Contents
- 1 What Is Lorazepam (Ativan)?
- 2 How Does It Work?
- 3 What Does Lorazepam (Ativan) Treat?
- 4 Dosage of Lorazepam
- 5 How Should It Be Taken?
- 6 Efficacy Of Lorazepam (Ativan)
- 7 Side Effect Of Lorazepam (Ativan)
- 8 Lorazepam Overdose
- 9 What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
- 10 When To Not Take Lorazepam (Ativan)?
- 11 Danger Of Lorazepam
- 12 Things To Discuss With Your Doctor Before Taking Lorazepam
- 13 Conclusion
What Is Lorazepam (Ativan)?
 Lorazepam (Ativan) is a benzodiazepine drug that can help relieve anxiety, insomnia, and other mental health conditions. The medication is typically prescribed for short-term relief of severe anxiety or insomnia. It belongs to the class of drugs called benzodiazepines which are used to treat many different types of medical conditions including muscle spasms, seizures, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and panic attacks
Lorazepam (Ativan) is a benzodiazepine drug that can help relieve anxiety, insomnia, and other mental health conditions. The medication is typically prescribed for short-term relief of severe anxiety or insomnia. It belongs to the class of drugs called benzodiazepines which are used to treat many different types of medical conditions including muscle spasms, seizures, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and panic attacks
Some people abuse lorazepam because it has a sedative effect that makes them feel more relaxed or sleepy. If you have been taking this medication as prescribed by your doctor then there should not be any risk of withdrawing from it abruptly unless advised otherwise by your physician.
How Does It Work?

Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine drug that can help relieve anxiety, insomnia, and other mental health conditions. The medication is typically prescribed for short-term relief of severe anxiety or insomnia. It belongs to the class of drugs called benzodiazepines which are used to treat many different types of medical conditions including muscle spasms, seizures, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and panic attacks
Benzodiazepines work by enhancing the effect of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. This neurotransmitter helps to regulate mood, emotions, and anxiety. When lorazepam binds to GABA receptors in the brain, it increases the activity of this neurotransmitter which results in a calming effect.
An ongoing debate exists as to the best way to use benzodiazepines such as lorazepam long-term. One point of view includes anxiety disorders in the category of diseases, such as panic disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder, that may result in long-term anxiety requiring medication (in contrast with phobias or acute stress reactions, for which brief therapy is indicated). Another perspective considers long-term benzodiazepine treatment to be appropriate when it suppresses dangerous forms of anxiety.
What Does Lorazepam (Ativan) Treat?
Lorazepam is in a class of medications called benzodiazepines, and it’s often used to treat anxiety and panic disorders. Lorazepam works by slowing activity in the brain to allow for relaxation. It comes as a tablet, an extended-release (long-acting) tablet, and solution (liquid), and it’s usually taken every 4 to 6 hours as needed. Lorazepam (Ativan) is a benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. It can be addictive, so it’s important to take it only as prescribed by your doctor.
Dosage of Lorazepam
 Lorazepam medication is taken orally as either a tablet or solution. The usual dosage for adults ranges from 2 milligrams (mg) to 8 mg per day, administered in two separate doses to minimize drowsiness and impaired coordination that may occur when taking the medication during the day.
Lorazepam medication is taken orally as either a tablet or solution. The usual dosage for adults ranges from 2 milligrams (mg) to 8 mg per day, administered in two separate doses to minimize drowsiness and impaired coordination that may occur when taking the medication during the day.
The prescribed medical dose for lorazepam is 2mg per day or as directed by a doctor. It can be taken with or without food but should be administered only when the patient is able to get a full night’s sleep before the next dose.
Lorazepam was approved by the FDA in 1977 and is available as a generic medication for between $0.05 to $1 per tablet or capsule, depending on how many milligrams are in the dosage form. The intravenous injection of Ativan (lorazepam) typically costs about $200 to $300.
How Should It Be Taken?
Take Ativan exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not take in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. Benzodiazepines are usually taken only when needed, about 4 to 6 hours per day. Do not crush, chew, or break an extended-release tablet ( Ativan ). Swallow the pill whole. Breaking or opening the pill may cause too much of the drug release at one time. To make swallowing easier, you may open the extended-release tablet and sprinkle the medicine into a spoonful of applesauce. Swallow right away without chewing. Do not save the mixture for later use.
Efficacy Of Lorazepam (Ativan)
The pharmacologic effects of lorazepam are similar to those of other benzodiazepines; however, the duration of its anxiolytic effect may be shorter than that seen with diazepam or chlordiazepoxide. Lorazepam has anticonvulsant properties in animal models. But these demonstrations have not been convincing in humans. The sedative-hypnotic action increases with dose and reaches a plateau at 4–8 hours after administration. The liver metabolizes Lorazepam into inactive lorazepam glucuronide.
Studies demonstrate the efficacy of Lorazepam in four short-term (total of 13 weeks) trials that compared lorazepam with placebo, alprazolam, or chlordiazepoxide. Patients were generally severely ill at baseline; however, most respond to lorazepam treatment. In patients who initially responded to lorazepam, efficacy was maintained without loss of effect for up to 13 weeks.
Side Effect Of Lorazepam (Ativan)
As with any medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you don’t understand something.

- Feeling drowsy
- Dry mouth
- Headache
- Nausea
- Lorazepam can also cause other side effects.
Call your doctor if you have
- Increased anxiety
- Difficulty breathing or a fast heartbeat
- Changes in vision, such as blurred vision, dilated pupils, or trouble telling blue and green colors apart
- Chest pain or chest tightness
- Rapid pulse rate
- A seizure (convulsions)
- Unusual behavior
If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
Short-term Side Effects
Short-term side effects of lorazepam (Ativan) may include:
If the medication is not taken as the doctor advises. Then there are higher chances of having withdrawal symptoms after stopping the drug abruptly.
When taking Ativan, it is important to follow your doctor’s dosing instructions very carefully. The medication works best when the patient takes it at the same time each day.
Lorazepam comes in an orally disintegrating tablet and an injectable liquid form. The doctors advise you to swallow it once a day, although your doctor might increase your dose according to the need. The patient can take the tablet with or without food. However, it works best when you lie down immediately after taking it.
Long-term Use Of Lorazepam And Addiction Risk
Some people abuse lorazepam because it has a sedative effect that makes them feel more relaxed or sleepy. If you have been taking this medication as prescribed by your doctor then there should not be any risk of withdrawing from it abruptly unless advised otherwise by your physician. Long-term use will depend on the medical condition that you have and your response to the medication. But most people have uses it daily or weekly at a constant dose over several months or years.
Lorazepam Overdose
An overdose of Lorazepam can be fatal, especially in a child or other person using the medicine without a prescription. If you suspect an overdose, seek emergency medical attention immediately. Symptoms of lorazepam overdose may include:

- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion
- Disorientation, seeing things that are not there ( hallucinations ), or hearing voices
- Depression or slurred speech
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Seizure (convulsions)
- A light-headed feeling, like you, might pass out
- Extreme drowsiness
- Shallow breathing
- Weak pulse
- Trouble breathing
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Ask your doctor if you should take Lorazepam at the same time each day. It’s important not to take lorazepam more often than prescribed. If you do not think your breathing is quite right, call your doctor for instructions.
When To Not Take Lorazepam (Ativan)?
In children younger than age 18 years old; and during pregnancy, which can cause harm to the unborn baby. Before taking this medication, tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant during treatment.
Also If you have used an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days, such as isocarboxazid, tranylcypromine, phenelzine, furazolidone, rasagiline, selegiline, or transdermal (for example, Emsam) . You should not take lorazepam when you have taken linezolid or intravenous methylene blue.
Severe drowsiness can occur, which may be very dangerous while you are doing normal activities such as driving a car. Avoid this risk by not taking lorazepam unless you are able to stay in bed for the full time prescribed by your doctor. If this drug makes you dizzy, it’s best to avoid driving or other tasks requiring concentration until the effects wear off.
Danger Of Lorazepam
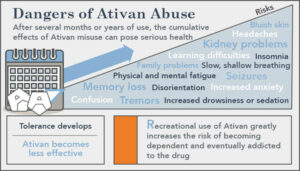
Lorazepam can cause drowsiness, dizziness, or lightheadedness. These effects may be worse if you take them with alcohol or certain medicines. Use Ativan with caution. Do not drive or perform other possibly unsafe tasks until you know how you react to them.
Other dangers include:
Signs of an allergic reaction may occur. These include a severe rash, hives, swelling of the face, mouth, or tongue, difficulty breathing, wheezing, or fainting. Also, do not drink alcohol or use medicines that may cause drowsiness (eg, sleep aids, muscle relaxers) while you are using lorazepam; it may add to their effects. Ask your pharmacist if you have questions about which medicines may cause drowsiness.
Signs of high or low blood pressure like very bad headache or dizziness, passing out, confusion, sweating a lot, shortness of breath, fast heart rate, chest pain, feeling very tired or weak, a fast heartbeat, seizures.
As with all benzodiazepines, lorazepam is habit-forming, and only patients that doctor prescribes should take it. Keep the medication in a secure place where others cannot get to it.
Things To Discuss With Your Doctor Before Taking Lorazepam
Before taking lorazepam, tell your doctor if you are allergic to it; or to other benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam (Xanax), chlordiazepoxide (Librium), clonazepam (Klonopin), diazepam (Valium), and others. Also, tell your doctor if you have:

- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Asthma or other breathing disorder
- A history of depression, suicidal thoughts, or addiction to drugs or alcohol
- If you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding
Some medicines can interact with lorazepam and cause a serious condition called serotonin syndrome. Be sure your doctor knows if you also take stimulant medicine, opioid medicine, herbal products, or medicine for depression, mental illness, Parkinson’s disease, migraine headaches, serious infections like HIV/AIDS, or seizure (epilepsy).
Avoid drinking alcohol while taking lorazepam. It can increase some of the side effects of lorazepam.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. You should not take lorazepam if you are allergic to benzodiazepines, or if: you have porphyria (a genetic enzyme disorder that causes symptoms affecting the skin or nervous system).
Conclusion
Lorazepam, also known as Ativan, is a benzodiazepine anxiolytic that helps treat anxiety disorders. Doctors commonly prescribe it for patients who are experiencing acute stress and short-term conditions such as insomnia or panic attacks. You can take it in pill form or inject the drug into your body with an IV line. If you do not have any of these treatments available to you, You may take Lorazepam through injections given by a doctor at their office using small doses that will wear off after about 24 hours. If you want to know more about this medicine then reach out to our team, and solve your queries.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session