Contents
What Is An Endocrine System?
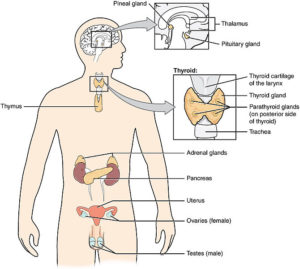
The human endocrine system is made up of many glands that produce hormones to regulate a range of functions. Hormones exit the glands and reach the bloodstream, where they are transferred to organs and tissues in the body. Various endocrine glands are part of this system including the adrenal gland, hypothalamus, ovaries, testicles, pancreas, parathyroid gland, pineal gland, pituitary gland, thymus gland, and thyroid gland. The working of the glands can be hindered by various factors and can lead to diseases and complications in the body.
Adrenal Gland
The adrenal gland can be found on the top of the kidneys and is divided into two distinguished regions. The right gland is triangular whereas the left gland is crescent-shaped. The adrenal glands release various hormones like corticosteroids, catecholamines, aldosterone, and androgens. The function of the corticosteroid is to regulate the stress response, immune system, and inflammation. Catecholamines are also responsible for the stress response.
Aldosterone is involved in the regulation of the function of the kidney. Androgen is the male sex hormone and is present in excess quantity in males as compared to females. If these hormones are released in less or excess quantity then they can cause complications in the body. Over-nervousness, sweating, elevated blood pressure, and Cushing’s disease are all symptoms of hypersecretion of the hormones released by the adrenal gland. Addison’s disease, mineralocorticoid deficiency, weight loss, energy loss, and anaemia are symptoms of hyposecretion of the adrenal gland.
Hypothalamus
Just above the brainstem and behind the thalamus is the location of the hypothalamus. Involuntary body functions such as respiration, heart rate, appetite, sleep, temperature, and the circadian cycles, or regular rhythms, are triggered and regulated by this gland. The pituitary gland, which is connected to the hypothalamus, connects the nervous and endocrine systems.
Ovaries And Testicles
In females, the ovaries are on either side of the uterus. The hormones estrogen and progesterone are secreted into them. Sexual development, fertility, and menstruation are all aided by these hormones. In males, the testicles are found in the scrotum, just below the penis. Androgen and testosterone are the hormones secreted by the testicles. Sexual development, puberty, facial hair, sexual activity, libido, erectile function, and the production of sperm cells are all affected by androgens.
Pancreas
The pancreas is both digestive as well as an endocrine gland. It releases hormones like insulin, somatostatin, glucagon, pancreatic polypeptide. Insulin is essential for the body’s carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Somatostatin governs the release of many hormones, including gastrin, insulin, and growth hormone, and regulates endocrine and nervous system activity. When blood glucose levels sink too low, the peptide hormone glucagon is released. Pancreatic polypeptide: This aids in the regulation of the pancreas’ release of substances. Changes in the level of the hormone secreted can cause diabetes and digestive problems. Hypersecretion can cause hyperinsulinism, and too much insulin can cause low blood sugar. One form of diabetes can be caused by the hyposecretion of the hormone.
Parathyroid Gland
The parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck that contain the parathyroid hormone, which controls calcium and phosphate levels in the blood. These chemicals must be present at the right levels for muscles and nerves to function safely and efficiently. Hypersecretion may result in fragile bones that crack quickly, as well as urinary stones. Hyposecretion can lead to involuntary muscle contractions which are caused by the low levels of calcium in the plasma of the blood.
Pituitary Gland
An endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, connected to the hypothalamus is the pituitary gland. Since it secretes hormones that control the activities of other glands, as well as development and many other bodily functions, it is often referred to as the primary endocrine master gland. Hormones that affect sexual development, thyroid function, growth, and skin pigmentation are secreted by the anterior, or front, pituitary.
Underactive anterior pituitary can induce stunted development in children as well as interactivity in other endocrine glands. The posterior, or back, the pituitary gland produces oxytocin, a hormone that stimulates uterine contractions, as well as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which allows the kidneys to retain water. Gigantism, or excessive expansion, may result from hypersecretion. Hyposecretion may result in stunted bone growth and short stature.
Thymus Gland
The thymus is an endocrine gland that is found under the sternum, or breastbone. Early in life, T lymphocytes, a kind of immune cell, develop and multiply in the thymus gland. The gland shrinks after puberty. The immune system, which defends the body from disease and illness, includes the thymus gland. Hypersecretion can result in an overactive immune system that responds inappropriately to potential threats. An autoimmune disease can evolve as a result of this. Hyposecretion can cause a compromised immune system, making the body vulnerable to infection and allowing viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens to take hold.
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck that produces hormones that control blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, metabolism, and how the body responds to other hormones. It is located just below Adam’s apple. Iodine is used by the thyroid gland to make hormones. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine are the two primary hormones it contains. Graves’ disorder is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Accelerated appetite, sweating, arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat), weight loss, and nervousness are also potential side effects. Tiredness, weight gain, nausea, irregular bone density, developmental delay, and stunted growth are all symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Who Is An Endocrinologist?
They are concerned with metabolism, or all of the biochemical processes that allow the body to function, such as how it converts food into energy and grows. When there is improper functioning of the hormones occurring in the body you need to visit an endocrinologist. Their goal of the treatment is to restore the normal levels of the hormones which are being either produced in excess amount or negligible amount.
Diagnosis By An Endocrinologist
The Pediatric Endocrinologist is the specialist who treats the children having problems in their endocrine system. The endocrinologist is involved in diagnosing and treating conditions like osteoporosis which occurs due to improper bone metabolism, irregular cholesterol level, improper functioning of adrenal gland, hypothalamus, pancreas, parathyroids, pituitary, and thyroid gland. They also treat conditions related to the secretions of ovaries in women and testes in men.
Qualification of An Endocrinologist
The people who study endocrinology need to have basic school qualifications. They should have cleared their medical school studies and have to undergo a specialization study for 2 years. When a person wants to achieve a deeper knowledge on the field they need to do another specialization course on the particular gland they are interested in. they should also gain experience in their field by working in clinics as residents or interns for at least 3 years. This whole process of gaining a specialization in Endocrinology takes about 10 or more years.
Workplace of An Endocrinologist
An endocrinologist may enter various fields of interest. They can work in their clinic, or along with different kinds of doctors, or may get a job in a hospital in the endocrinology department. All the endocrinologists do not necessarily take patients. Some are interested in teaching and teach aspiring medical students in medical colleges or direct the residents present in their hospital with work. They can also enter the field of research where they can conduct their research in the endocrinology field. Doctors of another field might suggest their patients visit an endocrinologist when there some underlying hormonal imbalance in the body occurring in the endocrine system.
For example, a doctor who treats diabetes may suggest you consult an endocrinologist if the insulin levels in the body are being affected and no treatment done by the doctor to manage your diabetes is working. This doesn’t mean that you won’t be meeting your primary healthcare doctor. They both just work together to balance your hormones and treat the disease in a better possible way. Endocrinologists help the patients to manage their hormonal level when the conventional treatment stops working on them.
When To Visit An Endocrinologist?
Patients are recommended to consult an endocrinologist when the endocrine disorders get complicated and the conventional method of treatment stops working. People should visit an endocrinologist if they have the following health conditions.
Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes are also included in this disease. To regulate symptoms such as thirst, exhaustion, and blurred vision, people with diabetes must control their blood sugar levels. A sugar called glucose reaches the body as food is digested. The body uses glucose as a store of energy. The pancreas is an organ that releases insulin. Insulin’s job is to transport glucose from the bloodstream to muscle, fat, and liver cells, where it can be burned for energy.
Insulin is a chemical that the pancreas produces to stabilize blood sugar levels. Diabetes patients have elevated blood sugar levels either their pancreas may not produce enough insulin, or their muscle, fat, and liver cells do not respond to insulin properly, or both. Help from an endocrinologist is needed to keep blood sugar levels under control.
Thyroid Disorder
Thyroid disorder is the leading cause of various disorders occurring in the world. The thyroid is in charge of regulating the metabolism. Thyroid hormone levels can be too high or too low, resulting in a variety of symptoms such as weight gain/loss, hair loss, anxiety, and more. To treat the disorders related to the thyroid, the levels of thyroid are normally regulated and symptoms are improved with drugs. Patients with too much or too little thyroid hormone due to an overactive or underactive thyroid are treated by an endocrinologist.
They replace or block thyroid hormones to help patients with thyroid disease achieve hormonal balance. Thyroid disorder is classified into four categories which can be treated by endocrinologist-thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormone), hypothyroidism (insufficient thyroid hormone), benign (non-cancerous) thyroid disorder, and hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormone).

Bone Disease
Osteomalacia also known as rickets, causes softening of the muscles, while osteoporosis weakens the spine. Both are bone disorders that are diagnosed and treated by an endocrinologist. The term “osteoporosis” refers to bone thinning. As the production of sex hormones reduces with age, some individuals are more likely to develop osteoporosis. This can be commonly seen in women who are advancing to the menopause stage or have reached menopause.
Osteoporosis is caused by a combination of genetics and drugs. Strengthening the bones and reducing bone deterioration are the primary therapies, which can be accomplished by strength-building workouts and medicine.

Low Testosterone
Millions of men suffer from low testosterone. Many people believe that low testosterone is just a problem for children and teenagers, but it may also have harmful consequences in older adults. Low testosterone levels can cause fatigue, depression, muscle weakness, and hair loss, among other things. Testosterone levels can be restored with hormone replacement therapy.
Endocrine Gland Cancer
Thyroid cancer, parathyroid cancer, adrenal cancer, and pituitary cancer are all endocrine gland cancers. Hormone levels can be affected by these cancers which might require the urgent attention of an endocrinologist. People with these cancers are usually treated by both an endocrinologist and an oncologist. The oncologist is in charge of cancer therapy, while the endocrinologist is in charge of hormone balance.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS causes elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) and insulin in women, which can result in enlarged ovaries, irregular cycles, metabolic issues, and cysts. PCOS can make it difficult to conceive when you’re younger. Older people can experience more metabolic side effects, such as weight gain and excessive hair growth. Proper hormonal balance restoration and diet changes can reverse the effect of the syndrome.
Pituitary Gland
Since it regulates other glands and contains many essential hormones, the pituitary is known as the “master gland” of the body. Infertility, menstrual problems, development disorders, and too much cortisol output (Cushing’s syndrome) may all be triggered by a deficiency or overproduction of pituitary hormone. An endocrinologist can help you with certain medications to control the symptoms and would refer the patients to a surgeon who needs surgery.
Switching From A Primary Healthcare Doctor To An Endocrinologist
Your primary healthcare doctor will recommend you to an endocrinologist if they suspect any hormonal imbalance in the body which is blocking the effect of the conventional treatment. Endocrinologists will perform a physical exam, check your pulse rate, heart rate, and blood pressure. They would also assess different body parts to check the symptoms related to hormonal disorders. After a proper diagnosis has been performed you and your primary healthcare provider would be notified of the treatment plan.
In some chronic hormonal disorders, you may be asked for a follow-up appointment but in other cases, you would continue to see your primary healthcare doctor. It’s a smart idea to have an endocrinologist on your healthcare staff if you have an endocrine condition. You’ll be able to get a correct diagnosis and can plan effective therapy this way.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.



Comments are closed.