Contents
- 1 What Is Diabetes?
- 2 What Are Diabetes Complications?
- 3 Types of Diabetic Complications
- 3.1 Cardiovascular Diseases
- 3.2 Diabetic Retinopathy
- 3.3 Retinal Hemorrhage
- 3.4 Retinal Detachment
- 3.5 High Blood Pressure
- 3.6 Diabetic Neuropathy
- 3.7 Skin Complications
- 3.8 Fungal Infections
- 3.9 Fungal Infections Of Nails And Hair
- 3.10 Foot Complications
- 3.11 Kidney Complications
- 3.12 Ketones
- 3.13 Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- 3.14 Diabetic Macular Edema
- 4 How To Avoid These Diabetic Complications
- 5 Conclusion
What Is Diabetes?
 Diabetes is a condition that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. It also happens if your body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. When you have diabetes, excess sugar (glucose) builds up in your blood. This sugar does not increase energy in your body. The buildup of glucose can lead to many diabetes complications. These are such as heart disease and stroke.
Diabetes is a condition that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. It also happens if your body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. When you have diabetes, excess sugar (glucose) builds up in your blood. This sugar does not increase energy in your body. The buildup of glucose can lead to many diabetes complications. These are such as heart disease and stroke.
You can control diabetes in various ways. These ways are maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking the appropriate medications.
What Are Diabetes Complications?
There are many complications that may occur with diabetes. These are including blindness, heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, or nerve damage in your hands and feet. This automatically causes you to lose feeling. These symptoms increase over time. That is why it is important to treat them immediately when you notice any changes in your body. This will help prevent further serious effects on your health. These effects are such as amputation of limbs. This is when glucose levels affect your blood circulation.
Types of Diabetic Complications
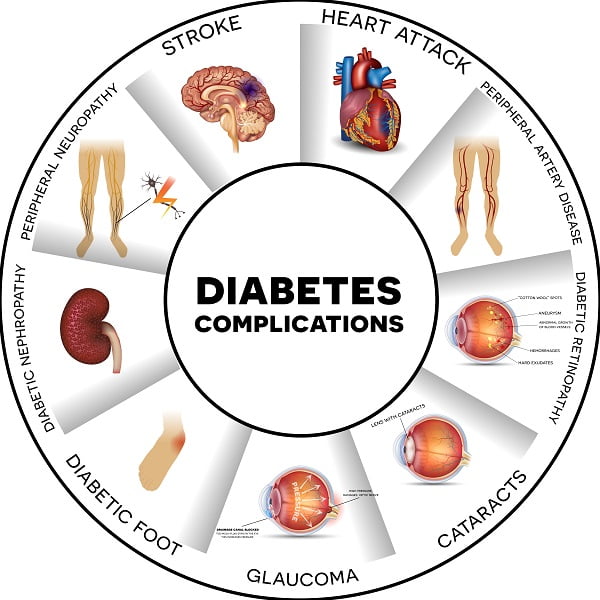
These are some different Diabetic Complications
Cardiovascular Diseases
The most common complication of diabetes is cardiovascular disease. Diabetes can damage small blood vessels through high blood sugar levels. This makes it easier for the vessel to get blocked by plaque build-up in the arteries. This condition increases the risk for heart attack and stroke later in life. It is because of a blockage that occurs in an artery that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the heart or brain. This results in a lack of oxygen. This can often cause permanent tissue death (infarction). Common types of vascular complications include coronary artery diseases. These diseases are such as angina pectoris, peripheral arterial occlusive disease. This leads to leg pain on walking. Carotid atherosclerosis causes transient ischemic attacks or strokes, mesenteric thrombosis (blood clots in the veins of the mesentery), and erectile dysfunction.
Diabetic Retinopathy
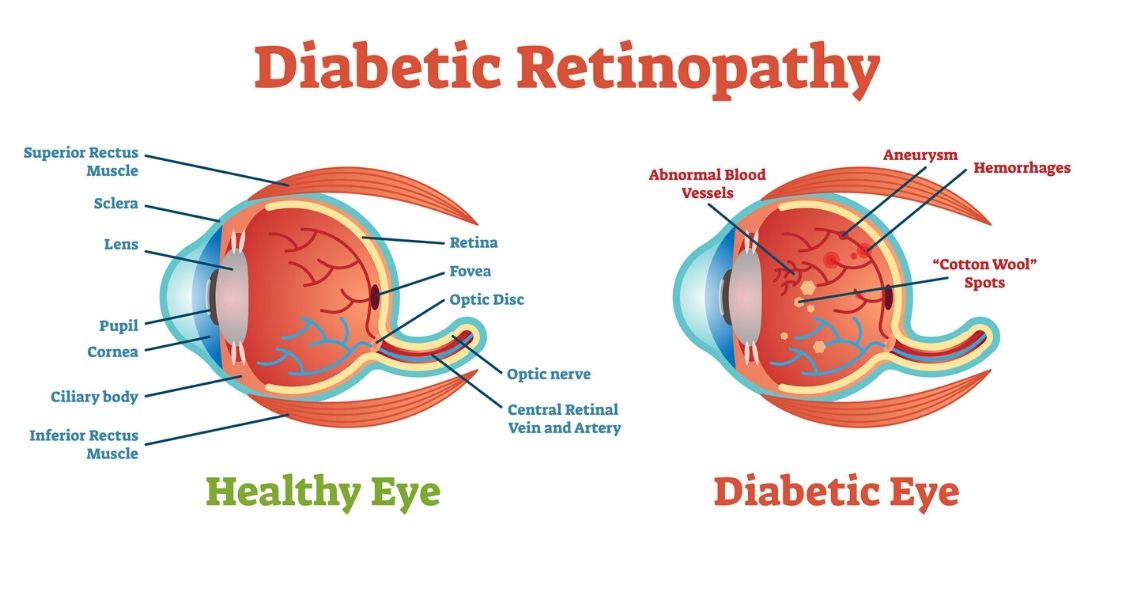 The next most common complication is diabetic retinopathy. This affects up to 80% of people with diabetes who have had their disease for 15 years or more. Diabetic retinopathy involves damage to small blood vessels in the retina. This retina is the back part of the eye. This leads to a loss of vision when it becomes severe enough. It also increases sensitivity to light, so even if you don’t lose your sight completely you may need sunglasses indoors. These are at certain times during daylight hours. The stages of development and progression stages are mild, moderate, and severe forms.
The next most common complication is diabetic retinopathy. This affects up to 80% of people with diabetes who have had their disease for 15 years or more. Diabetic retinopathy involves damage to small blood vessels in the retina. This retina is the back part of the eye. This leads to a loss of vision when it becomes severe enough. It also increases sensitivity to light, so even if you don’t lose your sight completely you may need sunglasses indoors. These are at certain times during daylight hours. The stages of development and progression stages are mild, moderate, and severe forms.
Retinal Hemorrhage
This is bleeding from fragile new blood vessels that have grown on the retina. This is caused by diabetes-related high blood pressure. This may occur in response to stress or not be seen at all.
Retinal Detachment
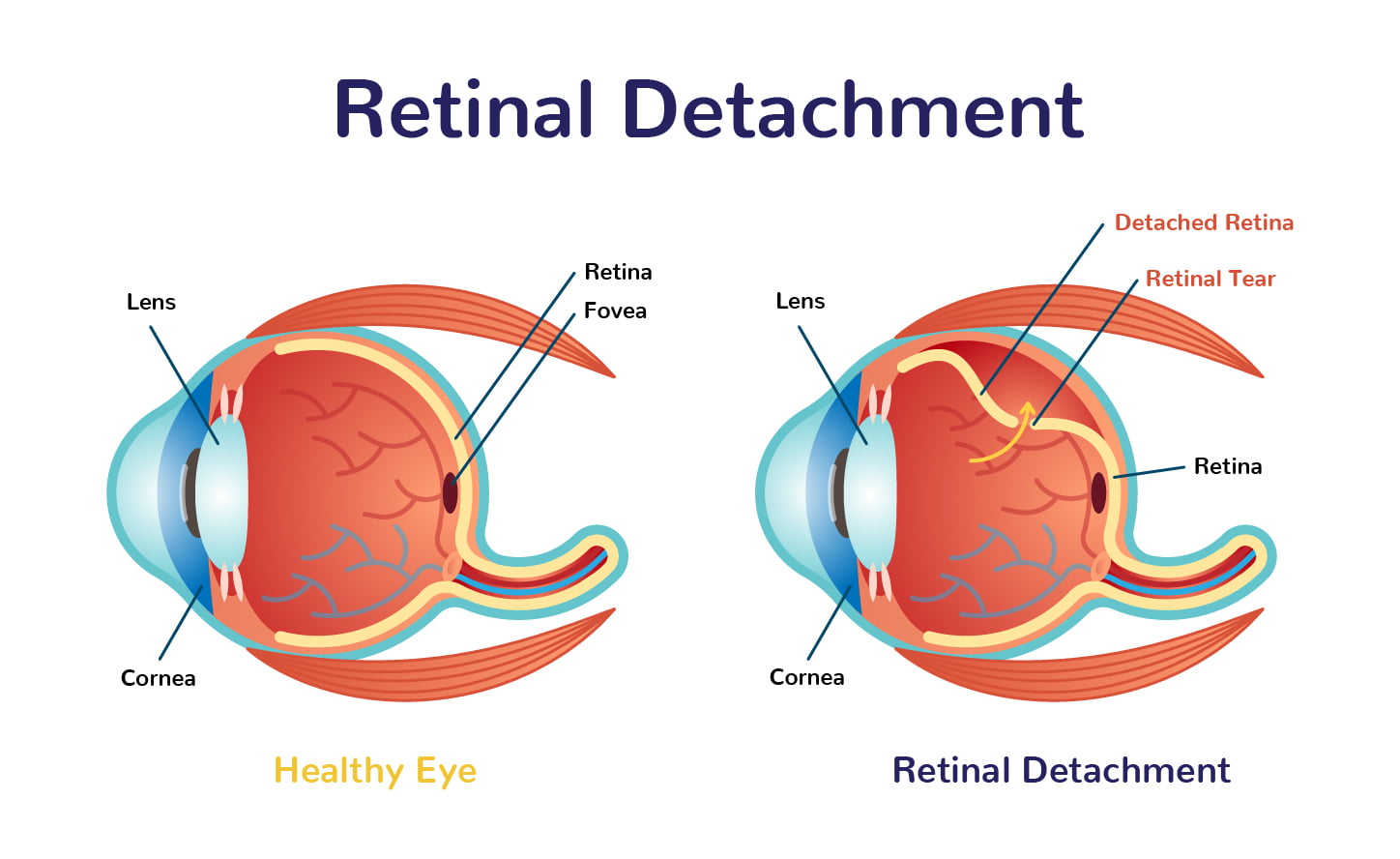 As retinal hemorrhage worsens and the retina becomes more fragile. It can separate from its underlying tissue outside of the eye (subretinal space). This causes “floaters” (seeing spots) that float about inside your field of vision. This also causes flashes of light when you move, blurred vision. This is because you’re seeing two images instead of one clear image. This is a medical emergency needing immediate attention. It is because blindness will soon result if left untreated. It’s unclear why some people develop diabetic retinopathy while others don’t even though they have had diabetes for many years. However, there are risk factors that may play a part in the development of Retinal detachment.
As retinal hemorrhage worsens and the retina becomes more fragile. It can separate from its underlying tissue outside of the eye (subretinal space). This causes “floaters” (seeing spots) that float about inside your field of vision. This also causes flashes of light when you move, blurred vision. This is because you’re seeing two images instead of one clear image. This is a medical emergency needing immediate attention. It is because blindness will soon result if left untreated. It’s unclear why some people develop diabetic retinopathy while others don’t even though they have had diabetes for many years. However, there are risk factors that may play a part in the development of Retinal detachment.
High Blood Pressure
Diabetes-related high blood pressure (hypertension) is a major risk factor in the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. You can track your blood pressure at home with a machine called an automated digital vital signs monitor. This machine you can get from your doctor’s office or buy online. This will help establish whether you have uncontrolled hypertension. A normal systolic reading is less than 120 mm Hg. It is when measured by this type of device; over 140 mmHg indicates hypertension requiring treatment. Other diabetes medications such as insulin injections may also lead to increases in peripheral arterial resistance. It can necessitate proper diagnosis and management of any resulting elevated diastolic readings. This might be seen with different combinations of drugs not working together well.
Diabetic Neuropathy
 The third most common complication of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy. This affects up to 50% of all people with the disease. Diabetic neuropathy may be caused by many factors associated with elevated blood glucose levels. These are including poor circulation that prevents nourishment from reaching nerve cells. Another is malnutrition due to lack of food intake. This is because you feel too sick or are losing weight despite eating normally. There are different types of diabetic neuropathies. These are such as autonomic (affects involuntary muscle movement), sensory (affects your ability to feel vibration and touch), and motor (affects voluntary muscles). Symptoms include numbness in the feet leading to loss of balance when walking. Other symptoms are having difficulty swallowing, urinary incontinence/fecal incontinence, constipation.
The third most common complication of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy. This affects up to 50% of all people with the disease. Diabetic neuropathy may be caused by many factors associated with elevated blood glucose levels. These are including poor circulation that prevents nourishment from reaching nerve cells. Another is malnutrition due to lack of food intake. This is because you feel too sick or are losing weight despite eating normally. There are different types of diabetic neuropathies. These are such as autonomic (affects involuntary muscle movement), sensory (affects your ability to feel vibration and touch), and motor (affects voluntary muscles). Symptoms include numbness in the feet leading to loss of balance when walking. Other symptoms are having difficulty swallowing, urinary incontinence/fecal incontinence, constipation.
Skin Complications
Skin complications are the fourth most common complication of diabetes. The skin damage may happen by both high glucose levels in the blood and poor circulation.
Fungal Infections
This is one of the Diabetes complications. These can be spread in moist areas. These areas are such as between toes, in skin folds, and beneath nail beds. that don’t receive much air circulation. They’re also worsened if you have reduced sensation due to diabetic neuropathy or another type of nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy). Signs include itching, redness, cracking at the edges of your mouth, burning pain. These are when you are walking on your feet without shoes. A foul odor from discharge is seen with the Athlete’s Foot. This usually affects only one foot. The other Jock Itch presents as itchy bumps. This is around the groin area where bacteria infect hair follicles and yeast grows on the skin.
Fungal Infections Of Nails And Hair
Nails can become pitted with pitting edema (swelling) around them. Other effects are discoloration or yellowing, thinning of nail tissue. These can be seen when you press your thumb against it. This causes a white spot to appear beneath. This was once healthy pink nail bed tissue. Hair loss is usually symmetrical in patches at first, then progresses into larger regions. It then involves more scalp area over time. Genital itching may also be experienced due to fungal infection transmitted. This can be via sexual activity by someone who has Athlete’s Foot. This can often infect their groin area before spreading elsewhere. If not treated properly fungi are easily spread between partners even after symptoms have gone away. This is because the fungus remains alive in the environment.
Foot Complications
 Athlete’s Foot which infects between 15% and 18% of all diabetics also causes a red, scaly rash on feet. This can cause painful cracks at the edges of your toes. This can cause it to bleed when not treated properly or become infected by bacteria from socks rubbing across them. It is without enough moisture in between fibers for skin cells to stay soft and moist. Both conditions are worsened if you have reduced sensation due to diabetic neuropathy or another type of nerve damage. If left untreated fungal foot infections may lead to ulcers developing within cracked skin areas. These are also associated with a high risk for cellulitis infection. The infections spread into tissues beneath an area. This is where death is being sloughed off and is unable to receive proper nourishment from fresh new cells being made in a healthy way.
Athlete’s Foot which infects between 15% and 18% of all diabetics also causes a red, scaly rash on feet. This can cause painful cracks at the edges of your toes. This can cause it to bleed when not treated properly or become infected by bacteria from socks rubbing across them. It is without enough moisture in between fibers for skin cells to stay soft and moist. Both conditions are worsened if you have reduced sensation due to diabetic neuropathy or another type of nerve damage. If left untreated fungal foot infections may lead to ulcers developing within cracked skin areas. These are also associated with a high risk for cellulitis infection. The infections spread into tissues beneath an area. This is where death is being sloughed off and is unable to receive proper nourishment from fresh new cells being made in a healthy way.
Kidney Complications
People with type II diabetes are more likely than those without it to develop chronic kidney problems over time. It begins by losing its ability to metabolize phosphorus properly. Leading to the loss of dietary calcium that we get from the food we eat on daily basis becoming deficient enough that bones become brittle. While joints feel stiffer when moving around during normal activities at home or work. Both conditions worsen as kidneys continue failing to filter blood properly.
Ketones
 While high glucose levels in the blood are linked to diabetic coma conditions. Ketone production is also believed to be worsened by extreme fatigue experienced during exercise causing insulin resistance. That results from the lack of energy needed for muscles cells to produce enough ATP (energy) molecules. It is when they contract and release due to muscle movement. Both situations worsen if you have reduced sensation or nerve damage. Because your body can’t properly regulate its response should it detect an imbalance between carbohydrate intake, excretion via urine. And any other factors that affect how glucose mobilizes.
While high glucose levels in the blood are linked to diabetic coma conditions. Ketone production is also believed to be worsened by extreme fatigue experienced during exercise causing insulin resistance. That results from the lack of energy needed for muscles cells to produce enough ATP (energy) molecules. It is when they contract and release due to muscle movement. Both situations worsen if you have reduced sensation or nerve damage. Because your body can’t properly regulate its response should it detect an imbalance between carbohydrate intake, excretion via urine. And any other factors that affect how glucose mobilizes.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
This condition causes frequent urination along with excessive thirst. It often leads people without diabetes who experience these symptoms. Instead of having hyperglycemia resulting in excess water loss through urine. That causes a person to become dehydrated leading to muscle weakness and fatigue, weight loss. As well as nausea or vomiting which results in dehydration. Before the patient gets so serious with ketoacidosis.
Diabetic Macular Edema
Vision problems such as diabetic macular edema typically begin by having your optometrist check retinal blood vessels for signs of damage. It happens when high glucose levels cause oxidative stress. This causes cells to line capillaries within the retina at the back of the eye. The retina swells up with fluid between them. Eventually resulting in blurred vision because they no longer function properly. If left untreated this condition can lead to blindness. But treatment often involves laser surgery along with injections into affected eyes once per month. This is until the swelling goes away allowing central vision to improve and restore.
How To Avoid These Diabetic Complications

Diabetes complications are very serious, some even life-threatening. It is important that you see your doctor on a regular basis. This is so they may monitor your condition and look for signs of these possible diabetes complications. If you have any concerns about the symptoms mentioned above please contact doctors right away. These are some ways you can prevent these diabetic complications :
- You can prevent diabetic retinopathy by controlling your blood sugar levels and not smoking.
- If you want to avoid peripheral neuropathy, make sure to keep a healthy weight with exercise and a proper diet.
- You can also prevent the vision from becoming blurred or fuzzy. This is if you control how much sugar is in your bloodstream.
- You should eat a low carbohydrate diet as well as regular check-ups at your doctor’s office. It will help monitor this condition for signs of it worsening.
- Get plenty of sleep each night and reduce stress whenever possible. So that your body releases less cortisol which would worsen these symptoms.
- Eat lots of vegetables and fruits daily. You can stay away from fatty foods such as fried chicken, cheese, etc. You should drink water instead of soda or other sugary drinks. Try to get plenty of exercise.
Conclusion
Diabetes can lead to a variety of complications that require constant monitoring and care. It’s important for people with diabetes, their families, friends, and caregivers to understand what they are at risk for. So they can prepare for the event these severe complications occur. The more you know about your risks or those of someone close to you who has diabetes, the better equipped you’ll be. This is in a situation if something happens. Having this information will enable them to take action quickly. It is while also being able to provide valuable support. These are during times when it is most needed. So please give some thought as we wrap up today on how knowledge can empower us all.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.


