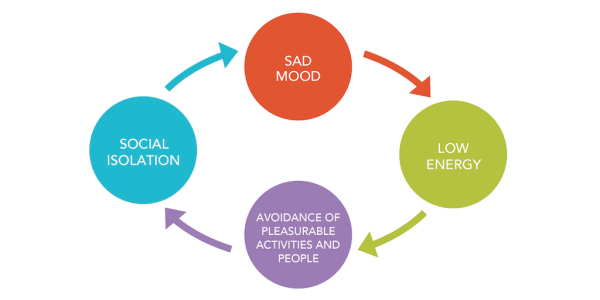
Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) is a form of psychological treatment designed to help individuals struggling with depression, anxiety, and other related disorders. This evidence-based approach focuses on increasing engagement in enjoyable and meaningful activities. By doing so, BAT aims to improve overall mood, functioning, and well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the core principles of Behavioral Activation Therapy, and explore its various components. And discuss how it can be effectively used to enhance mental health.
Contents
What Is Behavioral Activation Therapy?
Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy approach. It is designed to help individuals overcome depression, anxiety, and related mental health challenges. It focuses on identifying and modifying unhealthy behavioral patterns that contribute to the maintenance of negative emotions. Through BAT, individuals learn to increase their engagement in activities that align with their values and interests while reducing avoidance behaviors. Ultimately, promoting a more balanced and fulfilling life.
BAT is grounded in the principles of behaviorism. And asserts that an individual’s mood and emotional well-being are closely tied to their actions and the environment. Helping individuals make changes in their behaviors and daily routines aims to alleviate symptoms of mental conditions. And improve overall functioning and well-being. This therapy has been proven to be effective for various populations and can be tailored to meet the unique needs and goals of each individual.
What Are The Key Principles Of BAT?
The key principles of Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) revolve around understanding and modifying an individual’s behaviors. These principles include:
- Identifying Values and Interests
A crucial step in BAT is identifying an individual’s core values and interests. As these serve as the foundation for choosing meaningful and enjoyable activities to increase engagement.
- Increasing Rewarding Activities
BAT encourages individuals to engage in activities that align with their values and interests. This can lead to a sense of accomplishment, pleasure, and improved mood.
- Activity Scheduling and Structuring
A central component of BAT is developing a structured activity schedule that promotes a balance between work, self-care, and leisure activities. This structure can help individuals gradually build a consistent routine that fosters mental well-being.
- Identifying and Overcoming Barriers
BAT involves recognizing the obstacles that may hinder behavioral changes and working on strategies to overcome these barriers. Such as addressing negative thoughts and building motivation.
- Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Goals
In BAT, individuals are encouraged to track their progress and evaluate the effectiveness of chosen activities. And adjust their goals as needed to ensure continued improvement in mood and functioning.
- Relapse Prevention and Maintenance
Finally, this therapy aims to equip individuals with the skills and strategies needed to maintain the gains made in therapy. And prevent relapses into depression or anxiety.
By incorporating these key principles, Behavioral Activation Therapy focuses on empowering individuals to take control of their mental health. Hence, it will create lasting and positive changes in their lives.
How Is BAT Differs From Other Therapies?
 Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) differs from other therapies in several key ways:
Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) differs from other therapies in several key ways:
- Compared to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), BAT focuses primarily on modifying behavioral patterns and environmental factors, with less emphasis on cognitive restructuring. It offers a more straightforward, action-oriented approach.
- In contrast to Psychodynamic Therapy, which explores unresolved past experiences and unconscious processes, BAT is a present-focused therapy that emphasizes the importance of current behaviors and environmental factors in shaping emotions.
- While both BAT and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) share a focus on values and taking action, BAT places more emphasis on changing behavioral patterns and environmental factors to improve mood. ACT, on the other hand, emphasizes psychological flexibility and mindfulness.
These distinctions make BAT a unique and effective option for individuals seeking a practical, action-oriented approach to improving their mental health.