Chronic illness is a condition that lasts for more than three months or recurs periodically. Some examples of these diseases include arthritis, asthma, cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. Different Chronic illnesses can affect the body in different ways. Some make you feel pain. Others make you feel tired all the time. One thing they have in common is that you need to keep them under control and not let them get out of hand.
Contents
What Is Chronic Illness?
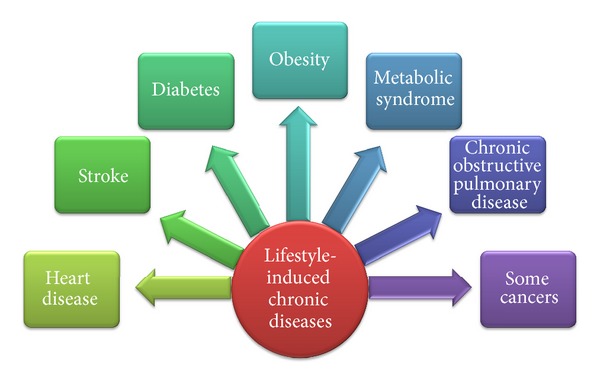
Chronic illness is a long-term condition that lasts for months or years. It can cause pain, disability, and even death. There are many different types of chronic illnesses, including cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis.
People who suffer from a chronic illness can’t always easily define their condition. Some of the most common conditions include epilepsy, cancer, multiple sclerosis, or arthritis. About these diseases, we talk with our friends and family members. Someone might even have them for life. These diseases don’t mean there’s nothing you can do to fix them.
People who have chronic diseases often get more than one type of treatment to manage their pain and slow down the damage to their bodies.
Types Of Chronic Illnesses
Types of chronic illnesses vary, but most fall into these categories:
Neurological
A neurological condition is the one that affects your nervous system. Neurological diseases can be either inherited or the result of injury to the brain or spinal cord. Some examples are epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Cardiovascular
Heart diseases fall under this category because it involves problems with the heart and blood vessels. Issues, like high cholesterol levels, obesity, smoking, and irregular heartbeat all contribute to cardiovascular disease. Cancerous tumors also affect this category by disrupting normal cell division in organs throughout the body. Respiratory.
This category includes diseases that affect your lungs and chest cavity. Conditions in this group include asthma, emphysema, and bronchitis.
Gastrointestinal Diseases
In this category affect the digestive system, including the stomach, small intestine, and colon. Disorders like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and hepatitis are all considered gastrointestinal illnesses.
Autoimmune
In autoimmune diseases, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. This can cause a wide range of problems throughout the body. Some common autoimmune conditions are rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. Endocrine/Metabolic.
Endocrine Disorders
This involves problems with hormones produced by glands in your body. Diabetes is an example of an endocrine disorder. Other metabolic disorders involve the way your body uses energy. These conditions can lead to problems like obesity and heart disease.
Dermatological Conditions
Diseases that affect the skin are dermatological conditions. Some common examples are psoriasis, eczema, and acne.
Causes Of Chronic Illness
There is no one answer to this question. Some chronic illnesses are caused by genetics, while others are the result of lifestyle choices or exposure to harmful chemicals. However, most chronic illnesses develop over time as a result of multiple factors.
- Genetics: Chronic illnesses can be passed down from parents to children. This is called genetic inheritance. Some diseases, like cystic fibrosis, are caused by a single gene mutation. Others, like diabetes, are the result of multiple genes working together.
- Lifestyle Choices: Certain lifestyle choices can increase your risk of developing a chronic illness. Smoking, drinking alcohol excessively and being overweight all put you at greater risk for conditions like heart disease and cancer. Additionally, lack of exercise and poor diet can lead to problems like arthritis and diabetes.
- Chemical exposure: Exposure to harmful chemicals can also cause chronic illnesses. Toxic metals like lead and mercury can cause problems to the nervous system and cause neurological problems. Chemicals in the environment, like pesticides and air pollution, can increase your risk for cancer.
Side Effects Of Chronic Illness
Living with a chronic illness can be difficult both physically and emotionally. People with chronic illnesses may have more health problems. They are not easy to deal with, such as:
- Pain and fatigue.
- These can also include feelings of isolation, fatigue, anxiety, and depression.
It is important to understand the common side effects and how to deal with them, in order to make the best possible life for yourself despite your chronic illness.
- Isolation is a common problem for people living with chronic illnesses. You might not want to do social activities anymore because you don’t understand them or you are tired.
- Fatigue is another common side effect of many chronic illnesses. This type of fatigue can be different than just feeling tired and can be difficult to manage.
- Anxiety and depression are also common problems for people living with chronic illnesses.
When you have a chronic condition, anxiety and sadness can come.
How Is Chronic Illness diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose chronic illnesses by asking patients about their symptoms and medical history. They may also run tests to measure specific proteins or chemicals that are associated with certain types of disease. For some conditions, doctors need to perform surgery on a patient’s organs before making an accurate diagnosis.
What Are The Treatment Options For Chronic Illness?
Treatment for chronic illnesses varies widely. Doctors will consider the type of condition you have and determine a treatment plan based on your symptoms, age, other medical conditions, and overall health.
Treatment options include medications like antibiotics or vaccines to prevent infection; lifestyle changes; surgery; chemotherapy; radiation therapy; stem cell transplants; physical therapy (PT); occupational therapy (OT); speech/language pathology (SLP); dietary therapies like the ketogenic diet
Medication Treatment 
Chronic illness can be treated with a variety of medications. However, some common medications used to treat chronic illnesses include:
- Antibiotics
- Painkillers
- Antidepressants
- Additionally, many people with chronic illnesses require regular injections or doses of medication to manage their condition.
Surgical Treatment 
There are a variety of surgical treatments available for chronic illnesses. For example, surgery may be used to treat chronic pain, obesity, or heart disease.
- Chronic pain is a common problem that can be caused by many different conditions. Often, surgery is the best option for treating chronic pain. There are a variety of different surgeries to treat chronic pain. Certain surgeries remove damaged tissue and spinal cord stimulators can reduce pain. But, nerve blocks can also be used and they make it so that not as many nerves send pain signals to the brain.
- Surgery can also be used to treat obesity. The two most common surgeries for weight loss are the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and vertical banded gastroplasty. When you have both of these surgeries, you will have two pouches in your stomach. One is smaller and one is larger. This way, you can’t eat as much food. The surgery can also bypass part of the small intestine, which reduces the number of calories and nutrients the body absorbs.
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death. There are many different types of heart surgery that can be used to treat heart disease. One common surgery is coronary artery bypass surgery. This surgery is used to improve blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked arteries. Another common surgery is a heart transplant. A heart transplant is a surgical procedure where a diseased heart is replaced with a healthy heart from a donor.
- Each of these surgeries has its own risks and benefits. It is important to discuss your options with your doctor to see if surgery is the best option for you.
Therapy Options
There are many therapy options to treat chronic illness, such as:
Physical Therapy (PT) 
- Physical therapy is a type of treatment that helps you regain strength and mobility after an injury or surgery.
- PT often includes exercises like stretching and weightlifting. It can also involve massage, heat therapy, and ultrasound.
- Physical therapy can help people with chronic illnesses by increasing strength and mobility. It also helps to improve patients’ circulation, flexibility, balance, coordination, endurance
Occupational Therapy (OT) 
- Occupational therapists work on a wide range of skills that are important for daily tasks like getting dressed or preparing food.
- OT may involve helping you develop adaptive equipment or strategies to make your life easier. This type of treatment focuses on the patient’s abilities instead of their limitations.
- A person with an illness is not able to do some things. A person who helps them with this is called an occupational therapist. They help people be able to do things they would not be able to do on their own, such as getting ready for the office or making their meal, and more.
- Occupational therapists work with you to find solutions that fit your lifestyle and help you manage symptoms so that daily tasks become easier
Speech/Language Pathology (SLP) 
- Speech-language pathologists help children or adults with speaking, cognitive-communication, or swallowing problems. They assess the situation, diagnose the problem, and treat the problem. Speech-language pathologists also try to make sure that people can still speak normally after they are done treating them.
- SLPs create a plan of action for each patient based on their individual needs from learning how to speak after an accident to preparing healthy meals as part of a medical diet.
- An SLP helps people with difficulties talking. They also help people who have difficulty understanding words or following directions because they had a brain injury or stroke.
- An SLP can help patients overcome communication barriers by creating an individualized plan that takes into account their strengths and weaknesses, as well as lifestyle goals
Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy is a type of medication that helps in treating cancer. It is also helpful to treat some chronic illnesses, like leukemia. Chemotherapy works by killing cells in the body that are dividing rapidly.
- There are different types of chemotherapy. It is different for different types of cancer, such as leukemia.
- The purpose of chemotherapy is to kill the fast-growing cells, so they do not take over your organs and cause damage. This helps treat chronic illness because it slows down the disease process.
Side effects can include
- Hair loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Mouth sores
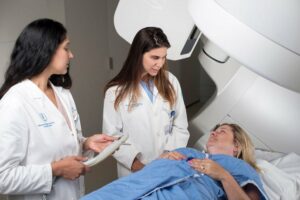
Radiation Therapy
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It is also very beneficial to treat chronic illnesses, like lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Radiation therapy is helpful alongside chemotherapy for more effective treatment.
- There are different types of radiation therapy, such as external beam radiation therapy, and internal radiation therapy.
- External beam radiation therapy is the most common type of radiation therapy. It uses a machine to send high-energy beams directly to the tumor. Internal radiation therapy is when the doctors put radioactive material into or near the tumor.
- Radiation Therapy helps in treating chronic illness by killing cancer cells and shrinking tumors. Radiation Therapy can also be very helpful alongside chemotherapy for more effective treatment.
Side effects can include
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Hair loss
- Mouth sores
Stem Cell Transplant
- Stem cell transplants are a type of treatment that replaces damaged or diseased stem cells with healthy ones from a donor. This helps the body to heal and can be very helpful to treat a variety of chronic illnesses, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
- Stem cell transplants are a type of treatment that replaces damaged or diseased stem cells with healthy ones from a donor.
- The stem cells help your body to create new blood cells and rebuild the tissues that have been destroyed by the disease.
- There are two types of stem cell transplants: autologous and allogeneic.
- Autologous stem cell transplants use your own stem cells as the donor.
- Allogeneic stem cell transplants use donated stem cells from another person.
Side effects
There are side effects that can occur after the stem cell transplant, such as:
- Lung damage, because by the high pressure of the liquid which is transferred into your body during surgery. This can cause trouble breathing or blockages in airflow through your lungs.
- Infection from bacteria entering your blood before, during, and after surgery. Signs of infection will depend on what type you have had done and where they are located but may include fever, chills, pain or redness at insertion sites for catheters (tubes), shortness of breath, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite.
- Serious infections can occur during the first few weeks or months after stem cell transplants, and they may require treatment with antibiotics.
- Doctors give Hepatitis B virus (HBV) with graft-versus-host disease which causes liver damage because your immune system does not recognize it as part of its own body anymore.
- If you already have HBV, this medication could reactivate it so talk to your doctor about getting a vaccination against it before starting therapy if possible.
- The severe allergic reaction can happen anytime without advance warning signs such as hives, trouble breathing, swelling in face/lips tongue, feeling faint.
How To Help Someone Suffering From Chronic Illness?
Chronic illnesses can be difficult to deal with, both for the person who is suffering from them and for their loved ones. There are a few ways that you can help someone who is dealing with chronic illness. such as:
- Be there for them: Chronic illness can be lonely and isolating, so offer your support and friendship.
- Listen to them: Let them talk about their feelings and experiences, and don’t judge or criticize them.
- Help them manage their treatment: Offer to help with tasks like taking medication or going to doctor’s appointments.
- Encourage them to stay active: Exercise can help improve mood and energy levels in people with chronic illnesses.
- Understand that they may not be able to do everything they used to: Don’t expect them to be able to do everything they did before their illness, and be willing to help out with tasks that they can no longer do on their own.
- Be patient: Dealing with chronic illness can be a long process, and there will be good days and bad days. Be understanding and supportive throughout the entire journey.
Conclusion
There are many ways to help with chronic illness, and you should feel empowered in your search for the right therapy. It is important to note that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to managing a chronic illness. what works for some may not work well for others. However, the trick is finding out which type of therapy can be most beneficial based on each person’s unique needs and personality. People who have chronic conditions still need to live their lives. We hope that after reading this, you will feel less stressed about living with a chronic condition. The next step is deciding how best to proceed. Whether you try alternative treatments like acupuncture or stay with traditional Western medicine, there are limitations.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session