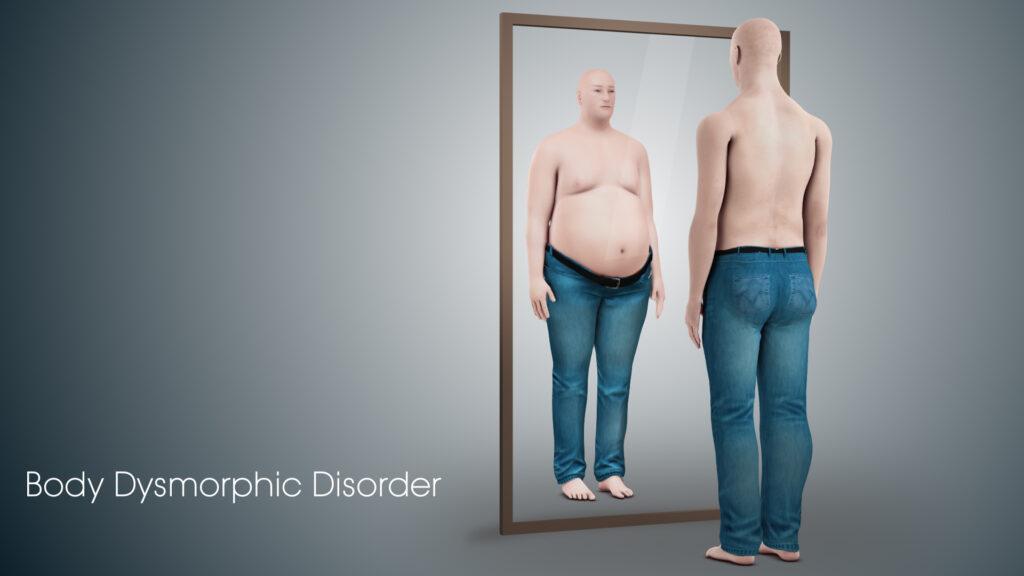
Body dysmorphic disorder is a mental health condition in which people are preoccupied with an extreme or unreasonable belief that some aspect of their physical appearance is severely flawed when the flaw has not been identified by others. It can be difficult to diagnose and often goes untreated because many individuals may doubt they have this disorder. The main symptom of BDD is an obsessive fixation on one’s own body parts, including skin texture, hair growth patterns, facial flaws, or other aspects that appear either normal or acceptable to most people. This blog post will cover what BDD is and how it affects you if you have it.
Contents
- 1 What Is Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
- 2 Types of Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- 3 Symptoms of Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- 4 Causes of Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- 5 Mental Illness Associated With Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- 6 Diagnosis of Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- 7 Treatment for Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- 8 How To Prevent Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
- 9 Conclusion
What Is Body Dysmorphic Disorder?

Body dysmorphic disorder is a mental disorder that causes people to have a distorted view of their appearance. They may see themselves as being ugly or deformed, even when they look normal to others. This can lead to an excessive focus on their appearance and severe distress.
People with body dysmorphic disorder may spend hours each day checking their appearance in the mirror or grooming themselves. They may avoid social situations or wear clothes that cover up their body. Some people even have surgery to try to fix their perceived flaws.
Body dysmorphic disorder can be very disabling and can interfere with work, school, and relationships. Treatment usually includes therapy and medication.
This disorder is just as common in men as in women. It usually starts during the teenage years, but it can also begin later in life.
Types of Body Dysmorphic Disorder

There are mainly two types of body dysmorphic disorder. These are:
Muscle Dysmorphia
This is where a person has an excessive focus on the size and shape of their muscles. They may think that their muscles are too small or not toned enough. This can be very distressing and can lead to eating disorders or steroid abuse.
Craniofacial Dysmorphia:
This is where a person has an excessive focus on the appearance of their face. They may think that their nose is too big, their eyes are too close together, or their chin is too pointy. This can be very distressing and can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. This situation is less common than muscle dysmorphia.
Symptoms of Body Dysmorphic Disorder

The main symptoms of body dysmorphic disorder are:
Need For Re-assurance
If a person is constantly asking for reassurance about their appearance, it’s likely that they have BDD. They may constantly ask friends and family if they look normal or attractive to other people.
Preoccupation With Appearance
A person with body dysmorphic disorder will spend a lot of time thinking about how they look, even when this is inappropriate (e.g., in-class). They’ll also compare themselves with others around them who are more physically fit or better looking than them.
Compulsions About Personal Appearance
People with body dysmorphia often feel the need to check parts of their body regularly to make sure that no flaws can be seen by anyone else. For example, some people might touch their nose over and over again every few minutes just to make sure it looks normal.
Avoidance Behavior
People with body dysmorphic disorder may avoid social situations, or certain activities that they feel might draw attention to their appearance (e.g., swimming). They may also wear a lot of clothes that cover up their body, even in hot weather.
Severe Distress
A person with BDD will often be very distressed about their appearance and this can lead to problems such as anxiety, depression, and thoughts of suicide. This can be very disruptive to their life and can make it difficult to do things that they used to enjoy.
Insecurity
People with body dysmorphic disorder often feel very insecure about their appearance and this can lead to a lot of self-hatred. They may also find it difficult to trust other people, as they fear that they might be judged harshly for their looks.
Mental Illness
There can be a link between body dysmorphic disorder and other mental illnesses such as anxiety disorders, depression, eating disorders (e.g., anorexia), or obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Self-Harm
People with BDD are at a higher risk of suicide than the general population because they find it difficult to cope when their appearance is constantly criticized by others around them. People with this condition usually have low self-esteem and poor quality of life due to being unable to function properly in society.
Causes of Body Dysmorphic Disorder
There can be many causes of body dysmorphic disorder. Some of these are:
Genetics
Genetics can be a factor in body dysmorphic disorder because it’s been shown that people with a parent or sibling who has the condition are more likely to have BDD themselves. This reason is not fully understood, but it’s likely that some genetic factors make a person more susceptible to developing BDD.
Trauma and Abuse
There can be a link between people who have been abused or traumatized in the past (e.g., emotional abuse) and body dysmorphic disorder because they may struggle with their appearance as a result of this trauma. However, again there isn’t enough research available on this subject yet so we don’t know for sure if this is true.
Drugs and Alcohol
This condition has also been linked with drug use such as cannabis which some studies suggest makes symptoms worse than before someone started taking drugs. Other types of drug use such as drinking alcohol excessively could also increase your chances of having BDD.
Stressful Life Events
Some people may develop body dysmorphic disorder after a very stressful life event such as the death of a loved one or being diagnosed with a serious illness. This is because they may feel like their appearance is the only thing that they have left to control.
Psychodynamic Theories
There are also some psychodynamic theories that suggest that unresolved conflicts from childhood (e.g., feeling neglected by parents) can lead to someone developing body dysmorphic disorder in later life. Again, this has not been proven yet but it’s something that researchers are looking into more closely.
Self-Esteem Issues
People with low self-esteem may start focusing on small flaws instead of appreciating their good qualities, leading them towards BDD behaviors like avoidance or compulsive checking. They might also form an addiction to plastic surgery because this is often seen as a way to “fix” their appearance.
Mental Illness Associated With Body Dysmorphic Disorder

There can be many mental illnesses that can be associated with body dysmorphic disorder. Some of these are :
Anxiety Disorders
This is the most common mental illness that is linked with body dysmorphic disorder. People with BDD may have excessive worries and fears about their appearance, which can lead to a lot of anxiety in everyday life.
Depression
People who are depressed often feel very down about themselves and their lives. This can be especially tough for people with body dysmorphic disorder because they may feel like they will never be happy or satisfied with how they look no matter what they do.
Eating Disorders
Some people with BDD may develop an eating disorder as a way to cope with their negative feelings about their bodies. This could involve restricting food intake, bingeing, or purging after meals.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Another common mental illness associated with body dysmorphic disorder is OCD because people may develop compulsive rituals such as checking or washing repeatedly. In some cases, this can get so bad that it takes over a person’s life and they are no longer able to function properly at work, school, or home.
Substance Abuse Disorders
People who have an addiction to drugs or alcohol may turn to these substances in order to cope with their negative thoughts about themselves more easily. This could lead them towards developing BDD behaviors. These are like avoiding social situations. This is where they feel uncomfortable around other people for fear of judgment on their appearance. This is instead of anything else going on in their lives.
Diagnosis of Body Dysmorphic Disorder

There are many diagnoses of body dysmorphic disorder. The most common one is a mental health professional such as a psychologist or psychiatrist. They will ask you about your symptoms and how long you’ve been experiencing them. They may also want to know if there’s anything that makes your appearance concerns worse, such as stress levels or alcohol use.
The other method can be a dermatologist who can diagnose you if you have any skin conditions that may be causing your appearance concerns. However, not all cases of BDD can be because of physical condition. This is so it’s important to see a mental health professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Another way is self-assessment which you can do by answering questions on a questionnaire. This questionnaire helps to find out if your appearance concerns are associated with BDD. You should see an expert for this, too, because it’s not always clear-cut whether or not someone has body dysmorphic disorder.
Treatment for Body Dysmorphic Disorder
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for body dysmorphic disorder, as the best approach will vary depending on the person’s individual needs. However, some of the most common treatments include:
Therapy
Therapy can be very helpful for people with BDD as it allows them to explore their thoughts and feelings about their appearance in a safe and supportive environment. The therapist can also provide useful coping skills and strategies to help manage BDD symptoms. This treatment may have some short-term and long-term benefits.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common form of therapy for BDD that helps people to recognize their triggers, change the way they think about themselves, and learn how to cope with any negative thoughts or feelings in a more positive way. It’s important to do this type of treatment under guidance from a professional though. This is because studies suggest that CBT might become less effective unless it includes techniques such as exposure therapy.
Another therapy that can help people with body dysmorphic disorder is Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). This type of therapy aims to help people manage their emotions in a more effective way, as well as improve their relationships with others.
Medication
There are some medications that can be helpful for people with BDD, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics. However, it’s important to speak with a doctor before taking any medication in case there are any potential risks or side effects. This treatment may have some short-term and long-term benefits. These medications can include antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antianxiety medications. However, it’s important to note that there is little evidence to support the use of medication in the treatment of BDD.
Plastic Surgery
While plastic surgery may seem like an obvious solution for someone with body dysmorphic disorder, it often does more harm than good in the long run. This is because many people with BDD become addicted to surgery and start to see themselves as “defective” no matter how many surgeries they have. That is why people usually recommend avoiding plastic surgery. It is unless it’s absolutely necessary.
Self-Care
This type of treatment includes things like relaxation techniques, journaling, and gentle exercise. These activities can help people to manage their stress levels and improve their overall well-being. People may use this treatment in conjunction with therapy or medication.
How To Prevent Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
There are some methods through which one can help prevent body dysmorphic disorder in oneself or others. These include:
Educating Yourself
This can be very helpful for people who have body dysmorphic disorder. Education can help them to learn more about what they’re going through, as well as the best way to manage this condition in order to prevent it from taking over their lives.
Promoting Body-Positivity
Promoting positive body image and self-esteem can be very effective in preventing BDD. This includes things like:
Showing appreciation for one’s own appearance Being comfortable with (and expressing) how we look Wearing clothes that make us feel confident & happy Not constantly comparing ourselves to others Showing our bodies love and respect through positive affirmations.
Talking To Others About It
People with body dysmorphic disorder often feel ashamed and embarrassed about their condition. It can be very helpful to talk to others who understand what you’re going through, as this can help to reduce the feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Finding Support Group
There are many support groups available for people with body dysmorphic disorder. This type of support can be extremely beneficial, as it allows people to share their experiences and advice with one another.
Seeking Professional Help
If symptoms of body dysmorphic disorder are impacting your life in a negative way, it’s important to seek professional help. A therapist or doctor can provide you with the tools you need to manage BDD and improve your quality of life. This can be an extremely effective way to prevent body dysmorphic disorder from taking over your life.
Focusing On Goals
To prevent body dysmorphic disorder, it’s important to focus on goals. These can be anything from career goals to personal hobbies and interests. It may also help people who are suffering from BDD to surround themselves with supportive friends and family members so that they have a network of positive influences in their lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, body dysmorphic disorder is a serious condition that can have long-term impacts on one’s mental and physical health if not managed properly. It’s important to avoid self-medicating or turning to plastic surgery as these approaches often only cause more harm than good in the long run.
You can manage this in several ways. This includes therapy and medication. It’s also important to promote positive body image by promoting positive affirmations and focusing on goals. If you or someone you know is suffering from BDD, it can help to talk about it with others who understand what you’re going through. This is so that you can reduce the feelings of isolation.
If you are looking for affordable Online Counseling MantraCare can help: Book a trial therapy session