Contents
The Role of Carb Counting in Diabetic Diet Plans

Carb counting is important for people with diabetes. Carb counting is a way of tracking the number of carbohydrates people with diabetes consume. In order to maintain their blood sugar levels. The two main types of carbohydrates are sugars and starches. To count carbs correctly, you must know which foods contain these types of carbs, what the grams are per serving size. And how many servings you can eat per day or meal.
Carb counting is also important for people with diabetes. Because it helps them control their blood sugar levels by eating the right amount of carbs per meal or day. Carb counting requires knowledge about which foods contain carbs as well as information on how many grams there are in serving size. And how many servings you should be eating each day.
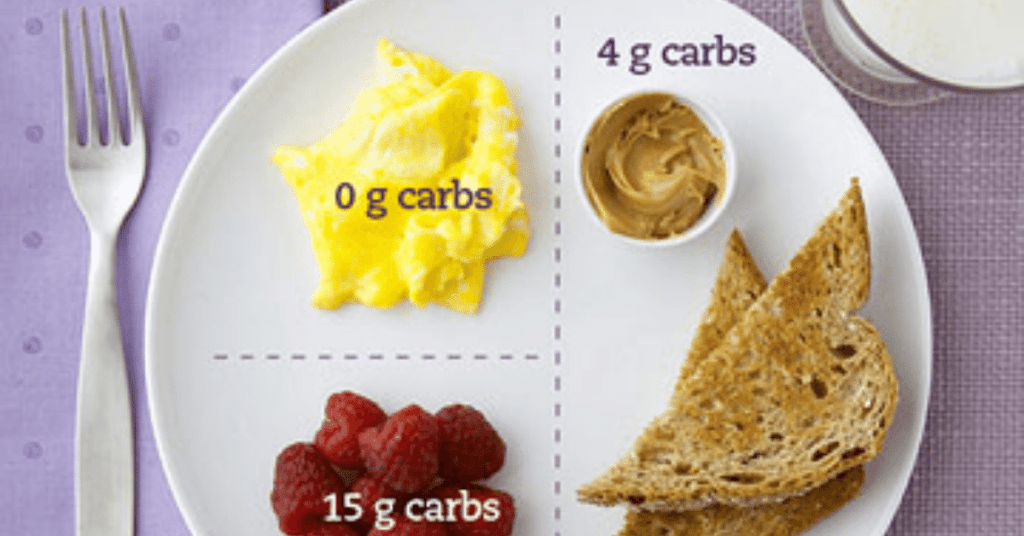
Knowing this information is important because foods that are high in sugars, starches, or are full of fat will affect the amount of insulin needed to maintain blood sugar levels. An example of this would be if you eat a tablespoon of jelly which contains 15 grams of carbs and no other food items. You may need to take more insulin depending on how many servings you are allowed to eat. Because it contains sugar that can affect your blood sugar levels.
To count carbs correctly, you must know which foods contain these types of carbs. What the grams are per serving size, and how many servings you can eat per day or meal. Carb counting is important for people with diabetes. Because it helps them control their blood sugar levels by eating the right amount of carbs per meal or day.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that can lead to insulin deficiency. This type of diabetes usually requires the use of insulin injections. Because the pancreas has either failed to produce enough insulin or has completely lost the ability to produce any at all. The most common form of type 1 diabetes is juvenile-onset. It affects children and teenagers by destroying their insulin-producing cells- beta cells.
Type 1 diabetes is less common than Type 2, but it requires insulin injections to break down sugars in the body. Therefore, more carbohydrates are required for good blood sugar control. A dietician will help you determine how many carbs you should eat per meal and snack. Your doctor may also provide this information based on your lab results. Most people with Type 1 diabetes need to eat between 45-60 grams of carbohydrates at each meal. Snacks, if necessary, should contain about 15-30 grams of carbs.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is also an autoimmune disease but does not necessarily require insulin injections. The pancreas may be able to produce some level of insulin, but not enough to control blood sugar levels effectively. With type 2 diabetes, there are many other different contributing factors. That needs to be taken into consideration before determining if you will require insulin injections.
Carb counting is important for people with diabetes. Because it helps them control their blood sugar levels by eating the right amount of carbs per meal or day. It is important for people with diabetes because it helps them control their blood sugar levels by eating the right amount of carbs per meal or day.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form and occurs when your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or use it effectively. If you have this type, you still produce insulin but your body has become resistant to it. You will need to monitor your diet and eat a moderate amount of carbohydrates each day. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you count the grams of carbohydrates if you are trying to lose weight.
Why Counting Carbs Is Beneficial?
 You can find out by looking at a food label since each serving contains the total grams of carbohydrates per serving. Knowing how many carb grams you should have at each meal and snack, allows you to track your food intake throughout the day so that your blood glucose levels are in a normal range.
You can find out by looking at a food label since each serving contains the total grams of carbohydrates per serving. Knowing how many carb grams you should have at each meal and snack, allows you to track your food intake throughout the day so that your blood glucose levels are in a normal range.
Counting carbohydrates may become more important as new dietary guidelines are introduced. Health care experts recommend counting carbohydrates if one is trying to lose weight and is not overweight. People with type 2 diabetes often control their blood glucose by counting carbohydrates while those with type 1 may be advised to do so if they are unable to produce any insulin.
So whether you’re diabetic or trying to lose weight, keeping track of carbohydrate intake can help you maintain good health. Carb counting requires knowledge about which foods contain carbs. And information on how many grams there are in serving size and how many servings you should be eating each day.
How Many Carbs Should I Eat?
It is important to know how many carbs you should eat with diabetes because it can affect your blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates are assigned a numerical value that is based on how many grams of carbohydrates are present in a food serving.
How many carbs you should have at each meal and snack depends on which type of diabetes you have, the medications you take, as well as your age and weight. In general, whether you’re diabetic or trying to lose weight, keeping track of carbohydrate intake can help you maintain good health.
Carbohydrates should not be counted if you are following a weight-loss diet unless it is advised by your doctor. Carbohydrate counting can be helpful for those with diabetes and can make losing weight easier. Try keeping track of the number of carbohydrates you eat to determine whether or not you will benefit from carbohydrate counting. If you do decide to count carbs, learn how to do it efficiently with this helpful nutrition guide.
Types Of Carbs

Carb counting is a popular dietary strategy that has been advocated as a way to control blood sugar, promote weight loss, and stabilize mood in those with diabetes. In general, the principle is to keep your blood glucose as close as possible to normal levels by limiting the consumption of high-GI foods and substituting low-GI foods.
Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrate and is the primary source of energy for many cells. Carbohydrates are divided into two types: simple (monosaccharides and disaccharides) and complex (polysaccharides). Glucose, galactose, and fructose are examples of simple carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates are more common and are found in starches, grains, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and fruits. Complex carbohydrates consist of hundreds or thousands of glucose molecules linked together into a polysaccharide chain. Thus complex carbs have a higher GI than simple carbs. Because they must be broken down by the digestive system before being absorbed as glucose.
How Do You Count Carbs?
The carbohydrate content of a food is provided on a food label. A carbohydrate-counting diet plan may follow one of the low carb, high carb, or medium-carb plans. The method of measuring carbs changed from grams to grams of total carbohydrates on the new food labels that were introduced in January 2005.
The following are some examples of what counts as a carbohydrate:
- Sugar
- Fructose
- Lactose
- Sucrose
- Honey
- Maltose
- Syrup
- Starch
Although many dieters are counting carbs to lose weight, diabetes patients should also take into consideration the number of carbs that they eat each day. As a reminder, carbohydrates are not just in foods that taste sweet. They are found in almost all foods because they’re the main source of fuel for the body. In addition, carbohydrates contain dietary fiber and other nutrients that the body needs. Carbohydrates are assigned a numerical value that is based on how many grams of carbohydrates are present in a food serving.
The healthcare experts recommend that people with diabetes should keep their daily intake of carbohydrates between 45 to 60 grams per meal. This is about the same as three to five slices of bread. The ADA also recommends that foods for diabetics have about 15-20 grams of carbohydrates per snack. And it’s best to evenly distribute them throughout the day.
Serving Size
Serving size can affect the glycemic index of a food. The glycemic index provides a measure of how much a serving of a particular food will contribute to your blood sugar over two hours, with 100 being pure glucose and 70 being an equivalent amount of complex carbohydrates.
Grams Of Total Carbohydrates
The GI of a food is a measure of how much a serving of a particular food will contribute to your blood sugar over two hours, with 100 being pure glucose and 70 being an equivalent amount of complex carbohydrates. The total grams of carbohydrates in food are found by multiplying the number of calories per serving times the grams per serving and dividing by 100 or one hundred. For example, if you have three servings at 20 carbs each, then your total grams would be 60.
The following chart provides a list of some common foods and their GI, total grams of carbohydrates per serving, and ranking out of 100. Carbohydrates play a beneficial role in the human diet as they are the main source of fuel for the body. When consumed, they contribute to feelings of fullness, metabolic health, stabilization of moods, and stabilized blood sugar. Carb counting is a good way to help manage your carbohydrate intake and blood sugar levels.
Low Carbohydrate Food

Foods can be divided into four groups: low-carbohydrate foods (less than 20 grams per serving); moderate-carbohydrate foods (20 to 50 grams per serving); high-carbohydrate foods (50 to 100 grams per serving); and very high-carbohydrate foods (more than 100 grams per serving). Carbohydrates play a beneficial role in the human diet as they are the main source of fuel for the body. When consumed, they contribute to feelings of fullness, metabolic health, stabilization of moods, and stabilized blood sugar. Carb counting is a good way to help manage your carbohydrate intake and blood sugar levels.
It’s important to consider the role of carb counting in diabetes. Carbohydrates are found in many foods, and they provide energy for your body. But if you have Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, it can be tricky figuring out how much carbohydrate is safe to eat at each meal. Especially because some carbs cause blood sugar levels to spike quickly while others don’t. So they can help avoid putting them at risk of high blood sugar.
Carbohydrates come from many sources, such as bread, cereal, and dairy products. Eating too many of these foods can raise blood sugar levels quickly. Carbohydrate counting is a skill that diabetics must master in order to make wise choices about what they eat. And how many carbohydrates they can safely eat at each meal or snack.
Many carbohydrate-rich foods are good for diabetics, including vegetables and fruits. However, grains like bread, cereals, and pasta can be especially problematic for diabetics (even whole grain versions). Because the extra fiber they contain slows down their effect on blood sugar levels. Therefore, diabetics should eat only low-carb snacks.
Conclusion
Counting carbs, especially if you have diabetes can be beneficial in planning diet and managing blood sugar levels. Carbohydrate counting can be confusing so consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian for assistance.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes consultation program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.