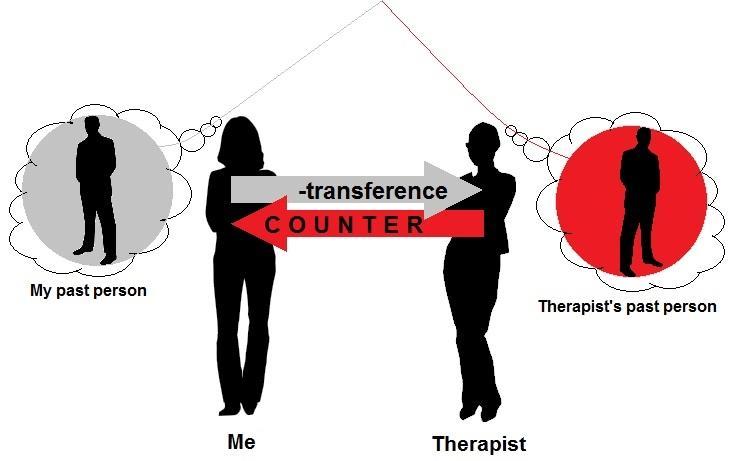
Countertransference is when the therapist looks like they are feeling what the patient feels. People use psychotherapy to understand themselves and others. People who are in therapy may also need it. This blog post is about countertransference. It is what therapists feel when they are with their patients. This will help them better understand their patients and themselves.
Contents
What Is Countertransference?

Countertransference is when the therapist begins to feel emotions for their client. This might happen because of the therapeutic relationship. Therapists can have feelings that are similar to the person they are helping. The therapist should know these feelings and manage them. They should not confuse therapy sessions.
The upside to countertransference is that it can help the therapist understand their client better. It can also help them to develop a more personal connection with their client. This can be helpful in terms of therapy sessions. The therapist will be able to understand their client better. This could lead to positive results.
Countertransference is not always a good thing, but it can be helpful in some situations. It is important for the therapist to be aware of their feelings and manage them properly. This will help to ensure that the therapy sessions are effective.
Types Of Countertransference
Types Of Countertransference
There are several different types of countertransference. They depend on the feelings that therapists have for their clients. This can range from emotions like love, hatred, or anger to embarrassment and disgust. There are also times when people might feel too close to their clients or disconnected from them entirely.
People who go through therapy sessions should know what they are getting themselves into. Therapists should also be able to manage their countertransference and use it in a positive way. This can help make therapy sessions more effective for everyone involved.
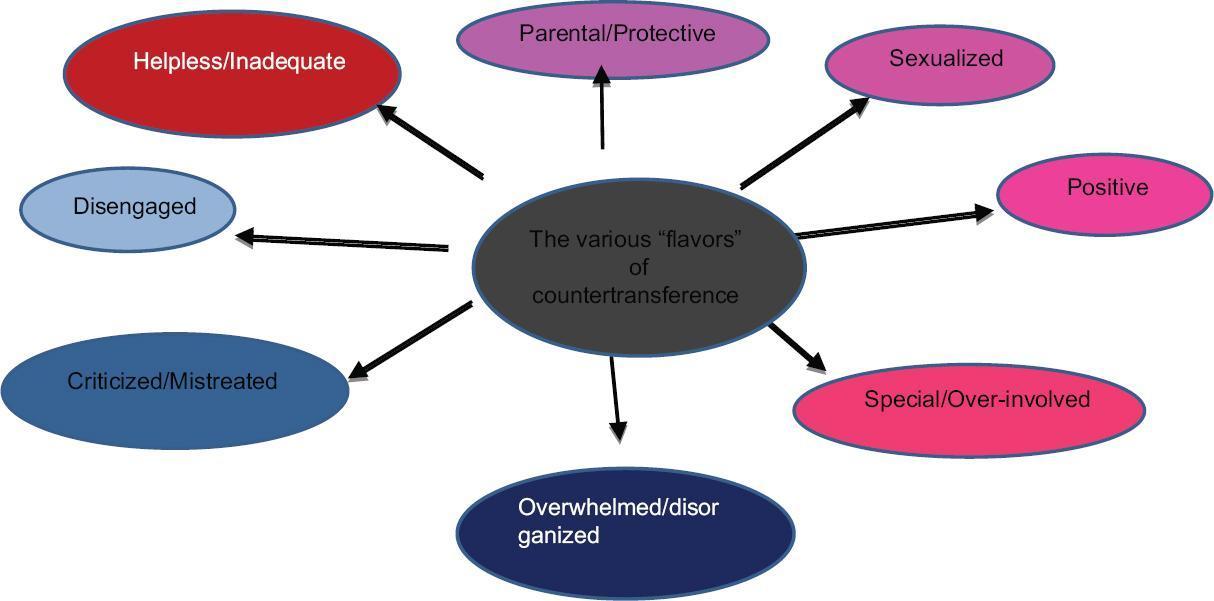
Flavours Of Countertransference
- Parental: This is when the therapist begins to feel like a parent for their client. They might start to feel responsible for them and want to take care of them.
- Sexualized: This is when the therapist begins to feel sexual attraction or arousal for their client.
- Positive: This is when the therapist begins to feel positive emotions for their client. They might feel happy, excited, or proud of them.
- Over-involved: This is when the therapist becomes too involved in their client’s life. They might start to feel like they are a friend or even a guardian angel.
- Disorganized: This is when the therapist cannot focus on their client. They might be distracted by everything in their life, even things that have nothing to do with therapy sessions.
- Self-disclosure: This is when therapists feel comfortable discussing personal information about themselves during therapy sessions. If you are not careful, this can lead to the client feeling uncomfortable.
- Mistreated: This is when therapists feel like they are being mistreated by their clients. They can begin to feel angry, annoyed, or even disgusted with them.
- Disengaged: This is when the therapist becomes disconnected from the client. They might stop feeling any emotions for them and feel like they are just another person in the room.
- Helpless: This is when therapists feel like they do not have control over their client. They might begin to feel powerless and overwhelmed by the situation that they are in.
- Unaware: This is when therapists do not realize what countertransference feels like for them. If you cannot identify your feelings, it will be difficult for you to manage them properly during therapy sessions.
Countertransference is a term that is often used in psychology. It refers to the emotions that therapists feel for their clients. This can be anything from love and care to anger and hatred. Therapists should be aware of these feelings and manage them properly. If they do not, it can lead to negative results during therapy sessions.
Signs Of Countertransference
There are a few signs that can indicate that the therapist is experiencing countertransference. These signs might include:
- Feeling overwhelmed by emotions: If the therapist is feeling overwhelmed by their emotions, it might be a sign of countertransference. They should not let these feelings get in the way of therapy sessions.
- Losing track of time: If the therapist loses track of time with their client, this can mean they feel connected to them. This could mean that there is a strong emotional connection.
- Having physical reactions: If the therapist experiences physical reactions such as sweating, shaking, or feeling sick, this could be a sign of countertransference. They should take steps to manage these feelings.
- Feeling sexually attracted to the client: This is not a common reaction, but it can happen. The therapist should take steps to manage these feelings.
- Becoming defensive when discussing the client with others: If the therapist has a strong emotional reaction when discussing their client, it might mean they have feelings for them. This could be countertransference.
- Being overly protective: Therapists should not feel like they need to protect their clients from other people in their life. They do not need to take care of them all the time and this can indicate that there is countertransference.
- Having trouble separating personal feelings from professional ones: If the therapist is having trouble separating their personal feelings from their professional ones, it might be a sign of countertransference.
- Developing strong feelings for the client (either positive or negative): Therapists should not develop strong feelings for their client either positive or negative. This could result in countertransference and it is important to manage these feelings properly.
Countertransference can be a good thing or a bad thing, depending on the situation. It is important for the therapist to be aware of their feelings and manage them properly. This will help ensure that therapy sessions are effective.
Causes Of Countertransference
There are different reasons that countertransference might develop. These include:
- Personal problems in the therapist’s life: If the therapist is struggling with personal problems, it could affect their client’s work. Therapists need to take care of themselves and do therapy sessions well. Therapists have feelings too that they need to manage.
- The therapeutic relationship itself: The therapist-client relationship can be a cause of countertransference. If the therapist does not manage their feelings properly, they can have problems in their relationship with the patient.
- Transference: Transference can also be a cause of countertransference. This happens when the client transfers their feelings to the therapist. If this happens, it is important for the therapist to manage their feelings properly.
- Personality: A person’s personality can also be a cause of countertransference. It might mean that they feel strong emotions when they are doing therapy sessions. This is why therapists need to take care of themselves. They cannot let these feelings affect them too much during therapy.
Stages Of Countertransference
There are different stages of countertransference that can occur. These include:
- Initial reaction: This is the initial reaction that the therapist has to their client. It might be positive or negative and it can last for a few sessions.
- Working through transference: The therapist will start working through transference during this stage. They will start to manage their feelings better and they will be more aware of them.
- Resolution: During this stage, the therapist is not affected by transference or countertransference anymore. They are able to manage these emotions effectively.
Countertransference can make therapy difficult for both the client and the therapist if it is managed poorly. However, therapists should not be discouraged from continuing therapy. If they take care of themselves and manage their feelings properly, they can continue to provide effective therapy sessions.
Managing Countertransference
Managing countertransference can be difficult, but it is important for the therapist to do so in order to provide effective therapy sessions. There are a few things that therapists can do to manage their feelings:
- Talk about them with other therapists: This can help the therapist understand what they are feeling and why. They can also get help with managing these feelings.
- Seek therapy themselves: Therapists should not feel bad about seeking therapy for their own personal problems. When people working for a therapist get to manage their feelings, it helps them take care of their clients better.
- Take a break from sessions if needed: If the therapist is feeling overwhelmed, they can take a break from sessions. This will help them manage their feelings and come back to therapy with a fresh perspective.
Countertransference is when you feel the same thing as the person you are talking to. It can be good or bad depending on what they say or do. You need to make sure that you are aware of how you are feeling because it could affect your job.
Helping Someone With Countertransference
If a therapist is having countertransference, it can affect the therapy sessions. It might mean that they are not providing effective help to their clients. Therapists need to manage these feelings and talk about them with other therapists. This helps them work better.
It is important for someone working as a therapist to understand how they feel during therapy sessions. When they understand their feelings, they can manage them better. This will help provide effective therapy to their clients.
If you feel bad, you can take a break from therapy sessions until you feel better. Countertransference is when the therapist feels what the patient does. It is hard to manage this feeling and it might affect the therapy sessions. But it is important for the therapist to deal with countertransference so they can provide effective therapy sessions. There are a few things that therapists can do to manage their feelings:
- It is important to be aware of how you feel during sessions. Talk with other therapists and understand the feelings so that they can work better for their patient’s well-being.
- If a therapist feels overwhelmed by emotions, it is okay to take a break from therapy until they are emotionally stable again. This will ensure effective sessions in the long run.
- When a therapist manages their feelings, it will help them provide effective therapy sessions to clients. The best therapists will talk about how they feel when working with patients and what the benefits are for both parties.
Conclusion
To help you understand the concept of countertransference, we’ve provided a brief overview in this article. The following may be difficult to understand. Countertransference is when people have feelings that are not their own. They then react to these projected feelings as if they were true. Understanding how this can affect your relationship with family members or friends can help you avoid any harmful reactions, which may damage your relationships with others who are important to you. If you want more information about countertransference, feel free to explore our blog posts for additional resources on this topic!
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session