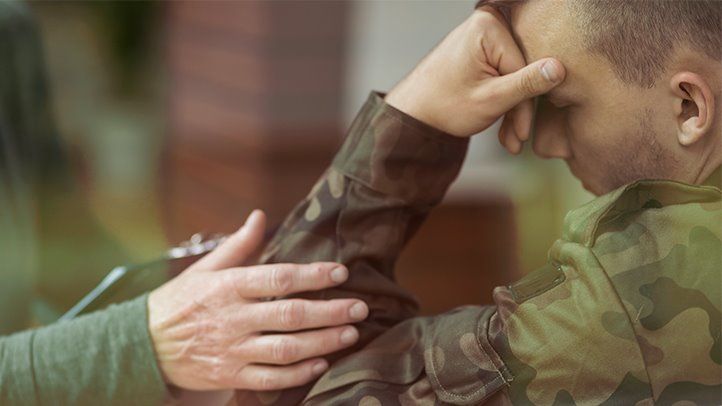
If you are a combat veteran, then there is a good chance that you have experienced some form of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). PTSD can be a debilitating condition that affects every aspect of your life. In this blog post, we will discuss what PTSD in combat veterans is, the symptoms of PTSD, and how it can be treated. We will also provide information on resources that are available to help combat veterans cope with PTSD.
Contents
- 1 What Does ” PTSD in Combat Veteran ” Mean?
- 2 Symptoms of PTSD in Combat Veterans
- 2.1 Reliving the event (also called re-experiencing symptoms)
- 2.2 Avoiding situations that remind you of the event
- 2.3 Having more negative beliefs and feelings
- 2.4 Feeling keyed up (also called hyperarousal symptoms)
- 2.5 Constant mental and physical re-experiencing of the traumatic event
- 2.6 Changes in how you react to things emotionally and physically
- 2.7 Changes in your Mood and Feelings
- 3 Reasons For PTSD In Combat Veterans
- 4 How To Treat PTSD in Combat Veterans?
- 5 How To Prevent PTSD In Combat Veterans?
- 6 How To Help Someone With PTSD In Combat Veterans?
- 7 Conclusion
What Does ” PTSD in Combat Veteran ” Mean?
 PTSD in combat veterans means that the person has post-traumatic stress disorder and has served in combat. This can be from any type of combat, such as in the Army, Marines, Navy, Air Force, or Coast Guard. When a person has PTSD, it means that they have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event and now have symptoms that make it hard for them to function in their everyday life. These symptoms can include flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, depression, and trouble sleeping. For some people with PTSD, these symptoms can be so severe that they can’t leave their house or hold down a job.
PTSD in combat veterans means that the person has post-traumatic stress disorder and has served in combat. This can be from any type of combat, such as in the Army, Marines, Navy, Air Force, or Coast Guard. When a person has PTSD, it means that they have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event and now have symptoms that make it hard for them to function in their everyday life. These symptoms can include flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, depression, and trouble sleeping. For some people with PTSD, these symptoms can be so severe that they can’t leave their house or hold down a job.
PTSD is not just something that happens to soldiers who see combat. It can happen to anyone who experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. There may also be a genetic predisposition to developing PTSD. This means that if someone in your family has PTSD, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
If you think you may have PTSD, it’s important to seek help from a mental health professional who can diagnose and treat the condition. There are many effective treatments for PTSD, including exposure therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and medication. With treatment, most people with PTSD can get better and live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Symptoms of PTSD in Combat Veterans

The symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can be different for everyone. Some people with PTSD have only a few symptoms while others have many. The symptoms tend to fall into four main groups:
Reliving the event (also called re-experiencing symptoms)
You may have bad memories or nightmares. You even may feel like you’re going through the event again. This is called a flashback. A flashback can come on suddenly and without warning. It can happen when you’re awake or when you’re asleep. There may also be many physical symptoms that go along with a flashback. You may sweat, have a racing heart, or feel nauseous.
Avoiding situations that remind you of the event
You may try to avoid anything that reminds you of the traumatic event. Also, You may not want to talk about what happened or see people who were there.
You might avoid crowds, driving, or even leaving your home. Or you might not be able to get certain thoughts out of your head. This avoidance can make it hard to keep up with work, school, or your social life.
Having more negative beliefs and feelings
After a trauma, it’s common to have more negative beliefs and feelings. For example, you may think the world is completely dangerous. Or you might not be able to enjoy your life like you used to. You may feel guilty or ashamed. You may also be irritable and have trouble concentrating or sleeping.
Feeling keyed up (also called hyperarousal symptoms)
You may be jittery, or always alert and on the lookout for danger. This is known as hyperarousal. It can make you startle easily, lose your temper often, and have a hard time sleeping. When bad things happen, it can be hard to stop thinking about them. But with PTSD, these feelings don’t go away and can get worse over time if they’re not treated.”
Constant mental and physical re-experiencing of the traumatic event
Another sign of PTSD is reliving the event through intrusive thoughts during the day and nightmares when you sleep. You may feel like you’re going through the trauma all over again. This can be extremely distressing and make it hard to go about your day-to-day life.
Changes in how you react to things emotionally and physically
Sometimes there are physical changes that accompany PTSD. You may startle easily, have trouble sleeping, or lose interest in things you used to enjoy. You may also become irritable and have a hard time concentrating. It’s not unusual for people with PTSD to self-medicate with drugs or alcohol.
Changes in your Mood and Feelings
There are also changes in mood that can come with PTSD. You may feel more anxious or depressed. You may feel hopelessness, guilt, or shame. It’s not uncommon to have negative thoughts about yourself or the world around you. Also, your sense of trust may be shaken, and you may feel isolated and alone.”
These are some of the signs of PTSD in many physical symptoms of these symptoms, it’s important to get help from a mental health professional. PTSD can be treated and there is hope for recovery.
Reasons For PTSD In Combat Veterans

There can be many reasons for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in combat veterans. Some causes are more common than others such as:
Experiencing a life-threatening event
One of the main causes of PTSD is experiencing life-threatening events. This could be something like being in a combat zone, being kidnapped, or being in a car accident. If over a period of something that left you feeling scared or helpless, it’s more likely that you’ll develop PTSD. Sometimes many physical symptoms go along with a flashback. You may sweat, have a racing heart, or feel nauseous.
Witnessing a traumatic event
Another cause of PTSD is witnessing a traumatic event. This could be something like seeing another soldier being killed in combat or watching someone being raped or murdered. If you’ve seen something so horrific that it’s hard to get the image out of your head, you may be at risk of developing PTSD.
Repeated exposure to trauma
If you’re repeatedly exposed to trauma, such as being in a war zone for an extended period, you’re more likely to develop PTSD. This is because your body never has a chance to recover from the several reasons before being exposed to more trauma. This can lead to your body and mind feeling constantly on edge, which can make it hard to function in day-to-day life.
Personal history
Your personal history can also play a role in whether or not you develop PTSD. If you have a history of anxiety or depression, you’re more likely to develop PTSD after a traumatic event. This is because your body may be more sensitive to the stress hormone cortisol, which is released during a traumatic event.
There may be also many other reasons that are unique to you that can make you more likely to develop PTSD.
Negative Impacts of PTSD On Combat Veterans

PTSD in combat veterans can have several negative impacts on their lives. These individuals may suffer from flashbacks, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts related to their time in combat. Some of these negative impacts are:
Difficulty In Concentrating
One of the most common symptoms of PTSD is difficulty concentrating. This can make it hard for individuals to perform simple tasks, follow conversations, or even remember important information. For combat veterans who are struggling with PTSD, this symptom can make it difficult to return to civilian life and succeed in school or at work.
Avoidance
Many individuals with PTSD will attempt to avoid anything that reminds them of their trauma. This may include people, places, activities, objects, and thoughts. While avoidance can provide some short-term relief from distressing memories, it ultimately prevents individuals from facing their fears and working through their trauma. In the long term, avoidance can lead to social isolation and further mental health problems.
Hypervigilance
Hypervigilance is a state of increased awareness and vigilance. Individuals with PTSD may be constantly on the lookout for danger, even when there is no threat present. This can lead to difficulty sleeping, irritability, and exaggerated startle responses.
Mood Changes
PTSD can also cause changes in mood and emotion. Individuals may experience feelings of guilt, shame, anger, or anxiety. These intense emotions can be disruptive and make it difficult to maintain healthy relationships or perform day-to-day activities.
Self-Harm
Self-harm is a common coping mechanism for individuals with PTSD. This may include cutting, burning, or other forms of self-injury. Self-harm can provide short-term relief from distressing symptoms, but it can also lead to further physical and emotional harm in the long term. There are also other risks associated with self-harm, such as infection and scarring.
Constant Nightmares
Nightmares are a common symptom of PTSD. These nightmares can be so realistic and distressing that individuals may avoid sleep altogether. This can lead to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Nightmares can also make it difficult to maintain healthy relationships or perform day-to-day activities.
Feelings of hopelessness
PTSD can also cause feelings of hopelessness and despair. This may be due to the trauma itself or the negative changes that PTSD has brought about in an individual’s life. Feelings of hopelessness can make it difficult to find meaning in life and make positive changes.
These are some of the negative impacts of PTSD on combat veterans.
How To Treat PTSD in Combat Veterans?
Treating PTSD in combat veterans can be difficult. These are some of the treatment options to help those suffering from PTSD:
Medications
Medications are one of the most common treatments for PTSD. These medications can help to control symptoms of anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Medications like antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can help manage symptoms. Some of these medications may have side effects, so it is important to talk to a doctor before starting any medication.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is another common treatment for PTSD. This type of therapy can help individuals to process their trauma, develop healthy coping mechanisms, and improve their relationships. There are several different types of psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and exposure therapy.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cogntive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that helps individuals to change their thoughts and behaviors. CBT can be used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including PTSD. This type of therapy can help individuals to develop healthy coping mechanisms, manage their symptoms, and improve their quality of life.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that involves exposing an individual to the thing they are afraid of. This may include reliving the trauma in imagination or real life. Exposure therapy can be very effective in treating PTSD, but it should only be done with the guidance of a trained therapist.
EMDR
EMDR is a type of therapy that is often used to treat PTSD. It stands for Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing. EMDR is a form of exposure therapy, which means it helps people confront their fears and memories in a safe environment.
EMDR is an effective treatment for PTSD in many studies. One study found that 84% of veterans with PTSD who received EMDR had a decrease in symptoms after just 12 sessions.
Support Groups
Support groups provide an opportunity for individuals with PTSD to connect with others who are struggling with similar experiences. These groups can offer support, advice, and information about resources. Support groups can be found online or in person. Sometimes there may also be many different types of support groups, such as for specific trauma types or family and friends of those with PTSD.
Self-Care
Self-care is an important part of managing any chronic condition, including PTSD. Many different things can be considered self-care, but some examples include exercise, relaxation techniques, and healthy eating. It is important to find what works for you and to make sure that you are taking care of yourself both physically and emotionally.
Eating Good Food: Eating nutritious foods helps the brain to function at its best. Many foods can help to reduce inflammation, which is believed to play a role in PTSD. Some examples of anti-inflammatory foods include omega-three fatty acids, turmeric, and green leafy vegetables.
Exercise: Exercise has many benefits for mental health, including reducing stress and improving sleep. It can also help to boost self-esteem and confidence. There maybe be some days when it is hard to motivate yourself to exercise, but even a short walk can make a difference.
Relaxation Techniques: Relaxation techniques can help to reduce stress and anxiety. Some examples of relaxation techniques include yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises. These techniques can be done anywhere and don’t require any special equipment.
Meditation: Meditation is a form of mindfulness, which is an approach that can help manage PTSD. Mindfulness means paying attention to the present moment and accepting things as they are. Meditation can help to improve focus, sleep, and mood. There are many different types of meditation, so it is important to find one that works for you.
Yoga: Yoga is one of the most popular forms of exercise in the world. It combines physical activity with breathing exercises and relaxation. Yoga can help to improve flexibility, strength, and balance. It can also help to reduce stress and anxiety.
Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises are a simple, yet effective way to relax the body and mind. They involve taking slow, deep breaths through the nose and exhaling slowly through the mouth. Deep breathing exercises can be done anywhere and only take a few minutes to do.
Journal Keeping
One of the best ways to process thoughts and emotions is to write them down in a journal. Journaling can help to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. It can also be a helpful way to track your symptoms and progress over time. There may sometimes be many different types of journals, such as for specific trauma types or family and friends of those with PTSD. Also, art journaling has been known to be helpful for individuals with PTSD.
How To Prevent PTSD In Combat Veterans?

Preventing PTSD in combat veterans is important. There are many ways to prevent PTSD, but the most important thing is to get help as soon as possible. If you or someone you know is suffering from PTSD, there are many resources available to help. The sooner you get help, the better chance you have of preventing further damage.
Some of these tips are:
Identify Your Triggers
One of the best ways to prevent PTSD is to identify your triggers. A trigger is anything that causes you to relive the traumatic event. Once you know what your triggers are, you can start to avoid them. Sometimes there may be many different types of triggers, so it is important to be as specific as possible.
Avoid Drugs and Alcohol
Drugs and alcohol can make PTSD symptoms worse. They can also make it more difficult to cope with stress and anxiety. If you are struggling with PTSD, it is important to avoid drugs and alcohol. Sometimes there are also many different types of support groups available to help with this.
Get Help From A Professional
One of the best ways to prevent PTSD is to get help from a professional. Many different types of therapy can help treat PTSD. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it is important to seek professional help.
Talk About Your Experience
Talking about your experience can be difficult, but it’s often helpful. Talking about what happened can help you make sense of it and start to heal. It can also be helpful to talk about your experiences with other people who have been through similar things.
These are just some of the ways that you can prevent PTSD in combat veterans. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it is important to get help as soon as possible. There are many resources available to help. The sooner you get help, the better chance you have of preventing further damage.
How To Help Someone With PTSD In Combat Veterans?

Helping someone with PTSD can be difficult. You may feel like you are walking on eggshells, tiptoeing around them, and never quite sure what will trigger a reaction. The most important thing you can do is to be patient, understanding, and supportive.
Some of these tips to help someone are:
Listen To Their Problems
One of the best things you can do is to listen to their problems. Many people with PTSD feel like no one understands what they are going through. Just by listening, you can show them that you care and that you want to help.
Encourage Them To Get Help
If someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it is important to encourage them to get help from a professional. Many different types of therapy can help treat PTSD. If they are reluctant to seek help, you could offer to go with them or even just talk on the phone.
Help Them Avoid Triggers
Healing from PTSD takes time, but there are things you can do to help your loved one through the process. One of the most important things is to help them avoid triggers. Triggers are anything—a sound, a smell, a place—that brings back memories of the traumatic event.
For example, many veterans with PTSD avoid crowded places because they fear being trapped or attacked. But avoiding triggers can make it harder for your loved one to heal. So it’s important to talk about what their triggers are and how they can be avoided or managed.
Make Sure They Have Support
PTSD can be very isolating and make people feel like they are all alone. It is important to make sure that they have a support system. This could be family, friends, or even a support group. Having people to talk to can make a big difference. Also, many organizations help veterans with PTSD.
Be Supportive
Support is crucial for someone with PTSD. Just being there for them can make a big difference. Listen to them when they want to talk about their experiences. And don’t judge them. It is also important to encourage them to seek professional help if they are struggling.
Be Patient And Understanding
Patience and understanding are key when supporting someone with PTSD. The healing process can be long and difficult. There will be good days and bad days. Just remember that you are there for them and that they are not alone. Also, try to be understanding if they need to cancel plans or avoid certain situations.
PTSD can be a difficult disorder to deal with, but there are ways you can help your loved one through the healing process.
Conclusion
PTSD in combat veterans is a serious problem that needs to be addressed. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, there are resources available to help. The Veterans Affairs website has a list of resources for combat veterans with PTSD.
If you are a combat veteran with PTSD, know that you are not alone. Others have been through what you have been through and understand what you are going through. Seek out help from those who understand and can offer support. With help, you can heal the wounds of war and live a full and productive life.
For more information, please contact MantraCare. PTSD or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a mental health condition that affects people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. If you have any queries regarding Online PTSD Counseling experienced therapists at MantraCare can help: Book a trial PTSD therapy session


