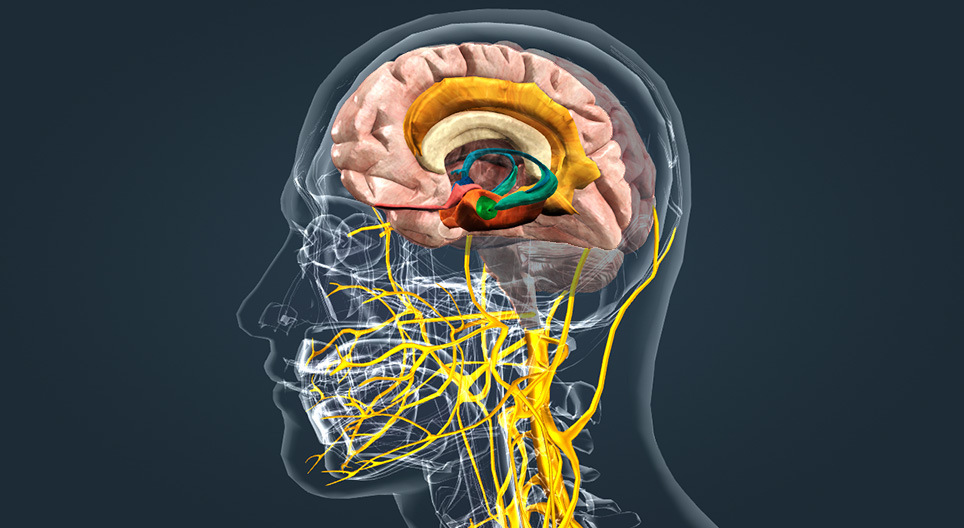
The Limbic System is a complex system of neural structures, which has been studied for many years by scientists. Its primary role is the regulation of emotion and motivation. There are many functions of the limbic system. The main limbic system function is memory formation. This blog post will discuss what the Limbic System does and how it influences memory.
Contents
What Is Limbic System?
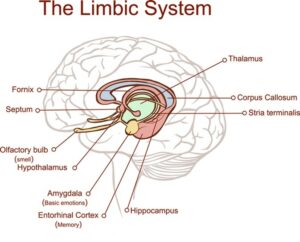 The limbic system is a set of brain structures that are located on the inner surface of the cerebral cortex. It is responsible for a variety of emotional responses, including fear, pleasure, and rage. The limbic system also helps to process memories.
The limbic system is a set of brain structures that are located on the inner surface of the cerebral cortex. It is responsible for a variety of emotional responses, including fear, pleasure, and rage. The limbic system also helps to process memories.
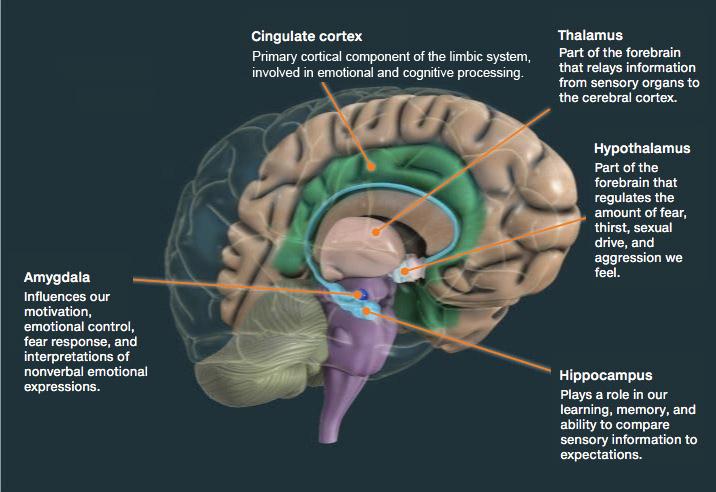
This system is divided into two regions: the hippocampus and the amygdala. The hippocampus is responsible for forming new memories, while the amygdala is responsible for storing emotional memories. This is why strong emotions often trigger memories. This in turn affects the overall mood. This is also why someone might not remember what happened during a traumatic event, but will feel anxious or fearful in that same situation again.
The hippocampus is located inside the medial temporal lobe of the brain, which is behind and below your temple. It is closely linked with another limbic structure called the mammillary body.
While most people think about memory as storing facts like names or dates, it’s actually more complicated than that. Our memories are important for forming our personal identities because they make us aware of our own experiences and knowledge gained from them throughout life. They can sometimes be inaccurate when there are certain factors involved such as stress levels at the time or depression after an experience has occurred.
Limbic System Function
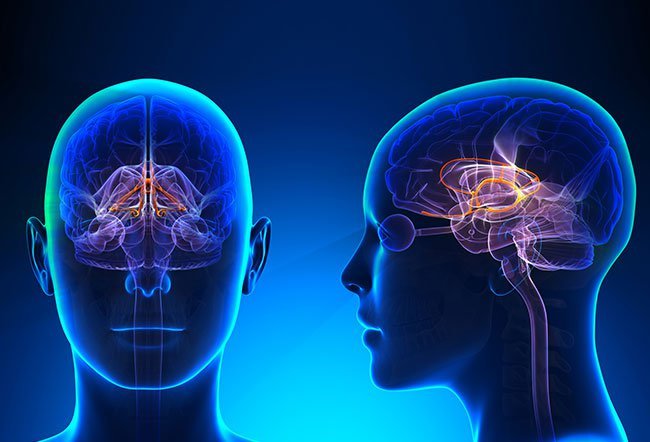
Limbic system function refers to the various tasks that the limbic system performs in the brain. This system is responsible for a variety of important functions, including memory, emotion, and motivation. This function is closely related to the hippocampus, which is a brain area responsible for consolidating short-term memories into long-term memories.
The limbic system was previously thought to be primarily involved in processing emotion and memory.
New studies have suggested that this region of the brain also has an important role in cognitive function as well as regulating autonomic processes such as heart rate and breathing both at rest and during exercise.
In addition, it appears that the functions of specific areas within the limbic system may vary depending on whether you are awake or asleep. Some research indicates that there are different functions for certain regions with regards to your state of consciousness. In particular, most scientists now believe that slow-wave sleep (SWS) is critical for promoting the transfer of memories from the hippocampus to other brain regions for long-term storage.
Working of Limbic System
There are many different ways to study the limbic system and its function.
One approach is to look at how damage or lesions to this area of the brain affect behavior. This has been done in animals as well as humans. For example, studies on patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) have shown that lesions in this region can cause memory problems and changes in emotionality.
Animal research has also been useful in understanding how the limbic system influences motivation and reward-seeking behavior. Lesions or damage to certain areas of the limbic system can result in an animal becoming more aggressive or less interested in food or sex. This research has also helped to identify the role of different neurotransmitters in these behaviors.
The working of limbic system function is also evident in functional neuroimaging studies which use MRI scans. These scans allow scientists to look at blood flow within the brain of living, intact individuals while they are engaged in specific tasks or experiences.
For example, experiments have been done where subjects might be shown pictures that cause increased activity in certain areas of the brain. This gives researchers insights into how different parts of this region influence behavior and cognition more generally. Neuroscientists can even study patients with TLE who already require surgery due to seizures so that they can better understand how this condition impacts neural processing throughout the entire brain rather than just one isolated lesion site.
Impacts of Limbic System Function
There are many impacts on limbic system function.
Memory
 Memory is one of the most well-known functions of the limbic system. The hippocampus is critical for consolidating short-term memories into long-term memories. This process involves transferring information from one part of the brain to another, and this appears to happen during sleep.
Memory is one of the most well-known functions of the limbic system. The hippocampus is critical for consolidating short-term memories into long-term memories. This process involves transferring information from one part of the brain to another, and this appears to happen during sleep.
There are many different ways that you can improve your memory, and some of these involve strengthening connections within the hippocampus. activities like learning a new skill or practicing regularly can help keep your hippocampus healthy and functioning optimally.
Emotion
 The limbic system also plays an important role in emotionality. Lesions or damage to certain areas can cause changes in mood or affective responses. For example, studies on patients with TLE have shown that they may become more emotional after surgery.
The limbic system also plays an important role in emotionality. Lesions or damage to certain areas can cause changes in mood or affective responses. For example, studies on patients with TLE have shown that they may become more emotional after surgery.
The role of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine in emotion is not fully understood, but it is clear that these substances play an important part in regulating mood and emotional responses.
Motivation
 The limbic system also regulates motivation. You can see this in experiments where animals with damage to certain areas of the limbic system lose interest in activities they would normally enjoy, like eating or sex.
The limbic system also regulates motivation. You can see this in experiments where animals with damage to certain areas of the limbic system lose interest in activities they would normally enjoy, like eating or sex.
This research has also helped scientists identify the role of different neurotransmitters in motivating behavior. For example, dopamine also helps in reward-seeking behavior.
Consciousness
 There is evidence that different parts of the limbic system have different depending on whether you are awake or asleep.
There is evidence that different parts of the limbic system have different depending on whether you are awake or asleep.
For example, during REM sleep the limbic system is more active. There are also connections between the limbic system and parts of other regions involved in consciousness like the prefrontal cortex. Researchers have used neuroimaging to study these relationships, which can help us better understand how different brain areas influence behavior and cognition as a whole. It’s also important to consider that this area of the brain is heavily influenced by neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
Sexual Drive
The limbic system is also involved in sexual drive and function. For example, the hypothalamus and amygdala both play a role in regulating sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen which influence libido or desire for sex.
Damage to these areas can cause changes in interest levels as well. There are even studies that show how certain neurotransmitters like serotonin may impact sexual response (e.g., SSRIs often lead to decreased sexual arousal).
Neuroscience Applications
Limbic System Function Technology such as fMRI imaging has allowed neuroscientists to study specific brain regions while individuals engage in different tasks or experiences — helping you learn more about how this region influences behavior and cognition overall (rather than just one isolated lesion site).
Attention
The limbic system also plays an important role in attention. For example, the amygdala is involved in both emotional responses and orienting behavior or attention to specific stimuli like a face or object that appears suddenly.
This area of the brain has been heavily studied by neuroscientists who are interested in understanding how different regions may be related to certain behaviors. fMRI imaging studies show that there are strong connections between this region and other areas. It also associates with memory retrieval (hippocampus), reward-seeking (nucleus accumbens), fear inhibition (inferior frontal gyrus) as well as vision processing at higher levels like the occipital lobe.
Learning
 The limbic system also helps in learning. For example, the hippocampus is important for forming new memories and connecting them to existing knowledge.
The limbic system also helps in learning. For example, the hippocampus is important for forming new memories and connecting them to existing knowledge.
There were a lot of studies to understand how this works by some neuroscientists. Studies have shown that activities like learning a new skill or practicing regularly can help keep your hippocampus healthy and functioning optimally.
Benefits of Limbic System
There are many benefits of limbic system function. For example, the limbic system helps us build strong social connections and form attachments with others. Some others are:
Helps To Maintain Memory
The limbic system also helps to maintain a memory. For example, the hippocampus helps to form new memories of events that have happened to an individual. The amygdala also plays a role in helping us remember emotions related to those experiences as well as other aspects like time and location (e.g., what you were doing when it occurred).
Maintains Healthy Body Functions
It maintains healthy body functions such as temperature regulation via the hypothalamus which receives direct input from thermoreceptors located near blood vessels close to your skin surface. Other examples include:
Helps To Process Emotions And Alter Moods
As indicated earlier, neurotransmitters like serotonin influence moods and behaviors through their effects on brain function. The limbic system is a key part of the brain that helps to process these emotions.
Prevents Depression and Anxiety Disorders
There’s evidence that suggests that when this area isn’t working properly, it can lead to conditions like depression and anxiety disorders. This is because the limbic system plays a role in our emotional responses and how we feel about things.
Regulates Sexual Activity
The limbic system also regulates sexual activity by controlling things such as sex hormones and libido. Damage or abnormalities to different areas within this region can often lead to changes in sexual interest or behavior.
Helps In Social Interactions
The limbic system helps us form social attachments with others and maintain strong social relationships. It does this by helping us process emotional responses like empathy and love.
Helps To Plan Future Events And Accomplish Goals
The limbic system helps to plan future events or goals. This is by allowing you to envision what might happen in the future. It then uses that information as motivation for achieving those things. It also plays a role in helping people find meaning in their lives. This is by connecting them with larger societal structures (e.g., religion). This is why individuals who are suffering from damage within this region may struggle socially or show signs of apathy toward day-to-day activities they once found rewarding before the injury occurred.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the limbic system function is important for the proper regulation of mood, emotions, memory, and learning as well as other important brain functions.
The main goal here was to describe some key concepts which relate to limbic system function. These are including social interactions, planning future events/goals by envisioning what might happen in the future then using those visions as motivation for achieving those things along with helping you process emotions. These emotions such as empathy and love.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session