Contents
What are Blood Glucose levels?

The blood glucose level is the amount of glucose in the blood. Around 4 grams of glucose is present in the body of around 70kgs all the time. Blood Glucose levels generally rise after you eat food. It later falls after a few hours when insulin moves glucose in your cells.
What is Blood Glucose?
Blood Glucose or Blood Sugar is the main sugar found in the blood. Glucose is an amount of sugar that comes from the food we consume, carried through the bloodstream to provide energy to the cells in the body. It forms and stores inside your body. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose to move in your body.
How does the body make Glucose?
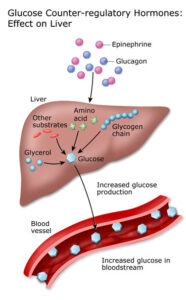
Glucose comes mainly from foods that are rich in carbohydrates like potatoes, bread, fruit, etc. As you eat the food travels down from your food pipe to your stomach. There, body acids break it down into tiny pieces during which glucose is released. It then goes into your intestine where it gets absorbed from where it passes into the bloodstream. After which insulin secreted from the pancreas, helps glucose to get into your body cells.
High Blood Glucose Levels

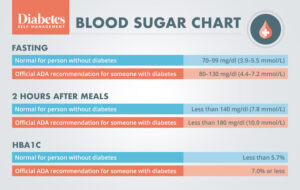
High Blood Glucose level also known as Hyperglycemia is a condition where there is an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a major concern and can severely affect people with both Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. Blood glucose levels are high if they are more than 130 mg/dL before a meal and 180 mg/dL after a gap of one to two hours of a meal.
Symptoms Of High Glucose Levels
Some early symptoms include

- Thirst
- Headaches
- Trouble Concentrating
- Blurred Vision
- Frequent peeing
- Weakness
- Weight Loss
- Blood Sugar more than 180 mg/dL
Ongoing High Glucose levels causes

- Vaginal and skin infections
- Cuts and sores
- Worse vision
- Nerve Damage causes insensitive feet, hair loss, or erectile dysfunction.
- Stomach and intestine problems
- Damage to eyes, blood vessels, and kidneys
Causes Of High Glucose Levels
This is caused by diabetes, and various non-diabetic diseases such as thyroid, pancreatic, etc. and excessive eating, physical trauma, and severe stress.
Treatment Of High Glucose Levels
A person having diabetes and having any early signs of high glucose levels should get blood sugar tested and consult a Doctor. However, there are some home remedies often recorded and observed as follows:

- Drinking more water: Water helps to remove excess sugar from the blood through urine, and it helps you to avoid dehydration.
- Doing Regular Exercise: Working out often helps to lower your blood glucose level but in some rare cases it can even make glucose levels very high. One should ask the Doctor for the right kind of exercise for them.
- Monitoring Ketones: If a person is having Type 1 diabetes and the glucose level is high, you need to keep a check on your urine for ketones. When you have them, you need to stop doing exercise. If you have Type 2 diabetes and the blood sugar is high and you have no ketones in urine, you should be well hydrated and the doctor may provide you with the exercise that you recommend.
- Altering eating habits: Patients should meet a dietitian to change the amount and types of food to eat to balance their diet.
- Changing Medications: Doctors may change the amount, timing, and the type of medicines you take if you are previously suffering from diabetes. Do not change without consulting an expert.
Prevention Of High Glucose Levels
There are ways by which you can prevent and keep your glucose levels in check. If one follows the proper ways, he/she shouldn’t worry about high glucose levels.

- Know your diet- know the number of carbohydrates you intake in every meal and snack and keep a check on it.
- Test blood glucose levels regularly.
- Keep checking if you have repeated abnormal blood glucose readings.
- In cases of emergency, wear medical identification so people know that you have diabetes.
Low Blood Glucose Levels
Low Blood Glucose Level also known as Hypoglycemia is a condition where your blood glucose is lower than normal. This situation can occur when a person is suffering from diabetes and is taking insulin or some medicines to control their diabetes. This can be harmful to a patient suffering from diabetes. Low glucose level is when a person is having 70 mg/dL or less reading.
Symptoms Of Low Glucose Levels
Some early symptoms include:

- Weakness
- Shaking
- Sweating
- Headache
- Hunger
- Feeling uneasy, nervous, or anxious
- Vision problems
- Trouble in thinking clearly
- Mood swings
- Fast heartbeat
Ongoing Low glucose level causes:
- Faint
- Have a seizure
- Coma
Causes Of Low Glucose Levels

- Taking Insulin and diabetes medicines at the wrong time according to the doctor.
- Taking the wrong amount of Insulin or medicine as prescribed
- Injecting Insulin without having food
- Skipping meals
- Exercising more than usual
- Alcohol Drinking
Treatment Of Low Glucose Levels
If a person is getting low glucose levels consistently, he/she should consult a doctor immediately. If you are already a patient, you should consult a doctor to check if you’re taking your insulin in the right way or there should be any change in type and amount of insulin. However, there are some home remedies often observed such as :

- Eat, drink or consume something that contains sugar so that it can immediately get into your body. Food or drinks which have a good amount of sugar present in it such as regular soda, orange juice, cake frosting or you can take glucose tablets or gel which will help to rise the blood glucose levels
- Wait for about 10 minutes so that the sugar can work.
- If the symptoms are severe and it worsens if you eat, drink or take glucose tablets you should get a glucagon shot. Glucagon is a hormone that helps to raise blood glucose levels to rise quickly.
Prevention Of Low Glucose Levels
Prevention is better than cure. Preventing low blood sugar is always better than treating it. One should always have a fast-acting sugar source with them. There are several other ways to prevent such as:
- When you exercise, check your blood sugar levels and you should make sure you have snacks along.
- Talk to your doctor about the intake of insulin on the days you exercise.
- Consult a doctor if you need any bedtime snack to prevent low glucose levels overnight.
- Avoid drinking alcohol without having food. Preferably women should limit themselves to one and men should limit to 2 drinks a day.
- For pregnant women, eating a small, balanced, and frequent diet is very important to keep blood sugar levels steady. Exercise regularly but if the doctor is advised against it, then avoid it.
Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Normal Blood Glucose levels can be measured when someone eats or after they have eaten. Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day such as how much food they have consumed, their physical activity, medical conditions, menstrual periods, alcohol, dehydration, etc..
Normal Glucose Levels without diabetes
Average blood glucose levels of any age in the morning should be less than 100mg/dL and at the end of the day, it depends on the conditions mentioned above.
Normal Glucose Levels with diabetes
Average blood sugar levels for those having diabetes depend on age and the time of the day.
 Children’s Glucose Levels
Children’s Glucose Levels
Children under 6 should have glucose levels that are between 80 to 200 mg/dL. This is an appropriate range and is considered healthy and the amount of glucose in a child’s body will now differ from the time they wake up, have food, and before bedtime. For eg. Before a meal, the average blood sugar level ranges from 100-180 mg/dL , a few hours after eating it is approximately 180 mg/dL and at the end of the day (bedtime) it ranges from 110-200 mg/dL. Sometimes kids with diabetes or in hypoglycemia cases, children may have to get tested by their parents in the middle of the night.
Adolescent’s Glucose Levels
Kids aged 6 to 12 must-have blood sugar ranges from 80 to 180 over the course of the day. For eg. in the early morning, it may range between 80 to 180 mg/dL, a before meal approximately 90 to 180 mg/ dL. Blood sugar levels may go up after eating food because the body breaks down the carbs into glucose, which gets distributed in the bloodstream like after a few hours it can range up to 140 mg/dL, and at the time of the sleep (bedtime), it ranges from 100-180 mg/dL.
Teen’s Glucose Levels
Teenagers should have an average blood sugar level that ranges between 70 to 150 mg/dL over the course of the day. For eg. in the morning, it may range from 70-150 mg/dL, before meals it may range from 90-130 mg/dL. After a few hours of food, it may rise up to 140 mg/dL. At the time of sleep, it may range between 90 to 150 mg/dL. Teenage years are often the most difficult times for adolescents with diabetes to manage because managing diabetes requires a lot of responsibility and responsible behavior which can be sometimes difficult for most of teenagers. They should keep an eye to maintain their glucose levels between 70-150 mg/dL throughout the day by watching what they are eating, exercising.
Adult’s Glucose Levels
Adults (20 years or more ) have glucose levels that range between less than 100-180 mg/dL during the day. When you wake up in the morning, your blood sugar should be at the lowest because you have not consumed food for more than eight hours. For eg. in the morning, the blood sugar levels should be less than 100 mg/dL. Before having food, it ranges from 70-130 mg/dL. After a few hours of eating it is less than 180 mg/dL. At the time of sleep (bedtime), it usually ranges from 100-140 mg/dL. If you are struggling with your glucose control, a Doctor will help you to provide a plan to manage your blood glucose level accurately.
Conclusion
Keep an eye on your Blood Sugar Levels, keep checking it from time to time with medical practitioners. Consult a doctor if there is a constant up and down on blood sugar levels. Follow the above-mentioned precautionary care and take appropriate steps before it gets too late.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.

 Children’s Glucose Levels
Children’s Glucose Levels
