Contents
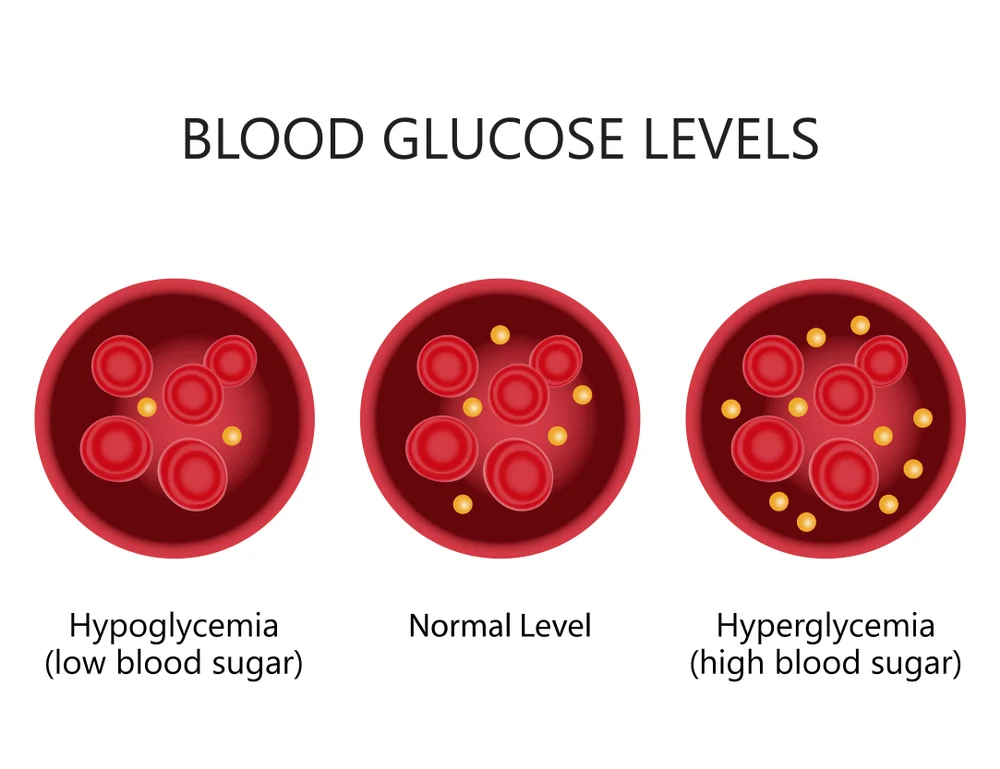
Blood Glucose Level
Glucose, or blood sugar, is the principal sugar found in your blood. It comes from the food you eat and is your body’s primary source of energy. Your blood carries glucose to the entirety of your body’s cells to use for energy.
Diabetes is a disease that makes your blood sugar high. If your glucose is excessively high, you may have to take medicines and additionally follow a special eating routine.
Blood glucose levels are the amount of glucose that some people have in their blood at some random time. Having high or low glucose levels could show basic health conditions that may require medical consideration. Utilize this outline of blood glucose levels to comprehend what your glucose levels mean.
What Is A Normal Blood Glucose Level?

Glucose levels can either be normal, high, or low, contingent upon how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a basic sugar that is available in the bloodstream consistently. Normal blood glucose levels can be estimated when someone diets, eats, or after they’ve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for grown-ups, without diabetes, who haven’t eaten for at least eight hours (fasting) is under 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for grown-ups, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Numerous factors influence glucose levels for the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Medications
- Medical conditions
- Age
- Stress
- Dehydration
- Illness
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal glucose level for anybody without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning ought to be under 100 mg/dL. Keep in mind, glucose levels can fluctuate for the whole duration of the day because of the factors that are mentioned above.
Factors That Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Before you had diabetes, regardless of what you ate or how active you were, your blood glucose (sugar) levels remained within normal reach. Yet, with diabetes, your blood glucose level can also rise higher, and some diabetes medications can make them go lower than normal. Numerous factors can change your blood glucose levels. Finding out about these variables can help you to control them.
- Physical activity: Physical activity can influence insulin affectability for as long as 48 hours which can prompt lower glucose over time. Sugar levels can at first can rise following a short burst of activity. Nonetheless, not doing any activity can prompt high blood glucose levels.
- Food, drink, and illness: Tiredness, food, and alcohol can lead to blood glucose levels. However, people are surprised also those proteins can also affect the blood glucose level. It also affects carbohydrates. After stopped drinking, alcohol continues effect for several hours.
- Where do you inject?: If insulin is absorbed faster then it can affect quickly in different parts of the body. When it is injected into lumpy skin, the effects are absorbed quickly also.
- Medications and conditions: Pregnancy, menstrual cycle, and other medications can affect your blood glucose level. However, missing out on a medication dose or irregular injecting can leads to fluctuating glucose levels.
Low Blood Sugar
Low glucose, also called hypoglycemia, can be a serious condition. It can occur in individuals with diabetes who take medications that expand insulin levels in the body. Taking an excess of medication, skipping meals, eating a bit less than normal, or practising more than expected can prompt low glucose for these people.
Glucose is otherwise called blood sugar. Glucose comes from food and fills in as a significant energy source for the body. Carbs — food varieties like rice, potatoes, bread, tortillas, grain, natural product, vegetables, and milk — are the body’s principal source of glucose. After you eat, glucose is consumed into your bloodstream, where it goes to your body’s cells. A hormone called insulin, which is made in the pancreas, helps your cells use glucose for energy.
People with hypoglycemic unawareness don’t have the idea about their glucose is dropping. In the event that you have this condition, your glucose can drop without you seeing it. Without prompt treatment, you can blackout, experience a seizure, or even go into a state of a coma. Low glucose is a medical emergency. If someone you know has diabetes and they’re encountering gentle to direct indications, have them eat or drink 15 grams of effectively edible carbs, for example:
- half a cup of juice or regular soda
- 1 tablespoon of honey
- 4 or 5 saltine crackers
- 3 or 4 pieces of hard candy or glucose tablets
- 1 tablespoon of sugar
On the off chance that someone is having a serious reaction, like unconsciousness, it’s imperative to administer a medication called glucagon and contact emergency services benefits right away.
People who are in danger of low glucose should talk with their doctor about getting a prescription for glucagon. You ought to never give an unconscious individual anything by mouth, as it could make them stifle or choke.
How Glucose Levels Affect Your Body?
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Skin problems
- Vision problems
- Digestive problems
- Shakiness
- Hungry
- Nausea
Risk of High Blood Sugar
High glucose (hyperglycemia) affects people who have diabetes. A few factors can add to hyperglycemia in people with diabetes, including food and physical activity decisions, diseases, non-diabetes medications, or skipping or not taking sufficient glucose-bringing down medication.
It’s imperative to treat hyperglycemia, supposing that it is left untreated. However, hyperglycemia can get extreme and lead to serious difficulties requiring crisis care, like a diabetic coma. Persistent hyperglycemia, regardless of whether not high, can also have complications affecting your eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart.
Many factors can contribute to hyperglycemia that includes:
- Not utilizing sufficient insulin or oral diabetes medications
- Not injecting insulin appropriately or utilizing expired insulin
- Avoiding or not following your diabetes eating plan
- Being inactive
- Having a disease or infection
- Utilizing certain prescriptions, like steroids
- Being harmed or having a surgery
How To Prevent High Blood Glucose Levels?

For maintaining a proper blood glucose level you must maintain a balanced diet for especially for people who are with diabetes. You may talk with your doctor or any dietitian to set up a diet plan. With type 1 diabetes, the timing will be according to its activity and diet. It is important to note that when you eat, how much you eat, and what you eat. Most doctors prescribe three to four snacks every day and small meals to maintain the balance between insulin and blood sugar in your body. The accompanying ideas can help keep your glucose within your objective reach:
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. If that you take insulin or oral diabetes medications, it’s significant that you be steady about the amount and timing of your meals and bites. The food you eat should be in balance with the insulin working in your body.
- Monitor your glucose. Depending upon your treatment plan, you may check and record your glucose level many times each week or several times each day. Careful monitoring is the best way to ensure that your glucose level remains within your objective reach. Note when your glucose readings are above or underneath your objective reach.
- Taking of your medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Change your medicine if you change your physical activity. The change relies upon the glucose test results and on the type and length of the activity.
- Encountering emotional stress, for example, financial loss or working environment challenges
Illness or stress can trigger hyperglycemia. It is because hormones produced to combat disease or stress can likewise cause your glucose to rise. Indeed, even people who don’t have diabetes may foster transient hyperglycemia during extreme sickness. In any case, individuals with diabetes may have to take additional diabetes prescriptions to keep blood glucose close to normal during disease or stress.
Blood Sugar Levels In Diagnosing Diabetes
If you control your blood sugar level then it will be good for your well-being life. Also, controlling your blood sugar level will help in reducing risk factors that are developing diabetes complications? However, one must know the complications in diabetes such as:
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Retinal disease
- Nerve damage
- Heart disease
The above list can be scarier but the point is the risks can vanish if you maintain a good blood sugar level. This needs to stay dedicated most of the days and improve your blood sugar level. This small way can make a big difference for you.
The following is the table for diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes:
| Plasma glucose test | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
| Random | Below 11.1 mmol/l Below 200 mg/dl | N/A | 11.1 mmol/l or more 200 mg/dl or more |
| Fasting | Below 5.5 mmol/l Below 100 mg/d | 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l 100 to 125 mg/dl | 7.0 mmol/l or more 126 mg/dl or more |
| 2 hour post-prandial | Below 7.8 mmol/l Below 140 mg/dl | 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l 140 to 199 mg/dl | 11.1 mmol/l or more 200 mg/dl or more |
Regular checking your blood glucose level will help your body to track the changing needs for insulin. However, you may also work with your doctor for having the best insulin dosage. Many people with diabetes check their blood sugar levels about many times a day with a device called a glucometer.
The glucometer is a device that measures your blood glucose level by the sample of your blood which is dabbed on a strip of treated paper. Continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) is another device that will be attached by your body to measure the amount of blood glucose level every few minutes within a day for up to a week. CGMS will check your blood glucose level from your skin rather than using your blood. They are not as accurate as compared to traditional glucometers.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.