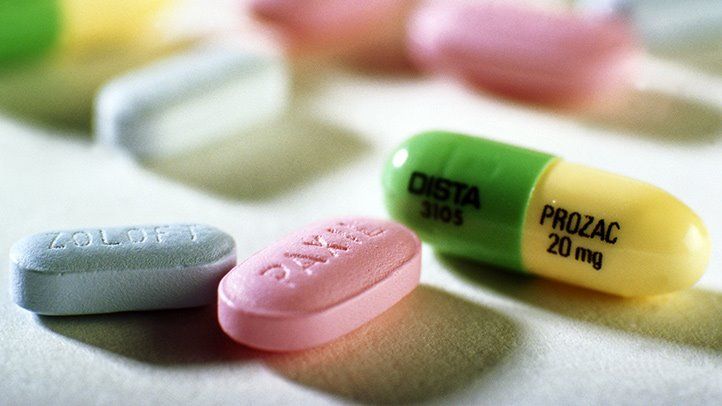
Depression is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people around the world. While therapy and lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms, medication remains an essential tool in many cases. In this blog post, we’ll explore the different types of drug therapy for depression, their benefits and risks, and how to determine whether they’re right for you. If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, keep reading to learn more about this crucial aspect of treatment!
Contents
What is Depression?
There are many different types of depression, and it is important to understand the specific type that a person is experiencing to most effectively treat it. Major depressive disorder, or MDD, is the most common type of depression.
People with MDD experience persistent sadness or emptiness, loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed, insomnia or excessive sleeping, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty concentrating or making decisions, and thoughts of death or suicide. While these symptoms can be debilitating, they are also treatable with medication and psychotherapy.
Drug Therapy For Depression
Depression is a serious medical condition that can negatively affect how you feel, think, and handle daily activities. If you are considering drug therapy for your depression, it is important to work with a mental health professional to determine if this treatment option is right for you.
Drug therapy is also known as antidepressant medication and is designed to correct chemical imbalances in the brain. Sometimes these drugs can take several weeks to start working, so it’s important to be patient and consistent with your treatment plan.
Types of Drugs Used In Drug Therapy For Depression
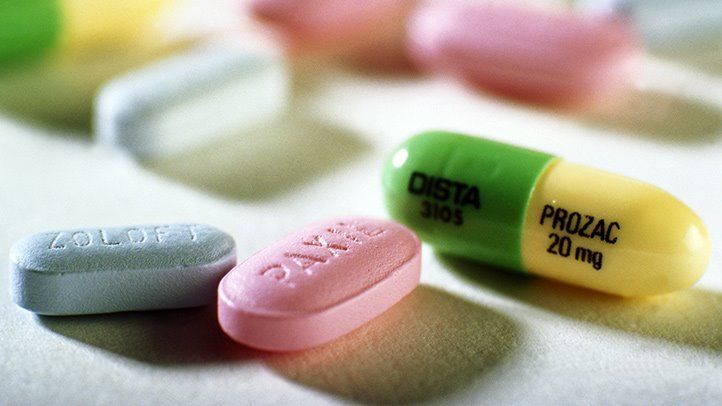
Many different types of drug therapy can be used to treat depression. These types are:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI)
One of the most common types of drug therapy for depression is the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). SSRIs work by blocking the absorption of serotonin in the brain, which can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Examples of SSRIs include Prozac, Zoloft, Lexapro, and Celexa.
These medications are generally considered safe and effective, but they do come with some side effects such as nausea, headaches, insomnia, and sexual dysfunction. It is important to talk to your doctor about any potential side effects before starting a medication.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are another type of drug therapy for depression. They work by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin in the brain, which can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Examples of TCAs include Elavil and Pamelor.
TCAs tend to be more potent than SSRIs so they may be used if you have failed to respond to other medications. However, they do come with more potential side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and weight gain. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting a medication.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are another type of drug therapy for depression. They work by blocking the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which helps regulate neurotransmitters in the brain and can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Examples of MAOIs include Nardil and Marplan.
The working of MAOIs is quite different from other anti-depressants, so they may be more effective for those who do not respond to other treatments. However, MAOIs can also cause potentially dangerous side effects when taken with certain foods and/or medications.
Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRI)
Another type of drug used to treat depression is a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters (chemicals in the brain) responsible for regulating mood. SNRIs are usually recommended when other antidepressant medications are not effective or well tolerated. Examples of SNRIs include Duloxetine and Venlafaxine. The most common side effects of SNRIs are nausea, headache, and constipation.
People may prefer this type of treatment if their depression is accompanied by symptoms such as pain, fatigue, or anxiety. SNRIs can also help reduce anger and irritability, which often accompany depression.
Atypical Antidepressants
Another type of drug used to treat depression is atypical antidepressants. These drugs work differently than the traditional SSRI medications and are sometimes prescribed as a second-line treatment for those who do not respond adequately to an SSRI. Atypical antidepressants can include tetracyclic, tricyclic, and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). These medications work by blocking the reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as norepinephrine and serotonin.
How Does Drug Therapy Work for Depression?

The working of drug therapy can be a bit confusing, but it is important to understand how it works to make an informed treatment decision. Drug therapy for depression involves taking medications that are specifically designed to help with symptoms of the condition. These medications are typically referred to as “antidepressants” and there are several different types available.
Many of these medications work to alter the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These chemicals are known to play an important role in mood regulation. When these chemicals are at healthy levels, they can help improve a person’s mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
Drug therapy is typically used in combination with other forms of treatment for depression. This could include cognitive behavioral therapy, lifestyle changes, and even talk therapy. The goal is to create a comprehensive approach to managing depression so that it can be managed long-term.
The dosage of medications and the specific types of medications used can vary significantly from person to person. It is important to talk with your doctor about how these medications will work for you and what possible side effects may arise.
Pros and Cons of Drug Therapy for Depression
Many different types of drug therapy can be used to treat depression, each with its pros and cons.
PROS
- Drug therapy can be effective in reducing symptoms of depression quickly and safely.
- It is often used in combination with other therapies, such as psychotherapy or lifestyle changes, to provide a comprehensive approach to treating depression.
- It can help people who have not responded to other treatments, allowing them to regain control of their lives.
CONS
- Drug therapy can have unpleasant side effects, including nausea, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and drowsiness.
- It is also important to be aware that medications for depression may take several weeks or even months before they start to take effect.
- In addition, drug therapy can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance.
- Finally, there is a risk of dependency or addiction to certain drugs, which is why it is important to follow all doctor’s orders when taking medication for depression.
Precautions To Keep In Mind While Taking Drug Therapy for Depression

There are some of the precautions to keep in mind while taking drug therapy for depression:
1. Do not stop taking medications without consulting your doctor first. Quitting medication suddenly can have serious side effects and increase the risk of relapsing into depression symptoms.
2. Tell your doctor immediately if you experience any troubling side effects from medication, such as extreme fatigue or suicidal thoughts.
3. Monitor your progress regularly to ensure that the medication is adequately treating your depression and not causing any further complications or side effects.
4. Ask your doctor about potential drug interactions before taking any other medications, including over-the-counter pills or supplements.
5. Do not drink alcohol while taking antidepressant medicines as it can increase the risk of side effects.
6. Avoid operating heavy machinery or driving while taking antidepressant medications, as they may cause drowsiness and other impairments to your ability to drive safely.
7. Speak openly with your doctor regarding any feelings of hopelessness or thoughts of suicide, as these may be signs that the medication is not adequately treating depression symptoms.
8. Take all medications as prescribed and do not increase or decrease dosages without consulting your doctor first.
Conclusion
Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders, and drug therapy is an important part of its treatment. Although it can be difficult to find a medication that works well for each individual, there are many options available that may provide relief from symptoms. It’s important to work with a doctor or psychiatrist to determine which medications will provide the best results and minimize the risk of side effects. With careful management, drug therapy can help many people living with depression to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
For more information, please contact MantraCare. Depression is a mental illness characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in daily activities. If you have any queries regarding Online Depression Counseling experienced therapists at MantraCare can help: Book a trial Depression Therapy session