Contents
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
DKA or diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening rare condition that can occur in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The omission of insulin from the body is the major cause of DKA. Acute medical conditions, infections that involve the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract, stress from recent surgery can lead to DKA in the body which can cause dehydration and worsen peripheral insulin resistance.
Initiation of DKA
The body is in constant need of energy which is derived from glucose. If the cells are not able to absorb the glucose due to the absence or lower amount of insulin then the body starts to burn fats for energy which in turn produces ketones. Ketones are the molecules that are formed due to the breakdown of fats to form energy.
The production of ketones is initiated when the body does not produce enough insulin to absorb the glucose into the cells. the blood becomes acidic in nature when there is an accumulation of ketones in the blood. It is a warning sign for diabetic patients who have uncontrolled blood sugar levels and need to get treated immediately.
Risk
High levels of ketone when present in the blood can lead to poison in the body. When the levels of ketones in the blood get high then it develops DKA. Diabetic ketoacidosis can occur in people who have type 1 diabetes and it rarely occurs in type 2 diabetic people. When you have uncontrolled blood sugar you need to check your ketones level in the blood regularly.
DKA Test
Ketone levels in the body can be checked easily by using a strip test. In this strip test, you would be provided with a small strip of paper on which few drops of urine need to be put and a particular color change in the strip would indicate your ketone levels. It is necessary to perform this test after every few hours if you are diabetic and have a cold or flu. Also, you need to perform this test after every 4-6 hours if your blood sugar level is high (240mg/dl). Stay aware of your body and when you notice the symptoms visit your nearby healthcare advisor.
Symptoms of DKA
The symptoms of DKA usually appear within 24 hours. These signs may be an indication of the uncontrolled sugar level in your blood. The symptoms generally include excessive thirst, frequent urination, vomiting, stomach pain, shortness of breath, confusion, and fruity-scented breath. You may also conduct a test to detect your symptoms related to DKA which include high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), presence of ketone in your urine. DKA can also cause excess dehydration in your body, worsening the insulin resistance in the peripheral part and increase the insulin amount in the counter-regulatory hormones.
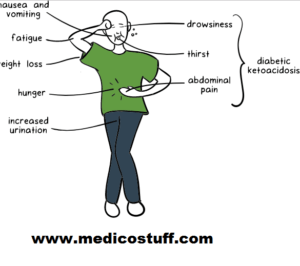
Causes of DKA
An increase in the level of ketones can be due to three major reasons which include high blood sugar levels, fasting done by diabetic people, and the reaction of insulin to the body. Constant production of insulin ensures that the glucose produced by the breakdown from the food materials consumed by you gets absorbed into the cells for its proper utilization. But in the absence of insulin or if there is a lower production level of insulin this glucose does not get absorbed by the cells in the blood and it remains accumulated in the blood giving a spike in the blood glucose level. This in turn initiates the release of the hormones that break down fats as fuel and produce ketones as the energy source. Excess amounts of ketones then get accumulated in the blood which gets filtered by the kidney and gets removed through the urine.
DKA Caused Due To Infection
Diabetic ketoacidosis is caused due to infection or illness which may produce high amounts of adrenaline and cortisol which counter the effect of the insulin and release ketones in the blood. Infections like urinary infection and pneumonia can also cause DKA. If you are under insulin therapy and have missed an appointment or have inadequate amounts of insulin present in your body then you are also prone to the disease and high blood sugar levels can trigger DKA.
Other Causes
Other factors which are responsible for diabetic ketoacidosis are heart disease, pancreatitis, emotional or physical trauma, substance abuse, and certain medicines. Medicines like diuretics, beta-blockers, anticonvulsants affect carbohydrate metabolism and result in the precipitation of ketones in the bloodstream causing DKA. Factors like psychological problems, eating disorders, alcohol addiction, and insulin pump malfunction also contribute to the DKA. People who have type 2 diabetes, are obese, and are extremely insulin resistant are also at risk of having DKA.
Diagnosis of DKA
Blood Glucose Level Test
The criteria for the diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis include the presence of blood glucose level higher than 250mg/dl, acidic arterial pH, and bicarbonate level less than 18mEq/L. The presence of ketones in the urine may further give the confirmation of the disease. Patients who have chronic kidney disease might face difficulty in the diagnosis of the disease as along with ketones other contaminants are also present in the urine which may contribute to the mixed acid-base disorders.
Blood Test
Blood tests are performed on patients who are suspected to have DKA. In the blood test blood sugar level, ketone level, and acidity of the blood are checked. Hyperglycemia is a condition in which the blood sugar level rises due to the absence or low production of blood sugar level and the blood sugar level continues to rise if the body starts producing ketones by the breakdown of the stored fat molecules. Increased production of ketone also leads to an increase in the level of acidity of the blood and hinders the normal functioning of organs. Other tests like blood electrolyte tests, urinalysis, chest X-rays, and electrocardiograms may be required to know the underlying cause of ketoacidosis.
Treatment of DKA
If you get diagnosed with DKA then the treatment options available are fluid replacement, electrolyte replacement, and insulin therapy. The goals of the treatment of DKA are to optimize volume status, hyperglycemia, and ketoacidosis, electrolyte abnormalities, and potential precipitating factors. People who are diagnosed with DKA are taken to the emergency room as they need quick treatment.
Early stages of diabetic ketoacidosis require a certain protocol to be followed which includes a collection of blood for a metabolic profile before intravenous fluids can be injected, infuse of sodium chloride is done after an hour of extraction of an initial blood sample, potassium level should be maintained before the insulin therapy and insulin therapy should be only done after all the steps of the protocol are executed. For treatment to be successful the patient should be monitored frequently.
Fluid Therapy
In DKA there is a loss of various fluids which needs to be restored within 24 hours and 50% of fluid should be infused within the first 8-12 hours of initiation of the treatment. Intravenous infusion of sodium chloride solution is done in the therapy so that reduction in plasma osmolality can be obtained and the water molecules can move into the intracellular compartments. The tonicity of the solution used in the therapy depends upon the hydration status, electrolyte balance, and urine output of the patient. continuous fluid therapy can lead to an increased risk of non-anion gap hyperglycemia acidosis.
The fluid therapy helps in decreasing hyperglycemia by the stimulation of osmotic diuresis and enhances the peripheral action of insulin. Patients who have chronic heart and kidney disease should be given special consideration. Urine output should be monitored regularly.
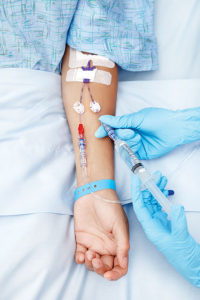
Insulin Therapy
Intravenous infusion of insulin is done in this therapy as it promotes the utilization of glucose by the peripheral tissues and suppresses the production of ketones in the body. High doses of insulin are infused into the body in this treatment. The patients who have DKA become sensitive to insulin as soon as it is infused into the body and improvement in the hyperglycemia can be noticed. It is important to frequently assess the situation to avoid hypoglycemia and rapid shifts of glucose and water occurring between the extracellular and intracellular compartments of the cell. larger doses of insulin should be infused to the patients who are obese and are more resistant to the insulin. This therapy is feasible for insulin-resistant. DKA patients also have extreme hyperglycemia.
Electrolyte Therapy
This therapy involves the infusion of potassium, bicarbonate, and phosphate. Potassium levels usually drop when an infusion of insulin is taking place and can cause hypokalemia which can further lead to cardiac arrest. If potassium levels decrease while insulin therapy is being provided then the infusion of insulin needs to be stopped and potassium should be administered intravenously. Infusion of bicarbonate is only done in severe cases of DKA as an infusion of bicarbonate can cause complications in the body and worsen the condition of the patient. if the pH drops to 6 then only bicarbonate infusion is done along with potassium chloride till the pH reaches greater than 7.
Infusion of Dextrose
DKA can cause complications like hypoglycemia which can be prevented by the timely adjustment of the insulin dose and frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels. Hypoglycemia is a condition in which the blood glucose level is below 70mg/dL and can be resolved by the intake of 15-20g of carbohydrates orally or by infusion of dextrose intravenously.
Prevention of DKA
DKA can be prevented by diabetic patients.
- It is important to regularly monitor your blood sugar level and receive insulin therapy as recommended by your doctor.
- It is important to stay committed to your diabetic diet plan and should also participate in physical activity.
- You should take the medicines and insulin as directed by the doctor.
- You should ask your doctor to teach you how to alter your insulin doses according to the stress, food you eat, and whether you are ill or not as the same amount of insulin dose is not used for all the different body conditions.
- If you are prone to DKA then you should regularly check your ketone level in urine.
- If the ketone level seems to rise in your body do not engage in physical activity to reduce the blood sugar level instead seek medical attention as soon as possible.
- Real-time glucose monitoring should be used by type 1 diabetic patients.
- Self-management
DKA can be prevented if the person identifies the symptoms at an early stage and receives proper treatment. Basic information like when to contact healthcare providers, use of insulin during illness, fever, and infection, and initiation of an easily digestible diet rich in electrolytes should be known to the person who is at risk of developing the disease. It is important for the medical instructor to advise patients to ever skip or discontinue insulin without prior recommendation from a medical instructor. The involvement of the family members should be encouraged to take care of the patient. A written care plan should be provided to understand the self-management of diabetes.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.


