Psychology is the study of the mind, and it has been around for centuries. One of psychology’s main goals is to understand how our minds work. This can help us better understand ourselves, as well as others. However, there are many theories in psychology. It can be hard to know which ones are important or relevant. In this article, we will talk about 12 different psychological theories that have helped shape psychology as a whole!
Contents
What Is Theory In Psychology?
The definition of a theory in psychology is “a set of principles that explain how something works”. In other words, a psychological theory is an attempt to understand and explain human behavior. Many theories well-researched, while others are simply ideas that come from some psychologists.
The 12 Theories Of Psychology
Below are 12 of the most important psychological theories. Some are well-known, while others are less famous. However, all of them have played a role in shaping psychology as we know it today!
The Structural Theory Of Personality
This theory is about the three parts of your personality. The id wants things it likes, but does not care about what other people want. It wants everything all the time. The ego only cares about what other people want so it can get more things for them to like it. The superego persuades you to do things that are good and not do bad things because they are bad.
- The id is our primal instinctual desire.
- The ego is our rational side.
- The superego is our conscience, and it represents the morals that we have learned from our parents and society.
The Cognitive Theory Of Personality
As Albert Ellis coined it, it states that our personality consists of three parts: the ego, reality testing, and self-concepts.
- Our ego represents how we see ourselves about others.
- Reality testing involves behaving based on what you think will happen as a result. If you predict something and it does not happen, then you have to change what you do.
- Your self-concept is made up of all the things you know about yourself. It can include things like whether you are intelligent or not. This helps determine how people behave when they interact with others.
The Humanistic Theory Of Personality
People need to reach their full potential and become actualized. This is the Carl Rogers theory. We have a “self-actualizing tendency” which leads us to fulfill our needs for personal growth. When these are met, we can view ourselves more positively. Our goal is self-fulfillment, which involves being totally free of psychological problems or neuroses (e.g., anxiety). We can achieve this through unconditional positive regard from other people, as well as empathy towards them. This allows us to grow psychologically at all stages in life!
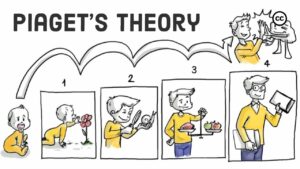
The Theory Of Cognitive Development
This theory was proposed by Jean Piaget. It states that there are four stages of cognitive development:
- the sensorimotor stage (birth to age two),
- the preoperational stage (ages two to seven),
- concrete operational stage (seven and older),
- the formal operational stage (puberty until death).
During these stages, we develop our ability for mental representation and thought. This gives us a better understanding of how things work in life.
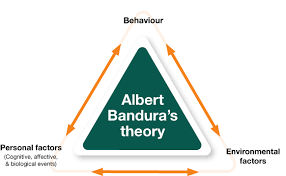
The Social Cognitive Theory
This theory was proposed by Albert Bandura, and it states that we learn from watching others. We observe their behavior, then imitate it. This can be either positive (model) or negative (Bobo doll experiment).
We also have what is called self-efficacy, which is our belief in our own ability to complete a task. This affects how likely we are to engage in certain behavior.
The Attribution Theory
This theory was proposed by Fritz Heider. It states that when we see someone do something, we make an attribution about why they did it. There are three types of attributions:
- internal (the person is doing this because of something within themselves),
- external (the person is doing this because of something outside of themselves), and
- situational (the situation caused the person to act in a certain way).
These help us understand why people behave the way they do!
The Multicultural Identity Development Theory
This theory was proposed by Patricia Hill Collins. It states that there are five stages of multicultural identity development:
- Mastery
- Pre-encounter
- Encounter
- Immersion-emersion
- Internalization
People go through these stages as they learn about their cultural heritage and the cultures of others. This helps them develop a more inclusive identity!
The Stress And Coping Theory Of Motivation
This theory was proposed by Robert Merton, and it says that motivation involves three components:
- Expectancy
- Value/goal importance
- Instrumentality
Expectancy refers to how likely you think something will happen if you try hard enough; this affects what goals we set for ourselves. Value refers to whether the goal seems worthwhile or not. Instrumentality means how successful we will be at doing a task. We also need to think about how much reward we will get.
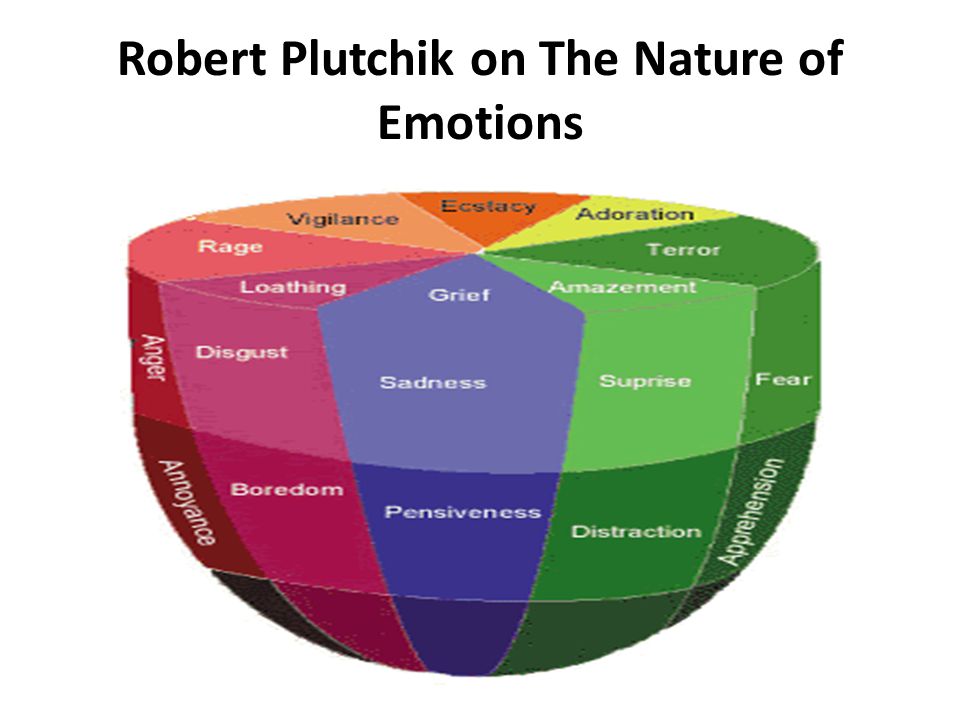
The Theory Of Motivation And Emotion
This theory was proposed by Robert Plutchik. It states that there is an emotion involved whenever motivation occurs:
- Anticipatory (eagerness)
- Comparison (to see what others have done)
- Approach/avoidance (move towards something positive or away from something negative).
Our emotions tell us which goals we want to achieve. The reason is called valence, which means that some emotions feel better than others. If you feel good about something, then it will be easier for you to do that thing.
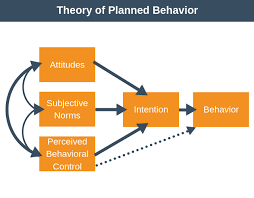
Theory Of Planned Behavior
This theory was proposed by Icek Ajzen. It states that three factors influence our behavior:
- Behavioral intention (the desire to do something),
- Attitude towards the behavior (whether we think it’s good or bad), and
- Social norms (what society tells us is acceptable).
These three factors together determine how likely we are to engage in a certain behavior!
The Social Exchange Theory
This theory was proposed by George Homans. It states that relationships are based on what is called social exchange: giving and taking. We keep track of what we put into a relationship (costs) and what we get out of it (benefits). If the costs outweigh the benefits, then we are less likely to engage in the relationship.
This theory says that people value different relationships differently. They have different exchange rates. You work hard for your money. You know what your job pays you. So you know how much you put into a relationship and how many benefits come out of it too. This helps us understand why people choose who they want as friends or partners!
The Interpersonal Reactivity Index
This test has 28 questions and measures how much you think about other people. There are four subscales within this test:
- fantasy (reflecting on thoughts)
- perspective-taking (imagining what the other person is feeling)
- empathic concern (concern for others’ welfare)
- personal distress (negative feelings towards others).
This scale can tell us how empathetic we are. It can show why some people might not be as good at empathy as others.
How Do These Theories Impact Our Life?
Theories of psychology are used to understand the behaviors and mental processes that occur in human beings. These theories were made by some people who were psychologists. It took some time to develop the theories, but some of them are not as good or recognized as others. Although these ideas might not be 100% accurate, they give us a good idea about why people act the way they do. These ideas can also help us better understand ourselves.
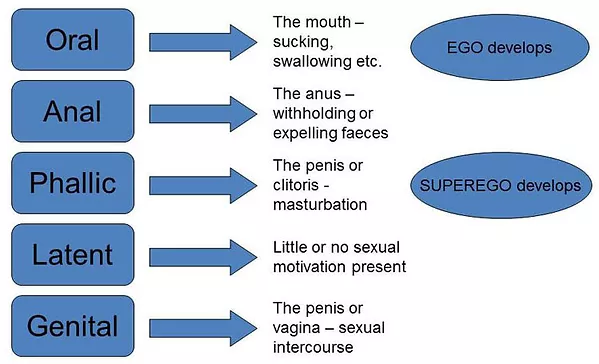
There are many theories about how we develop psychologically. I find Sigmund Freud’s theory to be the most interesting. This theory says that people go through five stages as they grow up. They all change at different rates. Each stage builds upon the last and causes a conflict between the needs of the id, ego, and superego.
Stages
- The first stage is called the oral stage. This is when a baby gets all of its needs met from its mother through breastfeeding or bottle feeding. The child’s mouth is their main source of pleasure at this time. Freud believed that how we eat later in life can be related to our experiences during this stage.
- The second stage is the anal stage. This is when a child starts to learn about discipline and how to control their bladder and bowel movements. They may start to become constipated or have diarrhea during this time. Freud believed that our habits as adults can be related to how we behaved during this stage.
- The third stage is the phallic stage. At this time, a child starts to notice that there are other sexual differences besides being either male or female. When one parent is preferred over the other, it can make children feel angry. The self feels bad about this and is afraid that of punishments because society does not accept sexual thoughts.
- The fourth stage is the latency period. When children are in school during the day, they have less freedom. They can’t explore their sexuality or fight with other kids about it.
- Finally, the fifth stage is adolescence or puberty. This is when all changes in a child’s body take place as they become an adult. During this stage, both the id and the superego are fighting with each other. The id wants to have pleasure but also feels like society will be mad at it if it does so.
Importance Of Theories of Psychology
Theories of psychology serve as the most important tool for psychologists. A theory is a way to organize or understand information. You can find theories in many different areas. These things support your position:
- A definition of what a theory is
- Different theories you might know about already (i.e., psychoanalytic, behavioral)
- Where we find them today (i.e., TV shows like Criminal Minds that reference psychological concepts such as cognitive distortions)
Sigmund Freud created psychoanalysis. Techniques like free association and dream analysis help find unconscious conflicts that people have in their childhood. Freud called these defense mechanisms. Neuroses are included, and he even coined a phrase, “the unconscious.”
This approach is about using behaviorism to understand how humans make decisions. If you put your dog in an experiment, then he will do what you teach him. We can see if rewards are good. He will do better because it’s a reward. This method got criticism for not being able to explain more complex feelings like love. It can still describe simple things like fear, though.
Behavioral psychology studies observable activities rather than internal thought processes; it uses objective experiments which allow us to make causal inferences. Ivan Pavlov fed his dog every time he rang a bell. Eventually, the dog would start to salivate when it heard the bell ring even if there was no food. This is classical conditioning. Operant conditioning is learning through rewards and punishments (punishments like punishment).
This theory comes from social psychology. When we make decisions, we think about the costs and benefits of our relationships with other people. We also look at what our friends and family think! The empathy scale measures how much someone thinks about another person’s feelings. It can help us understand why some people might not be as good at empathy as others. Theories help psychologists understand the information in an organized way that makes sense. A theory is like a map- it helps us find our way around different areas of knowledge. Theories are present at many different places- like TV shows! They explain behavior, feelings, and thoughts. We use theories to better understand the world around us!
Limitations Of Theories of Psychology
Theories of psychology help us to understand concepts that were once unapproachable. It is easy to forget that they are just models, but you should always consider their limitations.
For example, Behaviorism is not always true. It might not happen in the real world. That problem is ecological validity. Some people think that all theories are too simple and focus on one factor at a time. They say that we should consider more than one explanation when we look at something. We should consider these problems whenever we think about psychological phenomena! The key thing here is making sure we do not take these theories too seriously. It can be easy to forget that they are just models!
Conclusion
Theories of Psychology can be difficult to understand, but it’s worth the effort. We hope our blog post has helped you gain a better understanding and that we’ll see you again soon! I know this is your first time reading about theories of psychology. But don’t worry, more posts are coming with tips on how to apply these principles in everyday life. Remember…awareness leads to change so keep learning all you can as often as possible! Stay tuned for future blogs which will cover important topics such as memory, motivation, and intelligence.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session