There are many types of stress in life. All of them can impact your mental and physical health. For example, if you have financial stress, it could lead to anxiety or depression. If you have relationship stress, it may cause anger or resentment. All of these are important to address for your overall well-being. In this blog post, we will discuss the different types of stress that can negatively affect our lives You will also learn how to cope with them better!
Contents
What is Stress?
Stress is a response the body has to any kind of demand. It can be caused by anything, whether it’s mental or physical, and even emotional. Stress isn’t always bad for you. In fact, short-term stress can actually enhance your performance. This is so because it increases alertness and motivation levels while suppressing pain sensitivity. However, chronic stress is a different story. It can have negative effects on the body.
Types of Stress
Broadly, there are four types of stress, which are:
- Acute Stress
- Episodic Acute Stress
- Chronic Stress
- Post Traumatic Stress
You can read about all the different types of stress in detail, further in this article.
Acute Stress

Acute stress is the body’s response to a short-term demand or change. This type of stress can last anywhere from minutes, hours, days, and even weeks. The duration depends on how long you’re exposed to an intense situation. Acute stress occurs when we need to fight off danger such as having a near-fatal experience or completing a marathon.
Symptoms
- Physical Symptoms:– Tightened muscles or muscle tension, chest pain or discomfort, trembling and shakiness, increased heart rate (heart palpitations), sweating more than normal, rapid breaths.
- Emotional Symptoms: Anxiousness fearfulness, feeling overwhelmed or helpless; overwhelming feelings of panic; irritability; restlessness; and/or difficulty concentrating.
Causes
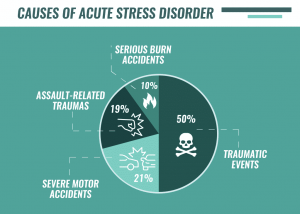
- Physical: Being in a dangerous situation, such as being close to someone or something that could cause you harm.
- Emotional: Getting bad news; thinking about life changes and their possible outcomes (i.e., death of a loved one), getting into an argument with your significant other, academic stress from school.
Treatment
- Medication: Some people with chronic or severe stress may be prescribed medication to help calm them down.
- Relaxation Techniques: Meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, etc. can lower your heart rate and blood pressure. They send more oxygen throughout the body.
Prevention
Some easy ways to avoid acute stress are:
- Staying with a friend or family member when traveling.
- Going outside for at least 30 minutes every day. Exposure to nature can help lower your levels of cortisol It is the hormone that releases during chronic stress and increases your heart rate. This high level of cortisol over a long period of time can lead to a slew of health problems.
Episodic Acute Stress

Episodic acute stress is the body’s response to a single, isolated stressful event. These types of events include traffic accidents and other kinds of emergencies. They may also involve some kind of physical danger. Episodic or time-limited stress can be short or long-term. This depends on how you deal with it emotionally.
Symptoms
Symptoms of episodic acute stress include:
- Muscle tension in the back, shoulders, and neck
- Rapid heartbeat
- Thirst or dry mouth
Symptoms of episodic acute stress typically resolve themselves within about 30 minutes. However, symptoms are likely to return if you do not find a way to manage your emotional response. If symptoms remain after six months, you should see a doctor.
Causes
- Traffic accidents and other kinds of emergencies involve some kind of physical danger.
- Trouble at home or work can cause stress. Any sudden change in your life such as a new job, marriage, divorce, birth, or death of a loved one.
- Health-related issues such as surgery, cancer diagnosis, and treatment can also cause stress.
Treatment
To treat episodic acute stress, it is important to find ways to cope with the emotional experience. Specific therapies that can help include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Interpersonal therapy
If you are suffering from an episode of high levels of stress, relaxation techniques. These techniques include deep breathing or meditation can be helpful in reducing your symptoms. You may also want to consider seeing a therapist.
Prevention
Rather than treating episodic acute stress, it is often more helpful to focus on the ways you can prevent its onset. Some of these include:
- Try to create a daily schedule that allows plenty of time for relaxation and reflection.
- Maintain good sleeping habits by going to bed at around the same time each night. Wake up at about the same time each morning.
- Don’t overload yourself with work and other responsibilities when you are already feeling stressed about something in your life.
- Eat a healthy diet and stay active.
If you are experiencing episodic acute stress, it is important to practice self-care. You can try relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. You may also want to consider seeing a therapist if symptoms continue for more than six months. It can be helpful to create a daily schedule that allows plenty of time for relaxation and reflection.
Chronic Stress

Chronic stress is when your body experiences low-grade demands and threats on daily basis. This may include things, such as traffic jams/delays, having an argument with someone close to you. Working multiple jobs while trying to get by in life can also cause chronic stress. It’s often caused by the pressure you put on yourself to meet all of your own expectations.
Symptoms
Symptoms of chronic stress include:
- Muscle tension in the back, neck, and shoulders
- Rapid heartbeat
- Difficulty sleeping
Chronic stress can lead to serious health problems if left untreated including diabetes, high blood pressure, digestive problems such as irritable bowel syndrome, and heart disease.
Causes
- Overwhelming responsibilities at work, home, or school
- Problems with relationships such as divorce and death
Treatment
To treat chronic stress, it is important to find ways to reduce your emotional response. Specific therapies that can help include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Interpersonal therapy
Prevention
It is often more helpful to focus on the ways you can prevent its onset. Some of these include:
- Setting realistic expectations for yourself and those around you
- Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep at night
- Having strong support from friends and family can also help to prevent chronic stress.
In order to prevent chronic stress from occurring, it is often helpful to set realistic expectations. You can do it for those around you as well as yourself. You should also try eating a healthy diet and staying active. Getting enough sleep at night also prevents chronic stress. Having strong support from friends and family can also help in preventing chronic stress from taking hold of your life.
Post Traumatic Stress
Post-traumatic stress disorder is a mental health condition. It is one of the most dangerous types of stress. It can develop after the experience or witnessing of traumatic events. Traumatic events are war, violent personal assaults like rape and mugging, or natural disasters. When your brain processes what has happened to you, it goes through three stages:
- The first stage occurs right after the traumatic event, usually within two days of it occurring. It’s called hyperarousal.
- The second stage occurs when you experience repeated memories and nightmares about what happened to you or if people in your environment trigger reminders of the trauma
- Finally, the third stage is when you isolate yourself from others and avoid things that trigger your memories.
Symptoms of PTSD
- Flashbacks and nightmares about what happened to you
- Being easily startled or frightened even when there is no threat around
- Feeling as though the world feels unsafe, constantly on guard for danger. You might also experience social withdrawal and isolation from family and friends which can lead to depression. There may be difficulty sleeping due to recurring nightmares or intrusive thoughts which can lead to you feeling tired and irritable.
- You may have a hard time concentrating, making decisions, or remembering things
- Your body might feel tense as the result of becoming easily startled by loud noises
- One might also experience feelings of guilt about what happened or whether it could have been prevented.
- You might also feel like you are always in danger even when there is no current threat. You may constantly be on guard for another attack
Causes of PTSD
- PTSD is caused by severe trauma, especially the type that threatens one’s life or survival.
- Severe childhood neglect and abuse are also associated with PTSD in adulthood.
Treatment of PTSD
Treatment for PTSD can include psychotherapy which includes cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) as well as medications to help reduce anxiety symptoms. Support groups can also help with socialization and grieving.
Prevention of PTSD
If you are experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is important to seek treatment right away. However, there are some things that can be done on your own to reduce stress and anxiety levels before they escalate into full-blown PTSD. Some ways include:
- Having a support system in place with friends or family members who understand what you are going through.
- Managing your time well so you can reduce feelings of being overwhelmed and having too much to do at once. This could include making a list of tasks for the day, prioritizing them, or setting deadlines for yourself when tackling large projects that are due soon
- Getting plenty of sleep every night because stress hormones spike during periods of sleep deprivation
- Practicing meditation or relaxation techniques like deep breathing to help reduce physical symptoms that accompany stress, such as muscle tension and tightness in the chest
- Exercising regularly because it releases endorphins which can relieve feelings of pain and depression. It also boosts your immune system so you are less likely to get sick and miss out on important appointments or events
- Eating a well-balanced diet to get the nutrients you need for your body to function properly. This will also help reduce feelings of fatigue and improve your energy levels
Chronic Stress vs. Acute Stress
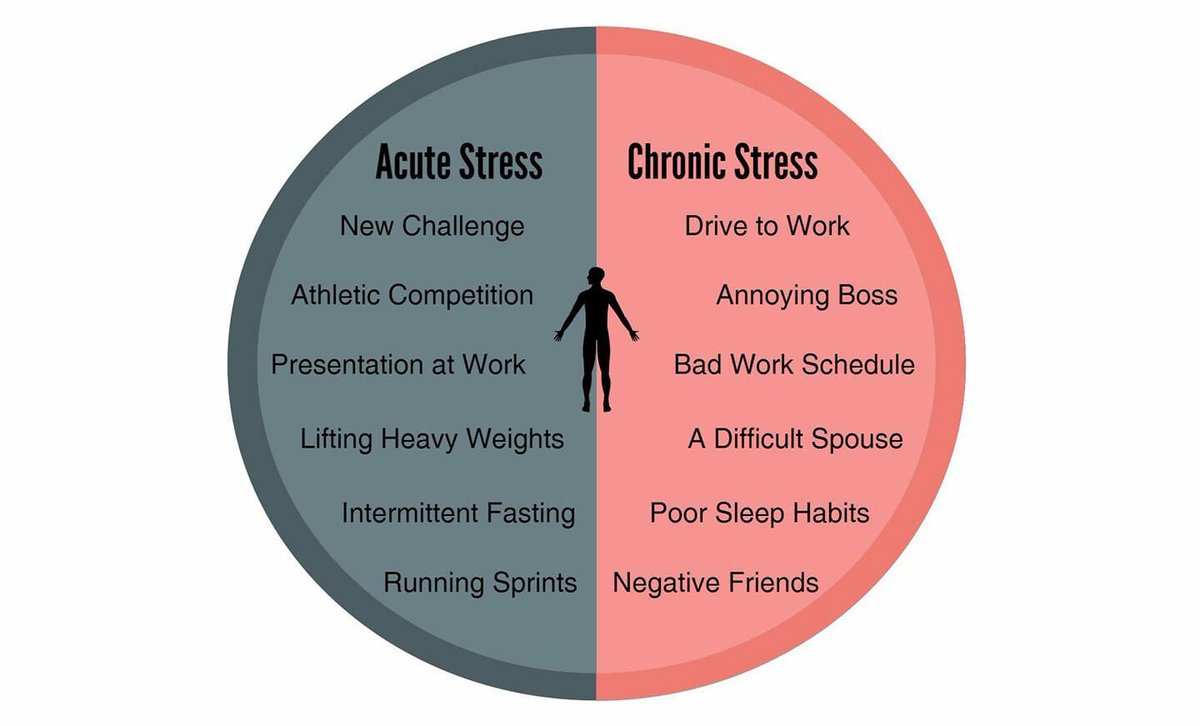
For many people, being able to identify the types of stress in their lives makes it easier for them to cope with difficult situations when they arise. Although both types of stress can impact your mental and physical health if you’re not careful, chronic stress is much more serious and can lead to health problems if left untreated.
Tips for Stress Management

- Exercise is a great way to help manage stress. Exercise gets your blood pumping and releases endorphins. These endorphins have been shown to promote feelings of happiness.
- Listen to calming music or take some time for yourself each day. This way you can practice relaxation techniques. These techniques include activities such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation. However, it’s important not to rely on these techniques alone.
- Maintain good sleeping habits by going to bed at about the same time each night. Also, you should not wake up around the same time every morning as well. You should also try eating a healthy diet, staying active, and getting enough sleep at night.
You can try all the above things if you want to prevent stress from occurring in your life.
In order to manage both episodic acute stress and chronic stress, it is helpful to exercise regularly. You can also listen to calming music or take some time for yourself. It is also important not to rely on these techniques alone. You should try eating a healthy diet, staying active, and getting enough sleep at night.
Stress can be a very unpredictable thing that impacts many people’s lives. However, it is often more helpful to focus on the ways you can prevent its onset. This can keep you from treating symptoms after the stress has already taken hold of your life. Set realistic expectations for yourself. Take help from those who are around you. Stay active, eat healthy food/meals regularly, get enough sleep at night, and have strong support from friends and family. You can prevent stress from negatively impacting your mental health.
Conclusion
We all experience different types of stress, but it’s important to understand what type you’re feeling so that you can take the proper steps for recovery. If your stress is coming from a lack of work-life balance, consider doing things like planning out your day or getting more sleep at night. For those experiencing physical symptoms due to their job, try taking time off and using meditation apps on your phone during stressful moments. There are many ways to help manage your level of stress in order to feel less overwhelmed by life! What kind of stress has been affecting you lately?
For more information, please contact MantraCare. Stress can have both physical and mental effects on the body, leading to negative consequences such as anxiety, depression, and even physical illnesses. If you have any queries regarding Online Stress Counseling experienced therapists at MantraCare can help: Book a trial Stress therapy session



