We all know that stress isn’t good for us. It can cause all sorts of problems in our personal and professional lives. But what many people don’t realize is the physical effects of stress on our bodies. Stress can lead to a wide variety of health problems, including heart disease, obesity, and diabetes. In this blog post, we will discuss the physical effects of stress and how they can harm your body. We’ll also provide some tips for managing stress and keeping yourself healthy.
Contents
What Is Stress?
 Stress is your body’s response to any demand placed on it. When you perceive a threat, your nervous system responds by releasing stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones increase your heart rate and blood pressure and boost your energy supply. This “fight-or-flight” response is a natural reaction that has evolved over time to protect us from danger.
Stress is your body’s response to any demand placed on it. When you perceive a threat, your nervous system responds by releasing stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones increase your heart rate and blood pressure and boost your energy supply. This “fight-or-flight” response is a natural reaction that has evolved over time to protect us from danger.
In small doses, stress can be helpful. It can motivate you to meet a deadline at work or study for an exam. But when the demands of work, family, and life, in general, exceed your ability to cope, stress can have harmful effects on your health and well-being.
There are many impacts of stress on one person that they may not even realize. These are physical or mental and can have short-term or long-term effects. It is important to be able to identify when you are under stress and the different impacts it may have on you so that you can take steps to mitigate them.
Physical Impacts of Stress
There are many impacts of stress on your body – both short-term and long-term. In the short-term, you may experience:
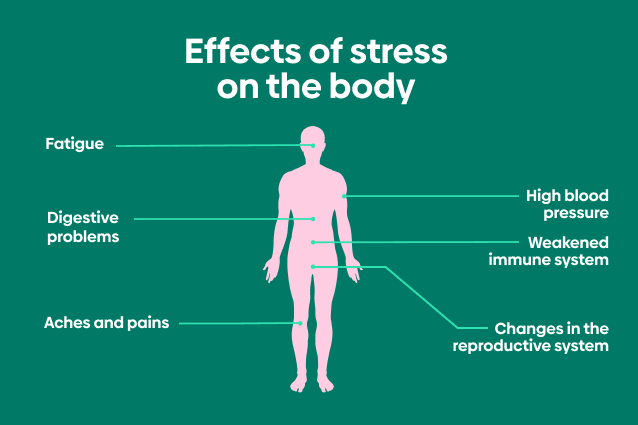
Headaches
Headaches are one type that is commonly associated with stress. This is because when you are stressed, your body tenses up and this can lead to tension headaches. Also, when you are stressed, you may clench your jaw or grind your teeth and this can lead to headaches as well. Sometimes there may be a migraine that is brought on by stress as well.
Upset stomach or indigestion
Stress can also impact your digestive system. When you are stressed, you may experience symptoms like an upset stomach, heartburn, or indigestion. This is because stress can cause you to produce more stomach acid than usual and it can also lead to spasms in your intestines. Stomach issues may also be caused by the fact that when you are stressed, you may not eat as healthy or take care of yourself as well.
High blood pressure
When you are under stress, your body goes into “fight-or-flight” mode and this can cause your blood pressure to rise. This is because your heart is pumping harder and faster to send more blood to your muscles. If you have high blood pressure, stress can make it worse. High BP can also make you more susceptible to heart attacks and strokes.
Anxiety
Anxiety is a common psychological effect of stress. When you are stressed, you may feel like you are “on edge” all the time or that you are in danger even when there is no real threat. This can lead to feeling restless, irritable, and having difficulty concentrating. You may also have physical symptoms like sweating, rapid breathing, or a racing heart.
Depression
Stress can also lead to depression. When you are under a lot of stress, it may seem like there is no light at the end of the tunnel and this can lead to feelings of hopelessness and despair. You may lose interest in activities that you used to enjoy, have trouble sleeping, or turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms like alcohol or drugs.
Long-Term Physical Effects of Stress

In addition to the short-term effects of stress, there are also long-term effects that can impact your health. These include:
Heart disease
Stress is a major risk factor for heart disease. When you are stressed, your blood pressure and heart rate go up and this puts strain on your heart. Over time, this can lead to damage to your blood vessels and increase your risk for heart attacks and strokes. Heart problems also make you more susceptible to other health issues like high blood pressure and diabetes.
Weakened Immune System
If you are constantly under stress, it can weaken your immune system and make you more susceptible to illnesses and infections. This is because stress hormones can suppress the activity of your immune cells. So if you are already sick, stress can make it worse and if you are healthy, stress can make you more likely to get sick.
Weight gain
When you are stressed, your body releases a hormone called cortisol. Cortisol is also known as the “stress hormone” because it helps your body deal with stressful situations. One of the ways it does this is by increasing your appetite so that you have more energy to deal with the stressor. This can lead to weight gain, particularly around your midsection.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition where your bones become weak and brittle. This can be caused by a lack of exercise, a poor diet, or hormonal changes. However, stress can also contribute to osteoporosis. When you are stressed, your body releases hormones that can cause your bones to break down faster than they can rebuild themselves. This can lead to bone loss and an increased risk of fractures.
Diabetes
Chronic stress can also lead to diabetes. This is because when you are under stress, your body releases hormones that can raise your blood sugar levels. If this happens over a long period of time, it can lead to insulin resistance and type II diabetes. Diabetes is also an increased risk for heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
Chest pain
Stress can also cause chest pain in some people. This is because stress can tighten the muscles in your chest and this can lead to a feeling of tightness or pain. Sometimes this chest pain may be mistaken for a heart attack. There may be also other physical symptoms like shortness of breath, sweating, or a racing heart.
If you are experiencing any of these effects, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you find ways to manage your stress and protect your health.
How To Manage Physical Effects of Stress?

Managing the physical effects of stress is a matter of first identifying the stressors in your life and then taking steps to minimize their impact. To do this, it can be helpful to:
Avoid Tabacco or Alcohol
Tabacco or alcohol can make the physical effects of stress worse. Also, try to limit your intake of caffeine as it can also make stress worse. Also, try to get enough sleep as this can help your body recover from the physical effects of stress. Alcohol sometimes makes it difficult to fall asleep and caffeine can make it difficult to stay asleep.
Exercise
Exercising is one of the best ways to manage stress. It helps your body release endorphins, which are hormones that can improve your mood. Exercise can also help you sleep better and reduce the physical effects of stress. Sometimes there may be pain with exercise, but it is usually temporary.
Yoga
Yoga is a form of exercise that can help you relax both your mind and body. Also, Yoga can help improve your flexibility, strength, and breathing. It can also help reduce the physical effects of stress by helping you focus on your breath and being in the present moment. Yoga can also help you sleep better.
Eat Healthy Diet
One of the best ways to take care of yourself is to eat a healthy diet. This means eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also means limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and alcohol. Eating a healthy diet can help you sleep better, have more energy, and reduce the physical effects of stress.
Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is important for both your physical and mental health. When you don’t get enough sleep, it can make the physical effects of stress worse. It can also lead to moodiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Aim for seven to eight hours of sleep each night. If you have trouble sleeping, talk to your doctor as there may be underlying medical conditions.
Talk to Therapist
If you are struggling to cope with the physical effects of stress, it may be helpful to talk to a therapist. A therapist can help you identify the stressors in your life and find ways to manage them. They can also help you learn how to cope with the physical effects of stress.
Take Care of Yourself
It is important to take care of yourself both physically and emotionally. This means eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly. It also means taking time for yourself to relax and do things that you enjoy. When you take care of yourself, you are better able to cope with stress.
Conclusion
Stress is something that we all experience at one point or another in our lives. And while a certain amount of stress can be beneficial, too much stress can have serious consequences on our health. If you’re feeling overwhelmed by stress, it’s important to take steps to manage it in order to protect your physical and mental health.
Sometimes there may be underlying health conditions that are contributing to your stress levels. If you’re concerned about the amount of stress you’re experiencing, be sure to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if there are any underlying health issues that need to be addressed. There are many things you can do to manage stress and improve your overall wellbeing. Exercise, meditation, and spending time in nature are all great ways to reduce stress. Make sure to find an activity or activities that work for you and make time for them each week. Taking care of yourself is important.
For more information, please contact MantraCare. Stress can have both physical and mental effects on the body, leading to negative consequences such as anxiety, depression, and even physical illnesses. If you have any queries regarding Online Stress Counseling experienced therapists at MantraCare can help: Book a trial Stress therapy session