Contents
- 1 Diabetes Insipidus
- 2 Diabetes Insipidus vs Diabetes Mellitus
- 3 Symptoms of Diabetes Insipidus
- 4 Causes of Diabetes Insipidus
- 5 Types of Diabetes Insipidus
- 6 Diabetes Insipidus Risk factors
- 7 Diabetes Insipidus Complications
- 8 Diabetes Insipidus Preventions
- 9 Diagnosis of Diabetes Insipidus
- 10 Treatment of Diabetes Insipidus
- 11 A Word From MantraCare
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes insipidus is a condition in which the body fluids get imbalanced. This condition is characterized by large amounts of frequent urination and excessive thirst. A diabetes insipidus patient usually produces about 20 liters of urine in a day. It’s logical to feel thirsty after losing so much fluid.
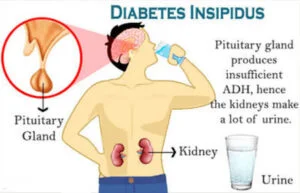
It is a rare and serious condition that can cause health problems like dehydration, depression, seizures, etc. when a person urinates frequently it tires him/her out, especially at the night. This disturbs sleep and causes stress, due to which the person may face depression. In some severe cases, diabetes insipidus can cause seizures and dehydration because of excessive fluid loss.
Diabetes Insipidus vs Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus may sound similar but they both are quite different from each other. In diabetes mellitus, the blood sugar is raised more than normal. That often causes frequent urination to get rid of the sugar. Whereas in diabetes insipidus the causes are different.
So, diabetes insipidus is not related to diabetes mellitus. The only thing common in these two is frequent urination and excessive thirst. However, the underlying reasons for these two symptoms are different.
Here are some key points that will help you understand diabetes insipidus.
- Diabetes insipidus is a condition where the body fails to control the water balance, which leads to excessive urination.
- A large amount of dilute urine is excreted causing increased thirst and increased water intake.
- This condition can cause serious dehydration, If not managed by high water intake. The patient needs to communicate his/her thirst for help in severe cases, or it may result in a seizure.
Symptoms of Diabetes Insipidus

The main symptom of all cases of diabetes is usually wanting to pass high volumes of diluted urine.
The second commonest symptom is polydipsia or excessive thirst. In this case, the loss of water results from urine. Thirst prompts the person with diabetes to drink large volumes of water. And the need to urinate can disturb sleep. The quantity of urine passed every day is often anywhere between 3 liters and 20 liters, and up to 30 liters in cases of central diabetes insipidus.
Another secondary symptom is dehydration. It happens because of the loss of water, especially in children who might not be mature enough to communicate their thirst. Children may become feverish, experience vomiting and diarrhea, and may even show delayed growth.
Other people who have some disorder and cannot help themselves to water, as people with dementia, also are in danger of dehydration.
Extreme dehydration can cause hypernatremia, which is a condition during which the sodium concentration of the serum within the blood becomes very because of low tide retention. The cells of the body also experience the loss of water. Hypernatremia can cause neurological symptoms. For example, overactivity within the brain & nerve muscles, confusion, dizziness, seizures, or maybe coma.
Without treatment, central diabetes insipidus can cause permanent kidney damage. In nephrogenic DI, serious complications are rare, if the water intake is sufficient.
Causes of Diabetes Insipidus
The function of the kidney is to filter all the blood again and again to remove all the waste products. Majorly the water is reabsorbed from the fluid portion of blood. However, waste products with a small amount of fluid are excreted through urine.
When the water level decreases in your body, the pituitary gland releases ADH to stop the production of urine for saving the water in the body. The fluid that is retained by the kidneys will need to go back into the bloodstream.
ADH is produced from the hypothalamus, an area in the brain that controls appetite. ADH or vasopressin is responsible for retaining fluid into the kidney. But in the case of diabetes insipidus, vasopressin can not regulate water in your body by controlling the urine production from the kidney. This causes an excessive amount of water to pass through the urine.
The common causes of diabetes insipidus could be:
- Genetic problems
- Head injury
- Autoimmune diseases
Types of Diabetes Insipidus
The types of diabetes are broadly described in 4 categories. Such as-
1. Central Insipidus
Central diabetes insipidus happens a person’s hypothalamus or pituitary gland gets damaged. This disrupts the normal production, storage, and release of a hormone called- vasopressin. The lack of vasopressin causes the kidney to release excessive fluids from the body. This increases urination. Damaged hypothalamus or pituitary gland can be the result of the following-
- Surgery
- Inflammation
- Injury (head)
- Tumor
Sometimes the cause of central insipidus is unknown. And sometimes it could be hereditary, the gene that produces vasopressin is defective.
2. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Nephrogenic diabetes when kidneys do not respond to vasopressin as they normally do. Kidneys keep removing too much fluid from the bloodstream of the patient. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus can be caused due to genetic changes such as mutation or inherited gene changes. Kidney stops responding to vasopressin in this case.
Some other possible causes of this type of diabetes insipidus could be:
- Severe kidney disease
- Certain medicines like lithium
- Low level of potassium in the bloodstream
- High level of calcium in the bloodstream
- Blockage of urinary tract
3. Dipsogenic Insipidus/ Primary Polydipsia
Dipsogenic diabetes is also called primary polydipsia. This condition is caused by a defect in the thirst mechanism that is regulated by the hypothalamus. In this condition, the water that patient takes suppresses the vasopressin release.
Lack of vasopressin causes the kidney to release fluids in a large amount. the reasons behind this type of insipidus are similar to others like head injury, tumor, inflammation. The other causes of dipsogenic insipidus may include certain medications or mental health problems.
4. Gestational Diabetes Insipidus
As the name depicts (gestation), this diabetes happens during pregnancy. In this condition placenta (a temporary organ that joins the baby to the mother) makes an enzyme that destroys the mother’s ADH. Or it may be caused by the high levels of hormone-like chemicals that develop less sensitivity in the kidneys towards ADH also called vasopressin. This condition disappears after pregnancy.
Diabetes Insipidus Risk factors
It is caused due to a lack of vasopressin or when it can not be used properly. These conditions can occur due to various reasons. The main risk factor is genetic inheritance. Specific changes in the genes inherited from your parents can cause diabetes insipidus. Although it only happens in 1-2% of cases.
An injury or surgery in the head near the pituitary gland can also be a factor for causing diabetes insipidus. Therefore, a person should always be careful with their head.
Diabetes Insipidus Complications
The complications of diabetes occur when it is not controlled or did not get proper treatment.
Dehydration
If you have this condition, your body will not be able to retain water, even if you drink water constantly. This can cause some serious complications like dehydration. Dehydration, which is the lack of water in the body may not sound severe, but it is. It can lead to danger if not get communicated or treated immediately. If you have diabetes insipidus, you are likely to experience dehydration. Know the symptoms of dehydration to treat it.
- Dry mouth or lips

- Headache
- Dizziness
- Confusion
Dehydration can be treated by drinking water again. You can also rebalance the water level in your body by intravenous fluid replacement in a hospital. This treatment is given when the condition is critical.
Electrolyte Imbalance
An untreated diabetes insipidus is more likely to cause electrolyte imbalance. Plus, electrolyte imbalance and lack of water go hand in hand. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, chlorine, magnesium, bicarbonates have a tiny electric charge and are important for body function. When water that holds these electrolytes is passed out through urine, the concentration of electrolytes goes up.
Electrolyte imbalance can disrupt body function, which can lead to:
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Pain in the muscles
- irritation
This is also treated with water intake.
Lack of sleep

Diabetes insipidus can also cause a lack of sleep. This is logical because when a patient has to go urinate frequently, their sleep gets disturbed. They have to wake up in the night several times to pee. That can lead to a restful night and a stressful day.
Diabetes Insipidus Preventions
This condition is very difficult to prevent because it is caused by genetic or other non-preventable problems. However, the good news is that its symptoms can be controlled effectively. This condition is treated for a long time, it can be a lifelong disease.
Diagnosis of Diabetes Insipidus

This disease may be diagnosed in a physical exam. You or your doctor may notice an extra-large bladder or you may be suffering from dehydration. Then the doctor will take some tests like:
- Urine Test- In this test, a sample of your urine will send to the lab to check if it’s diluted or concentrated. Glucose in your urine will diagnose if you have, diabetes mellitus or diabetes insipidus.
- Blood Test- A blood test is also performed to determine whether you have diabetes insipidus or diabetes mellitus. It may help your doctor understand the condition better.
- Fluid Deprivation Test- This test is used to measure your body weight ratio, urine concentration, and the amount of sodium in the blood. You are not supposed to eat anything for a while before this test is performed.
- MRI- This is performed when a detailed picture of your hypothalamus or pituitary gland is needed to check any issue.
Treatment of Diabetes Insipidus
It can be managed with few efforts and care. The patient has to take enough water or fluids to make up for the constant water loss. This disease could be a problem for those who cannot replace the fluids.
The best treatment for any disease is to work on its root causes. If the underlying cause is treatable like diabetes mellitus or the use of certain medications or drugs, then treating these can help resolve the condition. Other treatments depend on which type of diabetes insipidus you have.
Vasopressin is replaced by drugs like desmopressin to control excessive urination, in central diabetes insipidus. This drug is available in various ways like nasal spray, injection, or oral tablet.
If we talk about nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, treatment could be hard. Medicines like Indocin, Microzide can ease the symptoms of nephrogenic diabetes. If the condition is caused by drugs, then cutting them back may help. The treatment of kidneys may be required in this condition.
For pregnancy-related diabetes insipidus, the treatment is similar to the central one, you can take desmopressin while you are pregnant. The condition disappears after baby birth.
There’s no such treatment available for dipsogenic diabetes insipidus, but some things can reduce the symptoms. Like boosting your saliva flow by eating sour candies or ice chips to moisten your mouth. A small dose of desmopressin before bedtime can also help in stopping frequent urination at night.
A Word From MantraCare
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse your Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, dieticians, and health coaches.



