Acute stress disorder is a mental health condition that is caused by an individual’s response to either traumatic events or when they are faced with the threat of death. Acute stress disorder symptoms include feelings of detachment, intrusive thoughts, and avoidance behaviors. This article will explore acute stress disorder symptoms, treatments, prevention strategies, and more in-depth information about this mental illness.
Contents
What Is Acute Stress Disorder?

Acute stress disorder is when you experience a traumatic event, and it causes intense fear or helplessness. You may also feel numb from the shock of what happened to you. This can happen in children as well as adults. The symptoms are similar to those found with PTSD (posttraumatic stress disorder). However, acute stress disorder does not last nearly as long as PTSD.
Types Of Acute Stress Disorder
There are three types of acute stress disorder. They are:
Acute dissociative reaction
This is when you have a lot of confusion and feel like you’re not in control of your body or thoughts. You may also feel numb or detached from what’s happening around you.
Acute traumatic stress reaction
This is when you have a lot of fear, anxiety, and shock following the traumatic event. You may also feel like you’re in danger, and have nightmares or flashbacks about the event.
Acute grief reaction
This is when you experience a great deal of sadness and anger after a traumatic event. You may also have trouble sleeping, and notice that you’re not interested in your normal activities.
Causes Of Acute Stress Disorder
There is not always a clear cause for ASD. However, some things that may contribute to the development of this condition include:
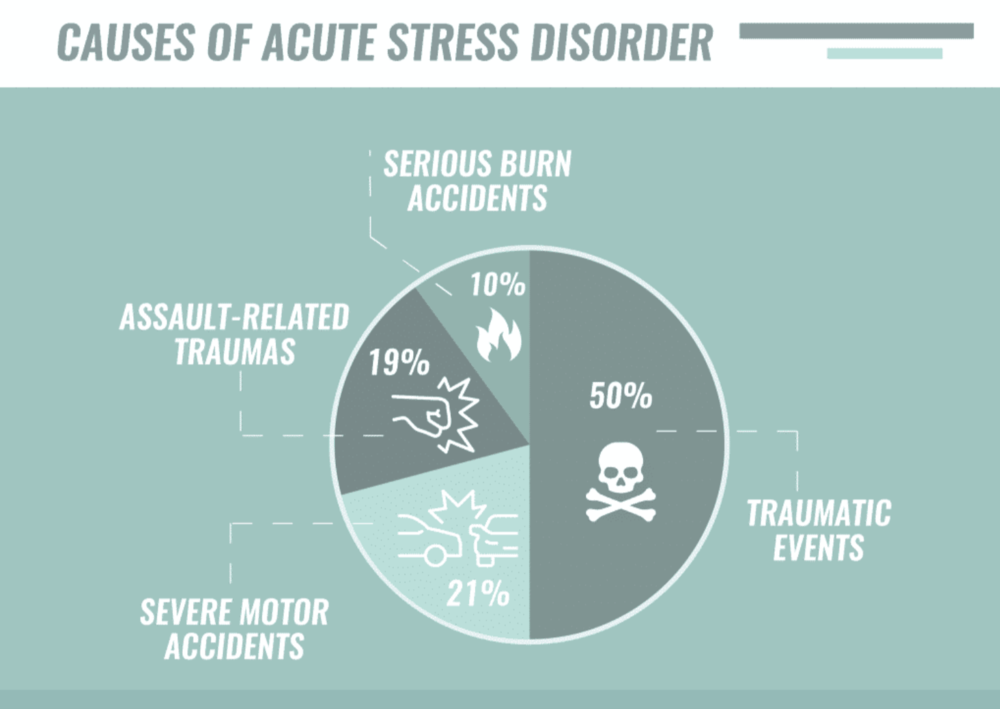
- Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event
- Having little or no support following the traumatic event
- Feeling like you’re in danger after the traumatic event
- Repeated exposure to trauma, such as in war zones
- Having a mental health condition before the traumatic event occurred
NOTE: It’s important to remember that not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop ASD.
In Short
- Traumatic event(s)
- Stressful life events or situations
- History of mental health issues
Risk Factors Of Acute Stress Disorder
There are a few risk factors that can increase your chances of developing ASD. They include:
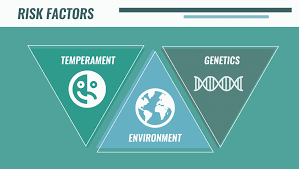
- Having a mental health condition before the traumatic event occurred
- Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event
- Having little or no support following the traumatic event
- Feeling like you’re in danger after the traumatic event
NOTE: It’s important to remember that not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop ASD.
Symptoms Of Acute Stress Disorder
Common Symptoms Of Acute Stress Disorder
- You may feel like what happened was surreal or dreamlike, and it’s hard to believe it really occurred.
- You may have trouble concentrating on things like schoolwork or tasks at work. It could be difficult for you to complete tasks, and you might feel like you’re watching yourself from outside your body.
- You may find that it’s hard to sleep or eat normally. This can be caused by feeling anxious and not wanting to talk about the event.
Specific Symptoms Of Acute Stress Disorder
Sickness
This is often similar to a flu-like illness and can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a general sense of feeling unwell
Nightmares or intrusive memories
These can be extremely vivid and realistic, and often involve the traumatic event itself
Flashbacks
It is reliving the experience in great detail as if it’s happening again
Difficulty concentrating
This may make everyday tasks, such as driving or reading difficult
Difficulty sleeping
This can range from insomnia to frequent nightmares that wake you up in the night
Anxiety and fearfulness
These may be triggered by things like loud noises or sirens for example which remind you of the traumatic event.
How To Diagnose Acute Stress Disorder?

If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, it is important to talk to a mental health professional. They will ask you about your symptoms and how long they have been going on. They will also want to know about any traumatic events that may have happened in your life. It is not easy to diagnose ASD, as it is close to PTSD.
How To Deal With Acute Stress Disorder?
Coping Tips For Prevention Of Acute Stress Disorder
If you are feeling anxious after a traumatic event, there are some things you can do to help prevent ASD from developing.
- Talk about what happened
- Create a plan of coping ahead of time so you know exactly what steps to take in case it happens again
Seek professional help if you are feeling overwhelmed
Recovery Strategies For Acute Stress Disorder
If you are already experiencing symptoms of ASD, it is important to get professional help. You can try some coping strategies until you see your therapist or doctor:
- Seek support from family and friends who understand what you’re going through
- Be mindful about how often and for how long you think about the event
- Limit your exposure to anything that may trigger memories of the event
- Challenge any negative thoughts you are having about yourself or the situation
- Make time for activities you enjoy and relaxants, such as reading, listening to music, or spending time outdoors
NOTE: If you are experiencing any suicidal thoughts, you should seek help immediately. Treatment options for acute stress disorder may include cognitive-behavioral therapy or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR).
Treatment Options For Acute Stress Disorder
There are many different treatment options that can be considered for ASD. Some people may only need one session with a therapist or counselor, while others may want to continue on a more long-term basis.
Some of the options include:
Counseling or therapy
This is a great way to talk about the traumatic event and what happened. It can also help to process any feelings you may be experiencing.
Medication
There are medications available that can help relieve some of the symptoms of acute stress disorder, such as anxiety and fearfulness. However, it is important to speak with a doctor before taking any medication.
Name Of Medications
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Citalopram (Celexa)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro)
NOTE: It is important to speak with your doctor before taking any medications.
Mindfulness or relaxation techniques
These can be helpful in managing the symptoms of acute stress disorder and helping you to feel more relaxed.
In Short
- Professional help
- Counseling or therapy
- Medication
- Mindfulness or relaxation techniques
Therapies For Acute Stress Disorder
There are many different therapies that can be used to help treat acute stress disorder. Some of these include:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
This type of therapy is very structured and works well for people who want a set number of sessions. There will usually be between eight and 12 weekly one-hour sessions.
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT)
This is a type of CBT, which focuses on the way you think about past events and how this affects your feelings now. You will have weekly sessions for six to eight weeks.
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
In EMDR, you will focus on a specific memory while the therapist moves their fingers back and forth in your field of vision. This helps to process the memories in a different way.
In Short
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Cognitive processing therapy (CPT)
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
Professionals On Acute Stress Disorder
If you are feeling anxious or stressed after a traumatic event, it is important to seek professional help. There are many different professionals who can help you if you are experiencing symptoms of ASD. These include:

- Psychologists
- Counselors
- Social workers
- Clinical psychiatrists
When To Seek Professional Help?
If your feelings do not subside within one week or two weeks after the event occurred, speak with a medical health practitioner for further assistance.
There are some factors that professionals look for when determining if someone has this stress disorder. These include:
- Anxiety or fearfulness
- Avoiding thoughts, feelings, or conversations related to the traumatic event(s)
- Repetitive play of the trauma in your mind with terrible images and memories affecting how you feel about yourself now
Conclusion
There are many different treatment options available for acute stress disorder. Some people will only need one session, while others may want to continue with therapy or counseling on a more long-term basis. People often find that the most helpful thing is to talk about what happened and process their feelings in some way. The main goal of treatment is to help you manage the symptoms of this stress disorder and move forward with your life.
For more information, please contact MantraCare. Stress can have both physical and mental effects on the body, leading to negative consequences such as anxiety, depression, and even physical illnesses. If you have any queries regarding Online Stress Counseling experienced therapists at MantraCare can help: Book a trial Stress therapy session


