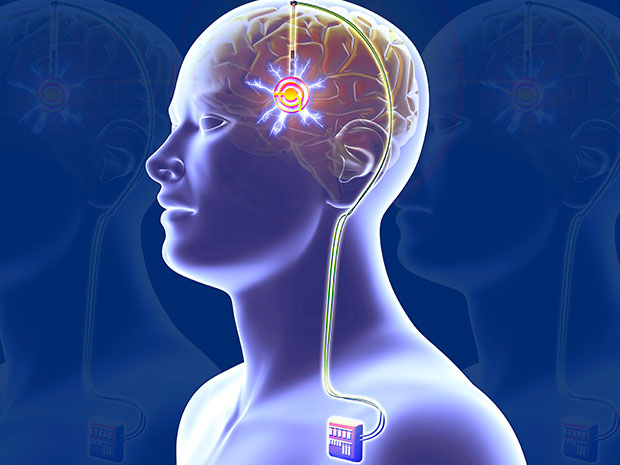
Transcranial stimulation therapy (TST) is a procedure that uses electric currents to stimulate the brain. This drug treats mental health issues but also can help people without any problems. TST involves placing electrodes on the scalp and delivering an electrical current to specific regions of interest. Changes in neural activity within these regions can lead to improved cognition or mood disorders.
Contents
- 1 Meaning Of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy
- 1.1 How does Transcranial Stimulation Therapy Works?
- 1.2 Benefits Of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy
- 1.3 How To Start Transcranial Stimulation Therapy?
- 1.4 What To Expect During Transcranial Stimulation Therapy?
- 1.5 How Will I Know If Transcranial Stimulation Therapy Is Working?
- 1.6 Is Transcranial Stimulation Therapy Safe?
- 1.7 What Are the Potential Side Effects?
- 1.8 What Are the Risks?
- 1.9 Who Is A Transcranial Stimulation Therapist?
- 1.10 Who Is A Transcranial Stimulation Patient?
- 1.11 Qualities Of A Transcranial Stimulation Therapist
- 1.12 Limitations Of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy
- 2 Conclusion
Meaning Of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a technique that uses electricity to stimulate the brain. This medicine treats mental health problems as well as those without any issues. TMS entails placing electrodes on the scalp and delivering an electrical current to targeted regions of interest. Changes in neural activity inside these regions might lead to enhanced cognitive or emotional function.
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change itself throughout a person’s life and this treatment can enhance it even further. TST has been used for more than 100 years. People have just recently started to see how it can help patients who have severe depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and anxiety. This medicine can be used for other conditions too, like ADHD and PTSD.
How does Transcranial Stimulation Therapy Works?
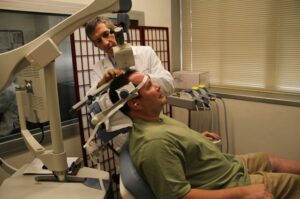
The way that transcranial stimulation therapy works are by sending an electrical current through the brain. This current will then stimulate the neurons in the brain which will cause them to fire. When the fire, this will create a change in the plasticity of the brain which will help to improve its function. Not only that but it can also help to increase the number of synapses between different cells in the brain.
One study found that people who received TST showed an increase in cortical thickness after just four weeks of treatment. This means that the brain was able to do both things which are changing its function and making parts bigger.
The study compared two groups of people, one who received TST for four weeks and another who did not receive any treatment at all. They found that those who had been treated with TST showed an average increase in cortical thickness by 0.023%. Those who hadn’t received any treatment showed a decrease in cortical thickness by -0.003% over the same period. This is an article about how TES (Transcranial Electrical Stimulation) can help with your brain. It can also help if your brain is hurt or has a disease.
Benefits Of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy

These are the benefits of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy are:
- Enhances memory and learning: One of the most well-known benefits of TST is that it can improve memory and learning. Dr. Cohen Kadosh from the University of Oxford found that transcranial stimulation improved memory in adults when they were trying to remember a sequence of numbers.
- Boosts cognitive performance: TST may help people with their brains. They can do better in school and be more focused. One study showed that the people who got the Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) for 5 days had better working memory and reaction time than those who didn’t.
- May help with depression: TST has also been shown to help with depression and anxiety, as well. In a study, some patients with major depression were found to get better when they took TST combined with medication.
- Acts as a treatment for brain injuries: Transcranial Stimulation Therapy can be used to help people who have brain injuries like strokes and TBI. People who have a brain injury and recover from it may be able to use a machine that sends electricity to their brain. This will help them with their recovery.
- An anesthetic during procedures: TST is helpful to adults with certain medical problems. It also helps children during medical procedures. In a study published in the journal Anesthesiology, Dr. Lidia Zaremba and her colleagues found that TST helped reduce anxiety levels and the need for sedation in children before procedures.
- Reduces stress and anxiety: Additionally, TST may be able to help reduce stress and anxiety. A study by two doctors has found that when used on mice with high levels of anxiety, Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) was able to lower their stress levels.
- Improves sleep: You can use transcranial stimulation to help you sleep better. There are a variety of ways to do this!
How To Start Transcranial Stimulation Therapy?
The first step is to find a therapist who specializes in transcranial stimulation therapy. You can ask your doctor for referrals or do some online research to find a therapist in your area.
Once you’ve found a therapist, you’ll need to schedule an appointment for an evaluation. This will help the therapist determine if transcranial stimulation therapy is right for you and how much treatment you may need.
What To Expect During Transcranial Stimulation Therapy?
Each session of transcranial stimulation therapy will last around 30 minutes. The therapist will place electrodes on your head and use a machine to deliver electrical current to your brain.
You may feel some mild discomfort during the treatment, but it should not be painful. Some people experience a tingling sensation or a sense of warmth.
After each session, you may feel tired and have a headache. These side effects should go away within a few hours.
How Will I Know If Transcranial Stimulation Therapy Is Working?
It can take some time to see results from transcranial stimulation therapy. You might not see any changes right away, but over time you should feel better. You will have more energy and be able to focus better.
If you’re not seeing any improvements after several sessions, the therapist may recommend discontinuing treatment.
Is Transcranial Stimulation Therapy Safe?
Transcranial stimulation therapy is considered safe for most people when used under the guidance of a doctor. Your doctor will be able to tell you if transcranial stimulation therapy is safe for your specific condition and health concerns.
People who have devices in their body, like a pacemaker or defibrillator should talk to their doctor before they get transcranial stimulation therapy.
What Are the Potential Side Effects?
Some people experience side effects during treatment that go away after they’re done receiving it. These include:
- headache
- scalp discomfort
- nausea
- tingling sensation in the face or extremities
- sleepiness/drowsiness
- fatigue (feeling very tired)
- agitation (restless feelings)
If you experience any of these side effects, let your therapist know.
What Are the Risks?
Transcranial stimulation therapy is safe for most people when used under the guidance of a doctor. Some risks might happen during or after treatment like:
Seizures
There are some cases in which people who had never had seizures before started having seizures while they were taking antidepressants. They also did transcranial stimulation therapy. This risk is very low if you do not have epilepsy or another disorder associated with seizures. If you feel like something might be wrong during your session, don’t worry too much. It will go away quickly and that feeling should not affect your daily life. Severe headaches can happen due to an increase in blood flow to the brain, however, they usually go away within a few hours of treatment.
Skin burns
Rarely, skin burns have been reported from the use of transcranial stimulation therapy. If this happens, stop using the device and contact your doctor.
There is also a very small risk that you could experience a seizure if you have epilepsy or another disorder associated with seizures. You should talk to your doctor before starting transcranial stimulation therapy if you have any history of seizures.
If you’re considering transcranial stimulation therapy, be sure to talk to your doctor first to see if it’s right for you. Transcranial stimulation therapy is a good way to help with many problems. There are risks, but also benefits. Make sure you know about both when deciding if this is the right thing for you.
Who Is A Transcranial Stimulation Therapist?

A transcranial stimulation therapist helps patients to improve their lives by stimulating the brain. These therapists are experts in the brain. They work with doctors and other medical specialists. In some cases, these individuals may also be called cognitive or behavioral therapists.
Who Is A Transcranial Stimulation Patient?
People who suffer from neurological disorders, mental illness, or cognitive impairments are potential patients for transcranial stimulation therapy. People may have other conditions besides autism. For example, people might have attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Parkinson’s disease, dementia, anxiety disorders, and posttraumatic stress syndrome. Some medical professionals have noticed that tDCS can help to treat various types of addiction including alcoholism or drug abuse.
Qualities Of A Transcranial Stimulation Therapist
A transcranial stimulation therapist must have advanced knowledge of neuroscience and neurology to properly treat their patients. They should be able to recommend the best course of treatment for each patient based on his/her individual needs. Doctors should do many tests before they can help fix someone’s brain. In some cases, these therapists may provide training for people to change their brain waves. They might do this by making someone play video games or watch TV shows. A good therapist will work with you to find a solution. They are innovative and will work on new ideas for you.
Limitations Of Transcranial Stimulation Therapy

- Transcranial stimulation is not a cure for every condition and it cannot help to improve brain function in all patients. Thus, medical professionals must carefully consider potential risks such as seizures before recommending this type of therapy.
- Furthermore, tDCS can only work if the patient does what the therapist tells them to do. They need to take part in cognitive exercises or practice techniques at home between sessions with their therapist.
- Sometimes, when you get the treatment with the machine, you might feel like it’s burning. The redness around the area and headaches can also happen.
- Some people have felt depressed after a transcranial stimulation session. But most of these symptoms go away after the session has ended.
Conclusion
Transcranial stimulation therapy is an experimental treatment that uses electromagnetic pulses to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. The idea behind TST is that it helps people with depression, OCD, and schizophrenia. There are many studies on this new treatment. We do not have enough data to know if it is more effective than medication or cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, some patients have reported significant improvements when using TST over traditional therapies alone. Researchers hope their work will lead to more understanding about how different parts of the brain hamper by this therapy process.
If you want to sign up for transcranial stimulation, talk to your doctor first. They will tell you about the risks before you make any decisions. You may want to talk to a therapist who can help you with tDCS.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session