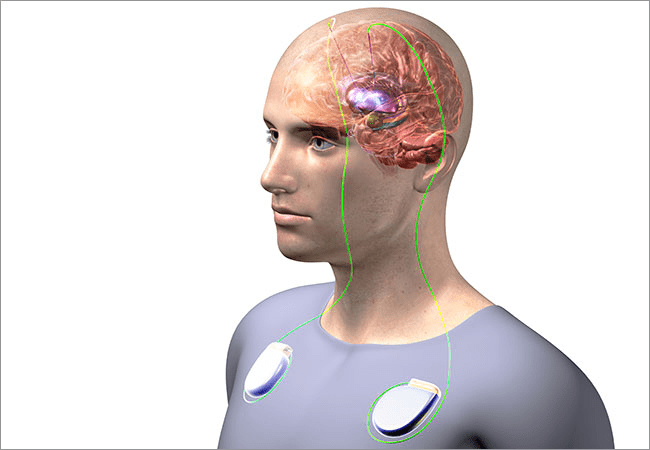
When it comes to OCD brain surgery, there are a variety of options available for evaluation. A person with OCD should carefully consider all surgical options before making a decision. While brain surgeries can be effective, they should be the last resort. Moreover, there are many excellent alternative treatment options available that one must try first. In this blog post, we will discuss the various surgical and non-surgical treatment options available for OCD.
Contents
Explaining Brain Surgery
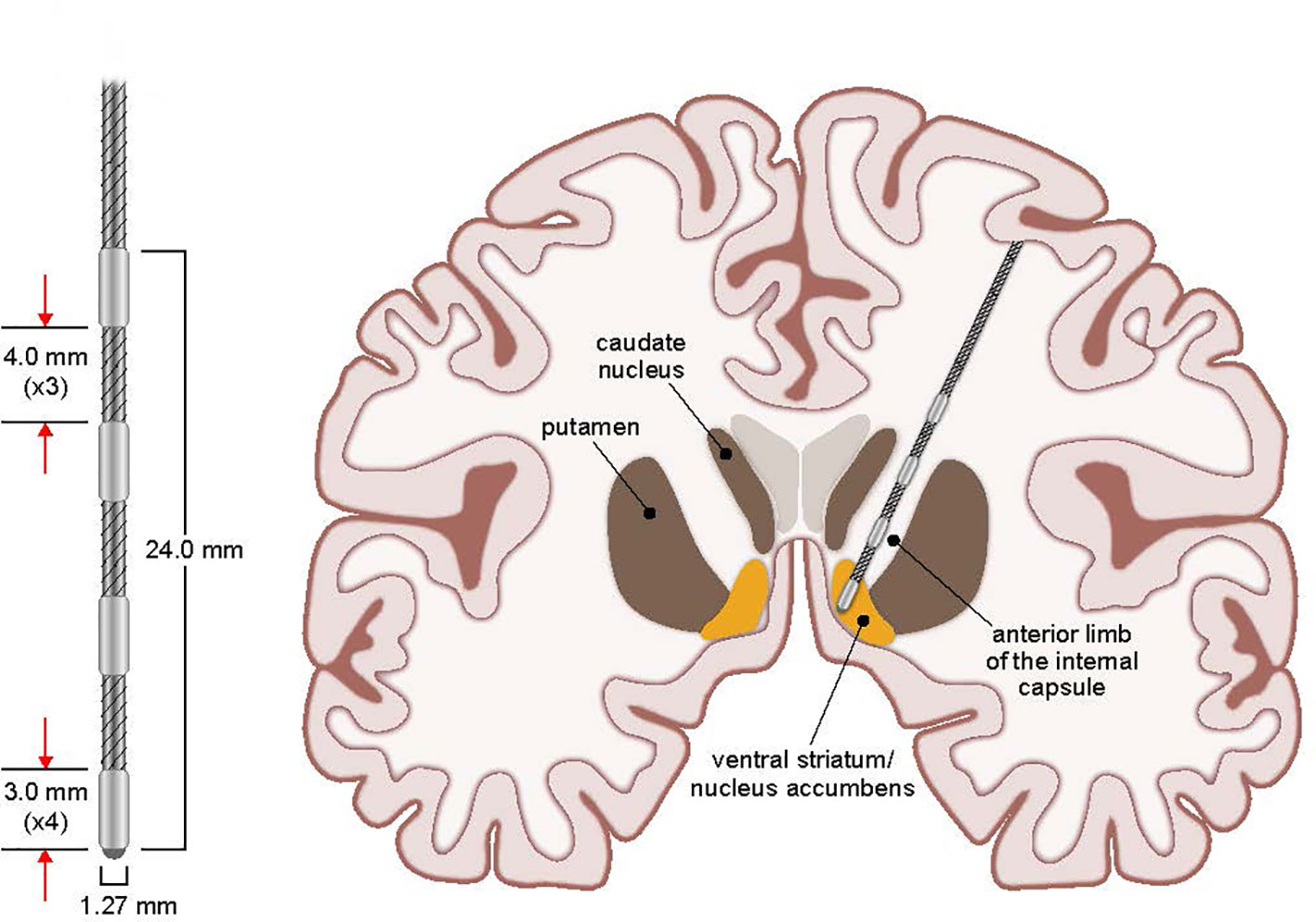
There are two main types of brain surgery: ablative and non-ablative.
- Ablative brain surgery involves removing part of the brain. According to research and studies, ablative brain surgery is usually more effective than non-ablative brain surgery. However, it is also riskier. The risks associated with ablative brain surgery include bleeding, infection, and stroke.
- Non-ablative brain surgery involves destroying or altering the function of the affected area of the brain. According to research and studies, non-ablative brain surgery is usually safer than ablative brain surgery. However, it is less effective. The risks associated with non-ablative brain surgery include seizures and paralysis.
Stages in the Development of Brain Surgery
- The first stage of development for brain surgery was in the 1950s. This is when doctors began to experiment with ablative techniques, such as cingulotomy and anterior capsulotomy.
- In the 1970s, doctors began to experiment with non-ablative techniques, such as deep brain stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation.
- Today, brain surgery for OCD is still considered experimental and is only done at a few specialized centers in the United States.
Listing Brain Surgery Options For OCD
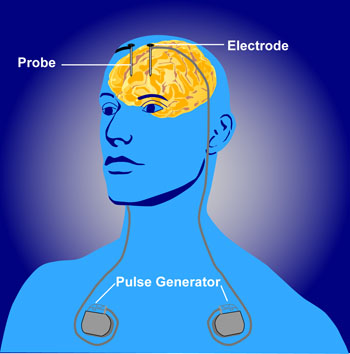
Noteworthily, both types of brain surgery i.e ablative and non-ablative brain surgery can help treat OCD.
Examples of Ablative Brain Surgery
- Bilateral cingulotomy: This procedure involves destroying the nerve fibers that connect the cingulate gyrus to other parts of the brain.
- Anterior capsulotomy involves destroying a part of the frontal lobe of the brain. It is the part of the brain that is responsible for OCD symptoms.
NOTE: Cingulotomy involves making a small hole in the skull and inserting a tiny probe into the cingulate gyrus. According to research and studies, it is the area of the brain responsible for OCD.
Examples of Non-ablative Brain Surgery
- Deep brain stimulation: This procedure involves placing electrodes in the brain and delivering electrical impulses to the affected area.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation: This procedure involves placing a magnet on the head and delivering electromagnetic pulses to the affected area.
Can DBS Help Treat OCD
DBS is effective in treating a variety of conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, and essential tremor. There is some evidence to suggest that DBS may also be effective in treating OCD.
A study that was published in the journal Neuron found that DBS was associated with a significant reduction in OCD symptoms. Another study that was published in the journal Biological Psychiatry found that DBS was associated with a decrease in compulsive behaviors.
At this time, DBS is still considered to be an experimental treatment for OCD. If you are considering DBS for the treatment of OCD, it is important to consult with a doctor who is experienced in performing this procedure.
Can TMS Help Treat OCD
TMS is effective in treating a variety of conditions, such as depression, migraines, and chronic pain. There is some evidence to suggest that TMS may also be effective in treating OCD.
A study that was published in the journal Biological Psychiatry found that TMS was associated with a significant reduction in OCD symptoms. Another study that was published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology found that TMS was associated with a decrease in compulsive behaviors.
At this time, TMS is also considered to be an experimental treatment for OCD. Again, if you are considering TMS for the treatment of OCD, it is important to consult with a doctor who is experienced in performing this procedure.
Evaluating Available Surgical Options
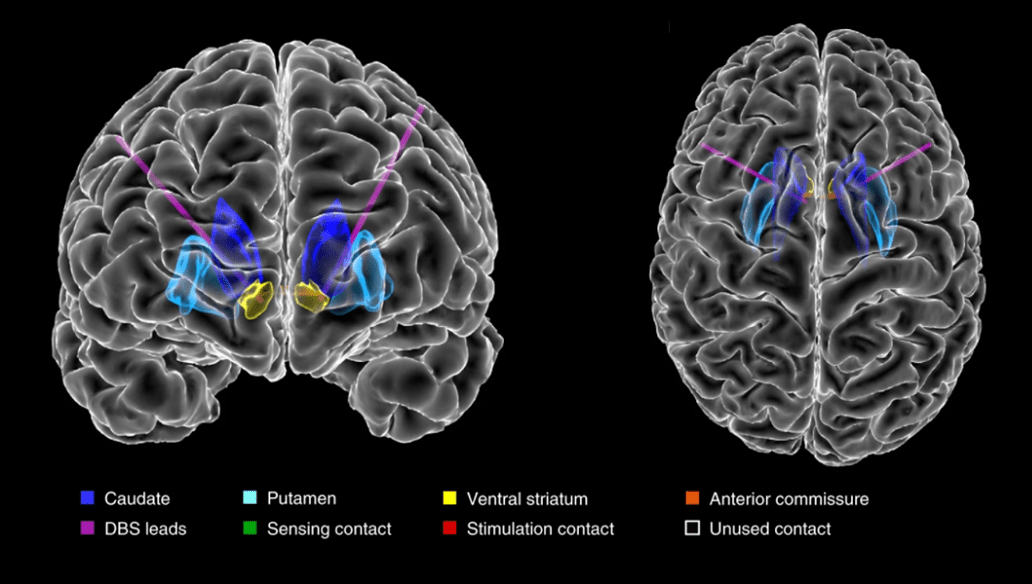
When considering brain surgery, it is important to know:
- There is no guarantee that brain surgery will be successful in treating OCD.
- Brain surgery is a very invasive procedure with potential risks and side effects.
- There are less invasive treatment options available that may be just as effective as brain surgery.
Thus, before deciding whether or not to have brain surgery, it is important to consult with a variety of experts. This includes mental health professionals, neurologists, and surgeons.
When Consider Brain Surgeries
Brain surgery should only be an option for people with OCD who could not respond to or cannot tolerate, medications and other available treatments. Since it is an invasive and risky procedure giving rise to cognitive side-effects. Thus, you should only consider brain surgery if:
- Your OCD is severely impacting your quality of life.
- You have tried a variety of different treatments and nothing has worked.
- You are unable to function in your day-to-day life because of your OCD symptoms.
NOTE: One should go for an invasive procedure like brain surgery after exploring and trying all other treatment options.
Suggesting Alternative Treatment Options
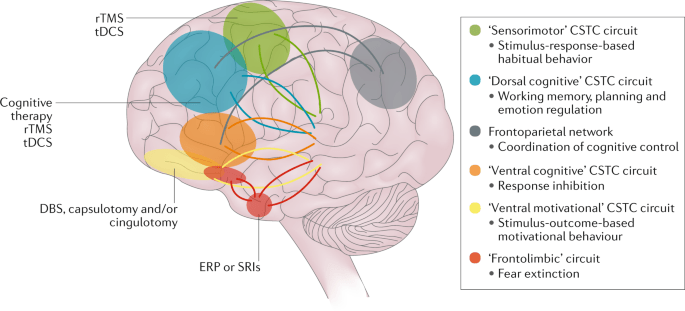
Several different therapies can help treat OCD. These include cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure and response prevention, and medication.
Therapies For OCD
Several different therapies can help treat OCD. For instance:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that helps to change the way you think about and respond to your OCD symptoms.
- Exposure and response prevention (ERP) is a type of therapy that helps you to face your fears and learn how to respond to them healthily.
- Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) is a type of therapy that helps you to accept your OCD symptoms and learn to live with them healthily.
Medications For OCD
Medication can also help to reduce the symptoms of OCD. Medications that commonly help treat OCD include antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and antipsychotics. For instance, examples of:
- Antidepressants include fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine.
- Anti-anxiety medications include lorazepam, alprazolam, and diazepam.
- Antipsychotics include risperidone, olanzapine, and quetiapine.
DISCLAIMER: The information in this blog post is for informational purposes only. Thus, it is not intended to be used as medical advice. So, if you are considering medication or surgery, you should consult with a medical professional.
Managing OCD Symptoms

It is important to find a treatment plan that works for you. Incidentally, this may include a combination of therapies and medications. Moreover, it is important to manage your OCD symptoms on a day-to-day basis. Fortunately, there are several self-help tips and tools that can help you to do this.
Self-help Tips
There are several things you can do on your own to help manage your OCD symptoms. For instance:
- Identifying your triggers and avoiding them
- Challenging your negative thoughts
- Exposing yourself to your fears
- Practicing relaxation techniques
Self-help Tools
Several different self-help tools can help manage OCD symptoms. For instance:
- Relaxation apps
- Mindfulness apps
- Online CBT programs
- Exposure and response prevention apps
Conclusion
If you have tried a variety of different treatments and nothing has worked, brain surgery may be an option. However, it is important to consult with a variety of experts and get a second opinion before making a decision.
If you are looking for affordable Online OCD Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial OCD therapy session