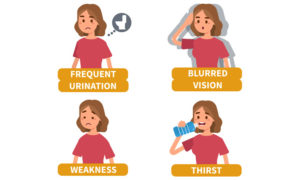
- Increased thirst
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Blurred vision
- Snoring
Risk Factors of Gestational Diabetes
There are some factors that play a role in developing gestational diabetes. You are more likely to develop this type of diabetes if you:
- Are African-American, Asian, Hispanic, Alaska Native, Pacific Islander, or Native American
- Have prediabetes– a condition in which blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes
- Were overweight before the pregnancy
- Have a family history of diabetes (your family member have diabetes)
- Have had gestational diabetes before
- Are suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS)
- Suffer from other problems linked with insulin
- Have conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, or other complications
- Have given birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- Are older than 25
- Have had a miscarriage or given birth to an immature child
Prevention of Gestational Diabetes

In most cases, gestational diabetes can be prevented but there is no guarantee. If you have had this type of diabetes before then you can take some precautions so you don’t develop it again. If gestational diabetes is controlled at an early stage, then you are less likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Eat healthily: people with diabetes should consume foods that are high in fiber and low in fat and calories. You should eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains for blood sugar control. There is a variety of foods available in the market which are low carbs, so you can enjoy these foods without compromising on the taste.
- Stay physically active: Physical activeness is important for everyone. But especially for people with diabetes. Exercising before and during pregnancy can help in preventing gestational diabetes. You are not supposed to do heavy exercises, just walk for some minutes, or do yoga. A short burst of daily activities like going to the park or doing daily chores will work the same.
- Monitor blood sugar often: Pregnancy affects your body’s function as the hormones are changed. Therefore, it’s important to take care of track your blood sugar for a healthier pregnancy. If you notice minor changes, there is no need to worry about them. Blood sugar fluctuates before and after eating. If you find the level worrisome, then talk to your doctor about it.
- Maintain a healthy weight: While planning for a child, try to reach a healthy weight before starting a pregnancy. Losing an extra pound will not only help in preventing gestational diabetes but will be good for you and your baby’s overall health.
Complications of Gestational Diabetes
If the blood sugar level is controlled then there is nothing to be worried about, but if it’s not that well-controlled then it can cause some complications in pregnancy like:
An extra-large baby
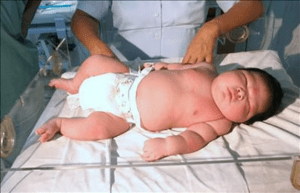 In gestational diabetes, the blood sugar of the mother rises due to various reasons we talked about. But in uncontrolled gestational diabetes, the sugar level is not controlled which can cause the baby to be extra-large.
In gestational diabetes, the blood sugar of the mother rises due to various reasons we talked about. But in uncontrolled gestational diabetes, the sugar level is not controlled which can cause the baby to be extra-large.
Extra-large babies- the ones who weigh more than 9 pounds can cause problems in a healthy delivery. In this case, the mother may need C-section to deliver the baby and the baby may be born with injuries due to extra pressure during birth.
C-section
The baby grows extra-large in case of gestational diabetes leading to complications in childbirth. Therefore, a c-sec is the method of delivery for a mother with gestational diabetes. The mother will need more time to recover from childbirth if the c-sec is performed.
Preeclampsia (high blood pressure)
There could be other complications of gestational diabetes depending on the level of sugar increased. One of them is preeclampsia or high blood pressure. High blood pressure can cause swelling in fingers and toes that do not go away easily. Preeclampsia can cause serious harm to both the baby and the mother.
To keep it in control, it’s necessary to monitor it closely. Some lifestyle changes like a healthy diet may also improve this condition. Women with diabetes are at a greater risk of high blood pressure.
Type 2 Diabetes Later In Life
Women with gestational diabetes have a great risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It also increases the risk of obesity after the child’s birth. Obesity brings other health problems along with it.
Early Birth or Still Birth
High blood sugar increases the risk of early childbirth. The mother may experience labor before the due date. Or there is a chance that early c-sec is recommended due to the extra weight of the baby. Untreated gestational diabetes can also cause a baby’s death before birth or later in life. Although it happens very rarely. The respiratory syndrome can also happen to babies born early to mothers with high blood sugar levels. They may face difficulty in breathing.
Target Blood Sugar Level During Pregnancy
The recommended blood sugar level for pregnant women is:
- Before a meal- 95 mg/dl or less
- One hour after a meal- 140 mg/dl or less
- Two hours after a meal- 120 mg/dl or less
Gestational Diabetes Diagnosis
It is recommended to follow all the check-ups that your doctor tells you to. Even if you do not have any possible risks of developing gestational diabetes, your doctor will test your blood sugar levels in 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. The American Diabetes Association also recommends routinely screening for gestational diabetes in pregnant women. The test for blood sugar is:
Glucose Challenge Test
Usually, this blood sugar test is performed for screening the blood sugar level in pregnant women. No preparations are required for this test. You will be given 50 grams of glucose to drink, to increase your blood sugar. An hour later, the blood sample is taken to check how your body handled all that sugar.
If your blood sugar level comes higher than normal then after 3 hours another test is performed. In this test, you will drink 100 grams of a glucose drink, and after 3 hours you’ll give another blood sample to test your glucose challenge test. If the doctor finds the blood sugar levels abnormal in these screenings, he might perform another test like fasting glucose blood sugar test.
Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
 Gestational diabetes is usually temporary and disappears after childbirth. However, you have to act quickly. The treatment of gestational diabetes is available, but if you don’t treat it at the right time, it may hurt you and your baby. To control it during pregnancy here is what you should do:
Gestational diabetes is usually temporary and disappears after childbirth. However, you have to act quickly. The treatment of gestational diabetes is available, but if you don’t treat it at the right time, it may hurt you and your baby. To control it during pregnancy here is what you should do:
- Eat right– you have to make sure that you do not skip your meals at any cost. Eat three meals a day at least. Another thing, eat healthy and natural foods that are low in sugar. You should also replace foods like cakes and ice creams with fruits, nuts, and seeds.
- Exercise regularly– Exercise regularly so you don’t gain weight and for normal delivery. You can choose to walk just for some minutes or you can do light exercises. However, before you include any exercises into your routine, do talk to your doctor first. Heavy exercises are not advised.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels- Keep checking your blood sugar levels 4 or more times a day. In any discomfort, talk to your doctor immediately.
- Take Insulin if necessary- If your blood sugar levels are not brought back to normal then your doctor will prescribe you some insulin. Oral medicines or Insulin injections will be given to keep your blood sugar in control.
- Monitor your pregnancy- Do keep checking your baby’s health more often if you have gestational diabetes. And the most important thing you can do is keeping in touch with your doctor and opting healthy daily habits.
Will Gestational Diabetes Affect The Baby?
 As discussed earlier, gestational diabetes can be controlled. If you manage to get the blood sugar levels to normal, there is nothing to worry about.
As discussed earlier, gestational diabetes can be controlled. If you manage to get the blood sugar levels to normal, there is nothing to worry about.
Right after childbirth, doctors will check the blood sugar of the newborn baby. If it is less than normal the baby will be put on IV until it does not back up to normal.
Your child will not face any major issues. Although the child may be extra large and it’s also linked to jaundice. Jaundice usually happens in many newborns and fades quickly after treatment. The child also has a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, but with a healthy lifestyle, it can be prevented.
Diet Plan For Gestational Diabetes

A pregnant have to be extra careful with the foods she eats. As it will affect her pregnancy and her child’s health as well. It is suggested to eat every 2-3 hours to keep the sugar levels normal. Pregnant women should focus on carbohydrates, protein, and fat intake.
Carbohydrates
Cutting carbs or simple carbs will help in managing diabetes and blood sugar spikes. Your doctor will tell you how many carbs you should take according to your height and health. You can eat some healthy carbs like-
- Whole grains
- Beans, lentils, and legumes
- Starchy vegetables
Protein
Everyone should take protein but for pregnant women, it’s a must. She should eat two to three servings of protein in a day. Good sources of protein are poultry, fish, and tofu. If you only eat vegetarian you can depend on pulses for it.
Fat
You have to be careful with the fats. You can not eat unhealthy fats as they will increase your weight, which could be harmful. You can include healthy fats in your diet like nuts, seeds, olive oil, and avocado.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.


