It is not an easy task to live with a mental illness, and there are probably many people who don’t even know they have one. There are various types of mental illnesses and the signs of hypomania may not be as obvious as those for other diseases.
This article aims to highlight some of the major symptoms that you should look out for if you think that you or someone close to you might be experiencing this condition.
We will also briefly discuss what this mental illness is like and how it is different from mania. In addition, we will suggest some management strategies as well as treatment options to cope better with this illness.
Contents
What Is Hypomania?

Hypomania is a type of manic episode that doesn’t quite meet the criteria for mania. It’s a less severe form of mania, but it can still cause problems if it’s not treated.
Signs Of Hypomania
The symptoms of hypomania are similar to those of mania, but they are not as intense.
A person who is experiencing hypomania may be more energetic, excitable, and productive than usual.
However, they are not likely to have the same delusional behavior or extreme lack of self-control that can happen during mania.
Some of the signs and symptoms of hypomania are as follows:

- Excessive energy and activity
- Rapid speech and racing thoughts (Talking more than usual)
- Risky behavior with poor judgment
- Sleeping very little, but feeling rested
- Increased irritability and agitation
- Less need for sleep without experiencing fatigue (hypersomnia)
- Compulsive behavior such as gambling, shopping sprees, hypersexuality (increased sexual thoughts, feelings, and behaviors), and eating more than usual
- Inflated self-esteem or a feeling of being “high”
- Distractibility
- Changes in sleep habits (either sleeping too much or not enough)
- Changes in appetite (eating more or less than usual)
- Alcohol and drug
- Impaired judgment
Manic v/s Hypomania
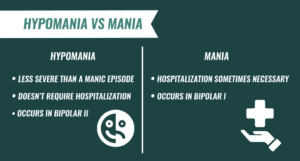
Mania is a more severe form of bipolar disorder. It’s diagnosed when a person has had at least one manic episode.
A manic episode is defined as a period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood that lasts for at least one week.
A person who is experiencing mania may have all of the symptoms of hypomania, as well as some additional symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions.
How To Manage A Hypomanic Episode

If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of hypomania, it’s important to get help right away. The goal of treatment is to stabilize the mood and prevent a full-blown manic episode. This may include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Some tips for managing a hypomanic episode are as follows:
- Get plenty of sleep and exercise daily
- Avoid drugs and alcohol
- Don’t make major life decisions during a hypomanic episode. Talk with someone you trust instead, such as your doctor or therapist.
- Do things that keep you busy and calm (such as coloring, watching movies, listening to music)
- Take medications exactly how prescribed by your doctor
- Stay connected with others and your routine (such as going to work, school, or church)
Treatment And Lifestyle
If you are experiencing hypomania, it’s important to get help right away. Talk with your doctor about treatment options that may include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Medication
Several medications may be used to treat hypomania. They include mood stabilizers, antipsychotic drugs, and antidepressants.
It’s important to work with your doctor to find the best medication for you. Each person responds differently to medications, so it may take some time to find the right one.
Therapy
Therapy is an important part of treatment for bipolar disorder. It can help you learn how to manage your moods and cope with stress.
Many types of therapy can be effective for bipolar disorder, including interpersonal and cognitive-behavioral therapies.
Some therapists may even use a combination of these approaches to meet your individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes
Your doctor or therapist might also recommend lifestyle changes as part of treatment for hypomania. This may include:
- Getting regular exercise
- Eating a healthy diet
- Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and drugs
- Sticking to a routine
- Developing stress-management techniques
Conclusion
Hypomania is a less severe form of mania. It can cause problems if it’s not treated, but it also has some benefits, such as increased energy and productivity. If you think you or someone you know is experiencing signs of hypomania, it’s important to get help right away.
Luckily, most people with hypomania don’t require hospitalization. However, it is important to get help as soon as possible to avoid the symptoms from getting worse. Also, it is important to remember your doctor must know about your mood swings. So they can help you manage them effectively.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session


