Contents
Diabetic Eye Disease
Prolonged diabetes can have serious effects on our eyes which can result in blindness for patients belonging to the age group of 20 to 74. Eye problems are a result of consistent high glucose levels that causes damage to the eye nerves following blindness. Excess dependence on cigarettes also leads to long-term damage along with uncontrolled sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol.
High glucose levels tend to change fluid levels and damage blood vessels. As a result of this, the fluid leaks out and causes swelling, scarring, and increases pressure inside of your eye.
Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Problems
Initial symptoms can be hard to detect for diabetic eye problems as the damage is inside and goes unnoticed even when it’s spreading rapidly throughout the insides of your eyes. Hence, you need to stay alert in case you notice any of these signs and symptoms and consult the doctor right away.
- Blurred vision
- Variation in clarity of vision
- Sudden vision loss
- Compromised colour vision
- Noticing floaters
- Light flashes
Types of Diabetic Eye Diseases
Most diabetic eye diseases occur due to major blood vessel damage due to overtime high glucose levels. And because of that, the new blood vessels that grow are even weaker making your eye even more prone to other complications.
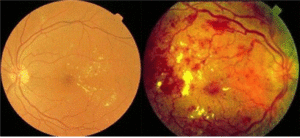
Diabetic Retinopathy
In the case of this diabetic eye disease, the retina is the one that gets damaged. The job of our retina is to sense the light coming from the source and then convert it into signals for the brain to interpret.
The damaged blood cells prevent the retina from functioning normally hence, leading to impaired vision.
- Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy shows symptoms of blood vessels bulging, weakening, and or a leak of fluid in the retina.
- If not treated at the right time, the disease worsens and results in the closing off of blood vessels. This leads to a new stage called Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. With this, the new blood vessels multiply on the surface of the retina causing seriously impaired vision.
Symptoms include:
- Patches or streaks blocking vision
- Reduced color vision
- Impaired night vision
- Sudden loss of vision
- Floating transparent spots and strings
- Spotting dark spots at the central vision
Diabetic Macular Edema
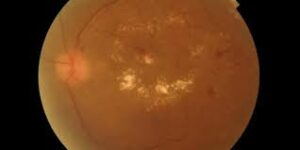
The macula is that part of your retina that performs the function of reading, driving, or sighting faces and objects around you.
In this particular diabetic eye problem, the macula of the eye swells up due to excess fluid and that causes loss of sharp vision in this particular region of the eye.
This destroys the ability of the macula to focus and see fine details. The reason for such complications is the increased levels of blood sugar levels in the body.
Symptoms to look out for:
- Gradual loss of vision
- Distorted vision
- Finding it hard to read or watch
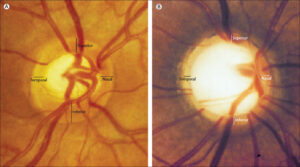
Glaucoma
Being another one of the diabetic eye problems, this disease is caused as a result of abnormally high pressure in your eye region.
Glaucoma is known to severely damage your optic nerves. The Optic nerve transmits information in the form of electrical impulses from the eye to the brain which in turn activates our vision.
Due to the damage Glaucoma often ends up leaving patients with complete blindness. In the majority of cases, vision loss caused due to glaucoma cannot be cured.
Symptoms include:
- Severe headache
- Nausea
- Blurry vision
- Halos around lights
- Eye redness
- Throbbing eye pain
- Dilated pupil
Cataracts
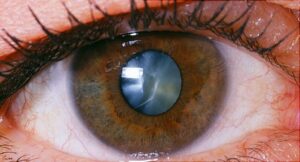
In patients with Diabetes mellitus, cataracts are one of the common forms of visual impairment. Being one of the earliest complications of diabetes mellitus, it is a result of high sugar levels in aqueous humor. Aqueous Humor is a space present between the eyeballs and the lens of the cornea.
Lack of supply of nutrients and oxygens to the lens leads to the formation of cloudiness around the eye lens. This blurry vision is similar to that of looking through a fogged-up window.
Another reason for cataracts is high blood sugar levels which could be due to could be the conversion of glucose to sorbitol whose excess presence in the eye lens can lead to cloudy vision as well.
Symptoms include:
- Dim vision
- Bad night vision
- Increased sensitivity to light and glare
- Frequent eyeglass and prescription changes
- Yellowing of colours
- Increased need for light
Background Retinopathy
The development of Microaneurysms on the retina of the eyes is the main cause of background retinopathy. Making it number 5th on the list of diabetic eye problems.
These Microaneurysms happen when there is swelling because of increased blood sugar levels in the capillaries. Background retinopathy is an early sign that your diabetes is starting to affect your eyes by showing damages in the small blood vessels.
Spotting the signs as early as possible will avoid further sight problems. Since there are no such noticeable physical symptoms, it is advised to get a retinal screen check done to assess the damage.
Managing Diabetic Eye Problems
The best ways to manage diabetic eye problems are by keeping a check on your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol. If you are a chain smoker try and reduce your smoking and eventually quit it as it worsens things for you. It is also recommended for diabetic patients to get their dilated eye exam once every year to be on a safer side.
- Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine.
- Make good dieting and active work part of your day-by-day schedule.
- Take oral diabetes prescriptions or insulin as prescribed.
- Screen your glucose level
- Get your A1C tests done to keep a check on your glucose levels.
- Monitor your Blood Pressure and cholesterol
- Focus on vision changes
- Quit smoking
Diagnosis For Diabetic Eye Diseases
Usually, certain tests are conducted to get a fair view of the level of damage that has been caused. The retina should be assessed for proof of macular oedema. Sings of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy include speck/smudge Haemorrhages or Microaneurysms, venous beading, and Intra-retinal Microvascular Anomaly (IRMA).
The optic circle should be assessed for optic nerve head Neovascularization. And the retina assessment should be done to recognize Neovascularization somewhere else. The doctors can also look for pre-retinal Haemorrhages, which are proof of illness. At long last, the glassy should be analyzed for any presence of glassy discharge.
Dilated Retinal Examination
Pupil dilation is a procedure performed by doctors to make a better assessment of the retina and the optic nerve. The examination plays an important role in preventing and treating the eye to protect it from further complications. The test is conducted by an eye doctor by using eye drops to increase the size of the pupils which gives a better view of a part of the optic nerve.
The undilated exam sometimes takes place before dilation to make sure that the visual pathways of the eyes are operating as they should.
Fundus Photography
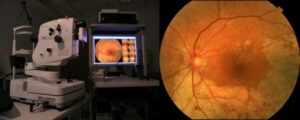
Retinal photos are a useful tool in examining and finding out the severity of retinopathy. And the occurrence of Neovascularization of the disc or in any place elsewhere. The photographs report the reaction to treatment and analyzing the need for extra treatment.
Fluorescein Angiography
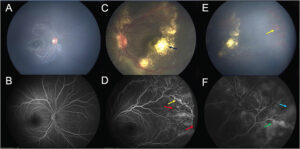
It is not one of the recommended routine tests for diabetic patients. However, it has proved to be helpful in detecting macular oedema or ischemia both of the diabetic eye problems that lead to unexplained vision loss.
Fluorescein Angiography has also proved itself to be useful in differentiating Neovascularization from IRMA. And even distinguish it from healthy retinal vessels, as well as for examining the peripheral retina for capillary nonperfusion.
OCT/ OCTA
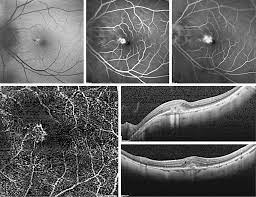
OCT offers high-resolution images of your vitreous and retina which is used to measure retinal thickness. It even helps in the diagnosis of macular oedema.
OCT is preferred over the clinical examination to get a better evaluation of macular oedema. Without any need for injecting dye, it provides a clearer picture retina. It has been proven to be a great test method for the diagnosis of ischemia in diabetic patients.
Medication For Diabetic Eye Diseases
Your doctor may treat your eyes with anti-VEGF medication, for example, Aflibercept, Bevacizumab, or Ranibizumab. These meds block the development of strange veins in the eye. Anti- VEGF medications can also stop liquid breaks, which can help with treating diabetic macular oedema.
The specialist will give you an anti – VEGF medication during your visits. You’ll be given few medicines during the initial months, then, fewer medicines after you finish the first round of treatment. Your doctor will use medication to numb your eyes so you don’t feel any pain. The needle is about the thickness of human hair.
Harsh VEGF medicines can stop further loss of vision and may even fix vision in some people.
Surgery For Diabetic Eye Diseases
Apart from managing your blood sugar levels, the above-mentioned diabetic eye problems might require surgical help. Especially in cases where things have complicated and can no longer be managed by self-management.
Laser Treatment
Photocoagulation is conducted to create tiny burns in the eye with a beam of light. This procedure is done for the treatment of bruised blood vessels and to fix extra fluid, called oedema. The doctor numbs the eyes with the help of medication before the starting of the procedure. Sometimes this can take a couple of tries to work at full efficiency. Laser treatment might control severe complications caused due to diabetic eye problems but sometimes it fails to bring back lost vision.
Focal laser treatment for diabetic eye problems works at a smaller scale by just treating a small portion of the retina for diabetic macular oedema. On the other hand, scatter laser treatment also called pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), covers a bigger space of the retina. This treats the development of unusual veins, called Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is another recommended surgery to cure diabetic eye problems. The procedure includes the removal of clear vitreous gel that fills up the centre of the eye causing bad vision. This procedure is used to treat complications like severe bleeding or scar tissue both of which are a result of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy.
The procedure of vitrectomy requires pumping of clear solution in the eye gently without causing any damage to maintain eye pressure. While the surgery takes place and the removed vitreous can be replaced without any difficulties.
Cataract Lens Surgery
In a medical procedure community or clinic visit, your doctor can remove the shady focal point in your eye. This is where the cataract has developed. They can then replace it with another lens. Medical procedures for the most part have a better vision a short time later. After your eye recovers, you may require another solution for your glasses. Your vision following the surgery may depend on any harm from diabetic retinopathy or macular oedema.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.