Contents
What Is Cognition?
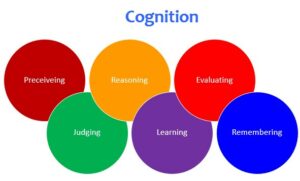 Cognition is the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses. It’s your brain’s ability to recognize patterns in your environment, think critically about what you’re seeing, hearing, and feeling – a vital skill for children as they explore the world around them.
Cognition is the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses. It’s your brain’s ability to recognize patterns in your environment, think critically about what you’re seeing, hearing, and feeling – a vital skill for children as they explore the world around them.
It has two common meanings:
(1) the act or process of knowing; knowledge
(2)all the intellectual faculties collectively, including judgment, reason, memory, imagination.
Cognition is the mental process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses. Children are capable of cognitive development from birth to adulthood, forming new connections in their brains that will allow them to learn and grow.
There are many different aspects of cognition, including but not limited to:
Attention: The ability to focus on a specific task or activity.
The ability to focus on a specific task or activity. Memory: The ability to store and recall information.
The ability to store and recall information. Perception: The process of interpreting what one sees, hears, tastes, smells, and feels.
Language: The ability to understand and use spoken or written words that represent objects or actions as well as the ability to combine those symbols with grammar.
Cognition Development

Infants are born with undeveloped cognitive abilities that are gained through the maturation of the brain, sensory development, and input from an individual’s social surroundings. Visual perception begins almost immediately but can last for up to six months. Infants gain motor skills at two to three months old by holding their heads up, rolling over, and sitting up. Babies also learn how to communicate through crying, cooing, and laughing by the end of their first year.
As humans grow so do their cognitive abilities. It is important for a child to understand how their body works, language, and social cues in order to develop empathy. Cognitive development occurs over a lifetime and includes changes in the nervous system, environment, culture, reasoning skills, problem-solving methods, and memory abilities. Children are not provided with all of these cognitive abilities at birth; they are acquired slowly over time.
Older children are able to think about abstract concepts, reason and problem solve. They can also understand other people’s points of view, empathize with them and cooperate in social situations. Adolescents develop the ability to plan for the future and think about what they want in life.
It is important for parents to provide a nurturing environment for their children in order to encourage cognitive development. This includes talking with them, reading to them, and letting them explore their surroundings. Parents should also be aware of the different stages of cognitive development so they can provide appropriate stimuli.
How Does Cognition Works?
Cognition is composed of many different aspects. The aspects are not neatly separated into compartments in terms of labor division. There are seven major types of cognition that constitute cognition in general: sensation, perception, conceptualization, symbolic thought or language (including art), imagery (pictorial thinking), memory, and related processes such as forgetting, retention and reproduction. These cognitive processes are interwoven with one another in many complex ways, and different classifications have been proposed.

Sensation– This is the process of taking in information through the senses. Perception- This is the interpretation of sensory information.
Conceptualization– This is the ability to think about objects and concepts abstractly.
Symbolic thought or language– This includes using words and symbols to represent ideas, as well as using language to communicate.
Imagery (pictorial thinking)– This involves a viewer’s ability to form mental images.
Memory– This is the process of retaining and recalling information. Related processes include forgetting, retention and reproduction.
Cognition can be classified into two major types: automatic cognitive process and controlled cognitive process. The automatic cognitive process allows us to carry out activities without thinking consciously about them. The controlled cognitive process is where we need to use our conscious effort to think about what we are doing.
There are also two types of controlled cognitive processes- primary control and secondary control. In primary control, the person is in direct contact with the object or task that they are trying to understand or manipulate. In secondary control, the person is not in direct contact with the object or task but uses their knowledge and understanding of it to guide their actions.
How Do We Learn New Information?

There are three main ways that we learn new information: through sensation, perception, and conceptualization.
Sensation
The sensation is the process of taking in information through the senses.
When we take in new information through sensation, we are directly aware of it. For example, when we see a red apple, we are aware of the color red and the shape of an apple.
Perception
Perception is the interpretation of sensory information. When we take in new information through perception, we interpret it based on our past experiences. For example, when we see a red apple, we may think of it as being a fruit that is edible.
Conceptualization
Conceptualization is the ability to think about objects and concepts abstractly. When we take in new information through conceptualization, we are not aware of it directly. For example, when we think about the color red, we are not aware of the color red as a physical object.
The three ways of learning new information work together to help us understand the world around us. The sensation provides us with basic information, perception helps us to assign meaning to this information, and conceptualization helps us to think about abstract concepts.
Evolution Of Cognition In Humans
There are many different theories on how cognition evolved in humans. One popular theory is that there was a cognitive explosion sometime around 50,000 years ago. This is when humans started to develop more complex forms of cognition, such as the ability to think symbolically and communicate through language.
Some researchers believe that the cognitive explosion was due to the development of new brain structures, such as the frontal cortex. Others believe that it was due to the emergence of new behaviors, such as tool-making. There are many different theories regarding how children learn and develop over time. Piaget’s theory of cognitive development is one of the most accepted theories in psychology because it can be used to explain how children think, act and reason. The process that follows consists of six stages that all children move through as they gain knowledge.
The brain is constantly making new connections as a person learns and experiences new things. This is why it is important for children to be exposed to a variety of activities, cultures, and languages. The more different types of information that are introduced, the more connections the brain will make. This helps to build a strong foundation for cognitive development.
Cognition For Social Work And Families
 Cognition is extremely important when working with clients and families. When considering the onset of an illness or disorder, it is important to consider how cognition has developed in the client. For example, in early childhood, if there was poor cognitive development due to malnutrition, this may affect the client’s ability to learn and process information as an adult.
Cognition is extremely important when working with clients and families. When considering the onset of an illness or disorder, it is important to consider how cognition has developed in the client. For example, in early childhood, if there was poor cognitive development due to malnutrition, this may affect the client’s ability to learn and process information as an adult.
When working with families, it is important to consider the family’s cognitive dynamics. This includes how family members think about each other, communicate with each other, and interact with their environment. Families that are able to effectively communicate and interact in a healthy way are more likely to have positive outcomes. However, if there are problems with cognition within the family, it can lead to dysfunction and conflict.
Cognition is important for social workers because it affects how clients take in new information. If a client has problems with any of the three types of cognition, then they may have trouble learning new information. For example, if a person has perception problems, they may not be able to understand the information that they are taking in. If a person has conceptualization problems, they may have difficulty understanding abstract concepts.
Cognition is also important for social workers because it affects how clients interact with their environment. If a client has cognition problems, then they may not be able to interact with their environment in a healthy way.
Conclusion
Knowing how the human brain works and what it needs to function at its best can help you make better decisions in your marketing strategy. Remember that understanding cognitive neuroscience principles goes beyond just considering the onset of an illness or disorder, but also includes a person’s ability to learn new information and interact with their environment.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session


