Contents
What Is Schizophrenia?
 Schizophrenia is a mental illness that causes significant disruption in a person’s psychology, affecting their ability to think, feel and behave. It can manifest as auditory hallucinations or delusions. Learn more about the cause, symptoms, and treatment for this mental illness.
Schizophrenia is a mental illness that causes significant disruption in a person’s psychology, affecting their ability to think, feel and behave. It can manifest as auditory hallucinations or delusions. Learn more about the cause, symptoms, and treatment for this mental illness.
The term schizophrenia refers to a mental illness that causes people to lose touch with reality in some manner. The symptoms of schizophrenia vary from person to person, but it’s likely that someone suffering from this disease would be unable to discern what is real and what isn’t. As a result, how to deal with schizophrenia is all too familiar.
People who suffer from schizophrenia may experience things that aren’t there, believe things that aren’t true, or feel sentiments that aren’t genuine. They may also have difficulties thinking logically and organizing their ideas, making it difficult to communicate clearly. People with schizophrenia frequently have problems with motivation and self-care as well.
Schizophrenia Symptoms
Schizophrenia symptoms can manifest in a variety of ways, and they may affect people in different ways. It’s crucial to note that not all persons who have schizophrenia will experience the same symptoms.

- Persistent depression
- Loss of interest in activities once previously enjoyed
- Lethargy
- Problems with attention
- Decision-making
- Memory
- Social withdrawal
- Decrease in energy levels
Positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms are the three types of signs associated with schizophrenia. A person suffering from the illness may display any number of these sorts of symptoms. The following are the most common indications:
Positive Symptoms
 Hallucinations and delusions are examples of positive symptoms in schizophrenia. Auditory hallucinations, visual hallucinations, and tactile or physical hallucinations are the three types of positive symptoms.
Hallucinations and delusions are examples of positive symptoms in schizophrenia. Auditory hallucinations, visual hallucinations, and tactile or physical hallucinations are the three types of positive symptoms.
Hallucinations: Being afraid of the dark or something, in particular, amnesia, hysteria. There is no cure for this disease; however, some therapies can help a person manage it and live an enjoyable life. People with koro are frequently afraid of the dark (hysteria), hearing strange noises, seeing things that aren’t real (hallucinations).
Delusions: Denial of objective reality is a common characteristic of mental disorders. Denial of objective reality includes things like false ideas about other beings, powers, or events that don’t exist; and strange delusions (for example, believing oneself to be endowed with special abilities). It’s hard to describe odd beliefs as anything less than non-league fantastic.
Negative Symptoms
Negative symptoms are those that interfere with a person’s usual behavior, such as a lack of interest in anything or the inability to feel joyful. Reduced motivation, blunted affect (emotional response), and social withdrawal are examples of negative symptoms.
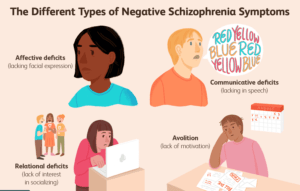
- Lacks of interest in everyday activities
- An inability to feel all emotions fully (as with a flat affect)
- Reduced facial emotions and body language
- Anxiety
- Low energy level
- Deficits in normal emotional reactivity abolished
- Apathy
- Disturbances in attention and concentration;
- Impairment in short-term memory
- Social Cognition
- A lack of pleasure throughout life
Cognitive Symptoms
Cognitive Symptoms Slows reactions to stimuli (slowed thinking); difficulty paying attention or concentrating.

- Difficulty making decisions or solving problems; organizing work or other activities
- Severe memory loss
- Trouble concentrating
- Memory loss
- Difficulty speaking
- Loss of energy
- Very slow movement
- Tiredness or lack of interest in things
Types Of Schizophrenia
There are several types of schizophrenia. Paranoid schizophrenia, catatonic schizophrenia, and undifferentiated schizophrenia are examples of these.
Paranoid schizophrenia
Paranoia schizophrenia is characterized by paranoid beliefs that other individuals are out to get, punish, or deceive them. People with this type of mental illness frequently suffer from excessive paranoia, believing that others are attempting to use, punish, or deceive them. They may be guarded and suspicious and have a difficult time establishing connections.
Catatonic Schizophrenia
 People with catatonic schizophrenia may experience excitement (agitation), daze, waxy flexibility (rigidity), agitation, perplexity, and aimless fidgeting. This type of schizophrenia is frequently associated with a reduction in activity and social withdrawal. Catatonic schizophrenics may engage in unusual movements such as staring off into space for lengthy periods.
People with catatonic schizophrenia may experience excitement (agitation), daze, waxy flexibility (rigidity), agitation, perplexity, and aimless fidgeting. This type of schizophrenia is frequently associated with a reduction in activity and social withdrawal. Catatonic schizophrenics may engage in unusual movements such as staring off into space for lengthy periods.
Undifferentiated Schizophrenia
The schizophrenia of this sort is the most prevalent form and is identified when a person fails to fulfill any of the other subtypes’ diagnostic criteria. This type of schizophrenia is characterized by a range of behaviors, including delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and thinking, and negative symptoms such as social isolation or lack of feeling.
Disorganized Schizophrenia
 People with disorganized schizophrenia have a hard time organizing their thoughts and activities. They may have disorganized speech, thinking, and conduct. They also have a hard time relating to others and are uninvolved in what’s going on around them. Another indicator is that they might display a significant loss of interest or enthusiasm, as well as a drop in goal.
People with disorganized schizophrenia have a hard time organizing their thoughts and activities. They may have disorganized speech, thinking, and conduct. They also have a hard time relating to others and are uninvolved in what’s going on around them. Another indicator is that they might display a significant loss of interest or enthusiasm, as well as a drop in goal.
Residual Schizophrenia
When a person has had a previous episode of schizophrenia but no longer meets the diagnostic criteria for the disease, he or she is said to have residual schizophrenia. People with residual schizophrenia may still experience certain symptoms, such as delusions and hallucinations.
Causes of Schizophrenia
The exact cause of schizophrenia remains an enigma, but it is thought to be the result of both environmental and hereditary factors.
Environmental Factors
Many experts feel that environmental factors may contribute to schizophrenia. During fetal development or early childhood, exposure to viruses, poisons, or certain stresses can cause these factors.
Genetic Factors
Schizophrenia is thought to be partly caused by genetics. It has been discovered that those who have a family history of the disease are more likely to get it themselves. People with a first-degree relative who has schizophrenia, such as a parent or sibling, are also at risk.
Treatment Options For Schizophrenia

There are a variety of schizophrenia therapies available. The treatment that an individual can receive will be determined by their symptoms and how severe they are. Psychotherapy and medicine might help to control symptoms and boost the quality of life. Family and friend support is also critical in the care of schizophrenia.
Medication
Schizophrenia is treated with antipsychotics, which are the most popular type of medication. These chemicals in the brain help to manage the symptoms of schizophrenia by blocking specific chemicals.
There are a variety of antipsychotics and they work differently in different people. Your doctor will work with you to find the medication that works best for you. You may need to try several before you find the right one.
Some people also require other medications, such as antidepressants or antianxiety medications, to treat co-existing conditions.
Therapy

Therapies for schizophrenia, including psychotherapy, are vital. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one example of a treatment that may help people with schizophrenia control their thoughts, feelings, and actions. CBT can also assist persons with schizophrenia in learning to monitor their emotions and cope effectively with stress. Supportive therapy and social skills therapy can also aid in improving social and work functioning.
Family members who provide emotional support to individuals with schizophrenia may be able to help improve their loved one’s interactions. It is also important that they maintain good hygiene, get enough rest, and avoid drugs and alcohol.
Support Groups
Another sort of treatment for schizophrenia is support groups. These organizations offer a venue where individuals who are going through similar circumstances can interact with one another to receive assistance and guidance. Family members of persons suffering from schizophrenia, other people with the disease, or anybody who wishes to learn more about it might participate in support groups.
Self-Care
Self-care can help those with schizophrenia improve their quality of life. This includes healthy eating habits and exercise, as well as finding ways to relax through dealing with unpleasant feelings or learning relaxation methods.
Tips for Family Members
When a loved one is suffering from schizophrenia, it’s critical that family and friends give him or her moral and emotional support. The goal isn’t to assume too much responsibility, and it’s vital not to forget that someone with schizophrenia is still the same person.

- Remember, schizophrenia is a genuine and serious disease.
- Do not put yourself in a position where you are taking on too much authority; allow the person with schizophrenia to run their own life as much as possible.
- Offer assistance when needed, but don’t push.
- Disclose your diagnosis candidly and honestly.
- Encourage your child to take his or her prescription and get the treatment he or she needs.
- Take care of yourself; be patient and tolerant, but also take time off when you need it (and try to do something enjoyable for yourself each day).)
- Try not to take the individual’s actions personally; it is a manifestation of their disease, not a reflection on your connection.
- Don’t make promises you can’t keep, and don’t agree to anything you don’t feel comfortable with.
- Look for support groups or therapy if you need it; it can be beneficial to speak with someone who understands what you’re going through.
- People coping with schizophrenia can learn how to handle their symptoms, regain control of their lives, and deal with the difficulties that come with this illness with time, patience, and love.
Therapies For Schizophrenia
There are a variety of treatment options for people with schizophrenia. Medication management is the most frequent sort of therapy. This, however, isn’t the only alternative. Other treatments may also aid in the reduction of symptoms and increased quality of life.
Medication Management
This sort of treatment allows patients to manage their medications in order to guarantee that they take them as directed by their doctor. It might assist people who suffer from schizophrenia and have difficulties remembering to take their medicine on a regular basis or who have trouble remembering to do so.
Psychotherapy

Patients can get help by learning to understand and manage their feelings and ideas through psychotherapy. It may be useful for persons with schizophrenia to learn how to deal with their illness. Psychotherapy also helps families and friends can provide support to the person with schizophrenia. This includes providing a safe and supportive environment, being understanding, and not taking things personally. It is also important to maintain good hygiene and get enough rest.
Family Therapy
Family therapy might help families dealing with schizophrenia. Members from the family also meet with a therapist to talk about how the illness is affecting them in this kind of session. They also learn how to best support their loved one who has schizophrenia.
ECT
The goal of ECT is to apply electrical stimulation to the brain in order to alleviate symptoms of schizophrenia. This technique may help reduce schizophrenia symptoms and is most effective when used with medicines and psychotherapy.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a severe mental illness that significantly affects a person’s thoughts, emotions, and behavior. It is a long-lasting disease that can be treated but cannot be cured. So hold on!
There are several treatments for schizophrenia, including medications, psychotherapy, and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). If you require support coping with the condition on your own, it’s critical to obtain expert help from a therapist or psychiatrist. Many people who have schizophrenia live full and productive lives when treated appropriately.
If you’re feeling overwhelmed or in need of guidance coping with schizophrenia, there are several places to turn. Therapists, psychiatrists, and social workers are just a few of the specialists that can assist you. Living with this condition does not have to be a life sentence. There is hope and assistance available for those suffering from it.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session


